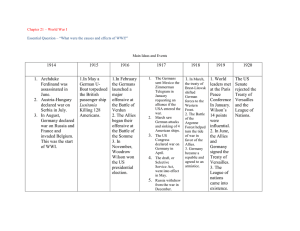
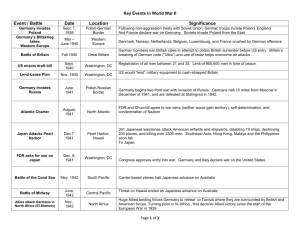
America in World War II Chapter 35 AP Notes
advertisement

America in World War II Chapter 35 AP Notes Why was time the most needed weapon? • Great Britain and S. U. could fall to the Germans • German scientists…. • Retool for war production • Needed to supply forces on 2 fronts How did Japan’s attack on Peal Harbor impact America? • Unified the nation on the war effort • Anti – interventionism withered away • WWII sped assimilation of ethnic groups • Italian and German Americans well established and supporters of FDR • Repression generally absent What actions were taken against Japanese Americans? • • • • Pearl Harbor… 120,000 Japanese Americans… Executive Order 9066… Rooted in racial prejudice and jealousy… • Korematsu v. U.S…. • Compensation…. How did the war affect the size of government and the budget? • Budget 10x its New Deal amount • Defense spending $9 billion $98 billion • Number of federal employees quadrupled What happened to the Depression? • It’s over • 1942 election more Republicans sent to Congress – block New Deal legislation • Concentrate on supplying planes, ships, guns, and food • 1942-1945 – GNP doubled How did America become the “Arsenal of Democracy”? • Wartime conversion – Automobile factories tanks and airplanes – Could not buy many consumer items – Major companies retooled to produce war material How did the U.S. out-produce the Axis? • • • • Large industrial base Natural resources Large labor supply American workers twice as productive as German and 5 x as productive as Japanese What was the role of the War Production Board? • • • • • Manage the economy… Factories operated around the clock Synthetic rubber and fabrics created Created 17 million jobs Increased American productive capacity by 50% • GNP in 1939 was $88.6 billon to $198.7 billion in 1944 How effective was the War Production Board? • 1940-45 totals – 250,000 planes – 80,000 landing craft – 650,000 artillery pieces – 15 million rifles – 100,000 armored cars – 75,000 tanks – Millions of tons of bombs – 41 billion rounds of ammunition Ship-building: Henry Kaiser • 1941 – 355 days to build a battle ship • 1945 – 14 days • Pre-fabrication desc detnews2 FILEDATE popupresu Search B-24s on the runway at Ford’s Willow Run plant Demographic Changes? • California received 10% of defense funds… • Movement from the South to Detroit and California… • Southern textiles profited… • Poor sharecroppers and tenant farmers got jobs in factories.. • Middle class doubled…. How was farming impacted by the war? • Good times for Am. Farmers… • Productivity soared • Technology and fertilizers improved… • Increased prices • Decreased farm population • Value of farm land increased How did the war affect employment? • Full employment – longer hours • Overtime – time and a half • Increased hiring of minorities and women… • Unemployment was 9.9% in 1941 and 1.2% in 1945 How did employment change for women? • • • • • • Women encouraged to work… Earned $0.65 on the dollar to a man Considered temporary… Broke stereotypes... Found work exciting… Better pay than traditional jobs… Norman Rockwell’s Rosie the Riveter What strains did war place on families? • • • • • • • Housing shortages… Rationing… Balancing work and households… Lack of child care… Latchkey kids… Juvenile delinquency… High school drop-outs… Ration coupons for meat, milk, sugar, cheese, coffee, butter, and gasoline Other war time trends? • • • • • Marriage rate up… Incomes up…. Divorce rate up… Public health improved… Death rate down… What was the “Double V” campaign? • Destroy racism at home and abroad • Victory on battlefield and over racial discrimination • Black support of war hinged upon America’s commitment to racial justice How was A. Philip Randolph a leader in civil rights? • President of the Sleeping Car Porters Union… • Organized a march on Washington demanding that the gov’t open jobs in the defense industry to blacks • Executive Order 8802… • Fair Employment Practices Commission… What was CORE? • Interracial – Congress of Racial Equality • Pacifists… • Sit-ins… • Integrate diners – Jack Sprat Coffee Houses in Chicago What were the goals of the NAACP? • Anti – lynching and poll tax legislation • End discrimination in the military • End black disenfranchisement • Membership grew from 50,000 in 1940 to 450,000 in 1945 What was the source of racial tension during the war? • Black migration -1.2 million left the South to work in defense industry… • Housing shortage… • Whites objected to economic equality.. • Increased black militancy… White mob in Detroit streets - 1943 How did blacks gain by the war experience? • More blacks are voting… • Other countries are aware of racism in the U.S… • The U.S. appears hypocritical…. • High expectations from blacks… • 1 million blacks in the military – slowly begins to integrate… The American G. I.? • • • • 16.4 million Americans served “Government Issue”… Considered temporary service… Beginning of a more homogenized society… • Depended on solidarity of the group for survival… How did women serve in the military? • • • • 350,000 WACS WAVES Better educated and more skilled than… • Administration, communication, clerical, health-care • Government feared “immorality”… WACS during WWII What was the status of the African American soldier? • 1 million served • All-black regiments with white officers… • Majority in Signal, Engineer, and Quartermaster Corps – construction and stevedore work… • Minority given fighting and low officer status near the end of the war… • Encountered discrimination