Level 3 Biology Mid-term Review Sheet Intro/classification and Scientific Method
advertisement

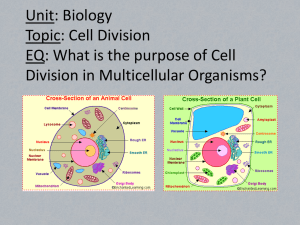
Level 3 Biology Mid-term Review Sheet Intro/classification and Scientific Method 1. List the 7 characteristics of life. 2. This term describes the addition of living material; the addition of more cells to an organism ________________________. 3. While observing a worm under the microscope, Max sees that the worm is eating a piece of food. What characteristic of life is he observing? _______________________ 4. The combination of genetic material from 2 individuals occurs during _____________ reproduction. 5. What is the correct way to write the scientific name of modern man? ___________ _______________ 6. This term describes the production of offspring _______________________. 7. What type of data includes numerical information? _____________________ 8. One cell splits to form 2 cells. This is called ____________________ reproduction. 9. This is something held consistent across all experimental groups _________________ 10. A unicellular organism has ______________ cell(s). 11. An organism maintaining its’ internal conditions regardless of external changes, such as keeping an internal body temperature of 98.6 degrees despite the heat outside. _______________________ 12. An organism’s scientific name uses which two taxa? _____________ and ____________ 13. The most specific level of classification is ________________. 14. The last step in the scientific method is considering ____________. 15. The ________________ variable in an experiment is intentionally changed. 16. The first step in the scientific method is to make an _____________________. 17. _________________________ is the transition in to the adult phase of an organism’s life. Look at the classification information below. Then answer questions 18-19. Human Kingdom: Animal Chimpanzee Animal Cat Animal Duck Animal Phylum: Chordata Chordata Chordata Chordata Chrysophyta Class: Mammalia Mammalia Mammalia Aves Xanthophyceae Order: Primate Primate Carnivores Algae Protist Anseriformes schococcales 18. Which organism is the human most closely related to? ______________ 19. What would be the next line on the chart after order? _________________ Biochemistry 20. Most atoms are most stable with _______________ electrons in their outer shell 21. ______________ and ___________________ are found in the nucleus of an atom. 22. DNA and RNA are both classified as __________________ acids. 23. Which of the following molecules can never be used for energy in living systems? (proteins, llipids, carbohydrates, or nucleic acids) 24. In an ionic bond, one atom ______________ electrons from another atom. 25. The __________ are found in the energy levels of the atom. 26. The atomic number of sodium is 11. Its atomic mass is 23. How many protons? 27. The atomic number of sodium is 11. Its atomic mass is 23. How many electrons if the atom is uncharged? 28. These molecules make up of proteins. _____________ _____________ 29. How many neutrons are in a Chlorine (atomic number 17) atom if it has an atomic mass of 36? 30. A charged atom that has gained or lost electrons. _______________ 31. __________________ are a source of stored energy. 32. Polar substances (do/do not) dissolve well in water because water also is polar. 33. This term describes the ability of water to stick to itself. ________________ 34. This type of bond exists when atoms share electrons. ________________ 35. Window cleaner has a pH of 12. Acid or base? 36. Coffee has a pH of 6. Acid or base? 37. In an uncharged atom, the number of protons is (less than/greater than/equal to) the number of electrons. DNA: DNA, RNA, and Protein Synthesis 38. A section of 1 strand of DNA has the sequence AAATGTCACGTA. What would the other half of the DNA strand look like? __________________________________ 39. The name given to the shape of the DNA molecule. __________________ 40. This molecule carries information from the nucleus to the ribosome. __________ 41. DNA ______________ is important to cell division because it ensures that each new cell gets a complete copy of the DNA 42. Guanine always bonds to the base __________________. 43. The process in which an exact copy of the DNA sequence is made. ____________________ RNA vs. DNA. For numbers 44-48, read each statement and identify whether the material being described is RNA, DNA, or both. 44. Contains the sugar ribose. 45. Is single stranded. 46. Contains the base uracil. 47. Contains the bases adenine, cytosine, and guanine. 48. Contains the base thymine. 49. This is a change in the base pair sequence of an organism. ________________ 50. The function of tRNA is to transfer ___________ __________ to the ribosome. 51. If the sequence of mRNA is CUC–AAG–UGC–UUC, what is the sequence of DNA from which the mRNA sequence was made? _____________________________ 52. A sequence of DNA has 10% thymine. What percent adenine would it have? ______________ 53. If the sequence of mRNA is CUC–AAG–UGC–UUC, what anticodons would pair with each codon? Match the terms below to the diagram of DNA below for numbers 54-56. Sugar/deoxyribose Phosphate Hydrogen bonds Genetics 57. The law of ___________________ states that alleles (copies) of a gene separate from each other during gamete formation. 58. Color blindness, a sex-linked disorder, is a genetic disease. A color-blind male (XbY) marries a normal homozygous female (XBXB). What is the probability that any female children would be a carrier for color blindness? 59. When two different alleles (forms of a gene) occur together, the one that is shown is called (dominant/recessive). 60. If a characteristic is X-linked, it occurs mostly in (males/females). 61. An organism that has inherited two different alleles (copies) of a gene from each parent is (homozygous/heterozygous) for that trait. 62. Long wings (L) on fruit flies are dominant to short wings (l) on fruit flies. A homozygous long winged male (LL) is crossed with a heterozygous (Ll) female. What is the probability that their offspring would be long winged? 63. A woman with AA blood marries a man with BB blood. What is the probability that they would have a child with type AB blood? 64. Genes are sequences of ________________ found on chromosomes. 65. When one allele is not dominant over another, and the presence of both results in the expression of both together, a pattern of inheritance called ___________________ exists. AB blood is an example of this. 66. A(n) _______________ is an alternate form of a gene, such as blue or brown eyes. 67. In 4 o’clock flowers the presence of a heterozygote reveals an intermediate between the 2 parents (Incomplete Dominance). Suppose 2 pink plants (RR’) were crossed with each other. What possible colors could their offspring be? (Red is RR, white is R’R’). 68. If a characteristic is sex-linked, it can never occur in females (true or false). 69. The trait that was expressed in the F1 generation in Mendel’s experiment is considered (dominant/recessive). 70. Crossing a snapdragon that has red flowers (RR) with one that has white flowers (R’R’) produces a snapdragon that has pink flowers (RR’). The trait for flower color exhibits ____________________ ___________________. 71. In the F2 generation in Mendel’s experiments, the ratio of dominant to recessive phenotypes was ____________ to __________. Cell Cycle: Mitosis and meiosis 72. A pair of similar chromosomes is known as __________________ chromosomes. (They have the same genes) 73. A male has these sex chromosomes. (XX or XY) 74. A diploid cell has how many of each chromosome? __________ 75. A female human egg cell contains how many chromosomes? ___________ 76. What is the uncondensed (uncoiled) form of DNA in a cell? ________________ 77. A female has these sex chromosomes. (XX or XY) 78. A human skin cell has how many chromosomes? __________ 79. Chromosomes are made up of ____________ and ____________. Matching: For numbers 80-83, use the following possible answers Interphase Anaphase Prophase Telophase Metaphase 80. Part of cell cycle in which DNA replication occurs. 81. Chromatids separate and move toward the opposite ends of the cell. 82. Chromosomes line up at the center of the cell. 83. Chromosomes becomes visible and the nucleus begins to disappear. 84. An animal cell divides when the ____________ _____________ pinches in. 85. A plant cell divides by using a __________ ____________. 86. Through what process is the number of chromosomes reduced by half? _______________ 87. Use the diagram on the following page to label the following. For letters A-E, identify the phase. Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Interphase Telophase For numbers 1-10, identify the cell part. Spindle fibers Daughter chromosomes Nuclear membrane Centrioles (used twice) Chromatin Daughter cells Nucleolus Chromosome Cell membrane Evolution 88. Fitness refers to an organism’s _____________________ success. 89. Where did people in the 1800’s believe that organisms came from? _________________ 90. Competition for _________________ most likely drives Natural Selection. 91. Which of the following terms describes differences in a population that will enhance an organism’s chance at survival and reproduction? (adaptation/variation) 92. Who discovered the mechanism of natural selection? _________________ 93. Organisms always evolve to have the best adaptations for their environment. (true or false) 94. This type of natural selection is evidenced by the fact that most human babies are not too big and not too small when born: __________________ selection 95. This type of natural selection is evidenced by the fact that the human brain has gotten larger over time: _________________ selection 96. Which of the following terms describes differences in a population that may or may not enhance an organism’s chance at survival and reproduction? (adaptation/variation) 97. If seeds are smaller one year, the beaks of birds born the following year will also be smaller. If the seeds the following year are larger, what will likely happen to the beaks of the birds born thereafter? ________________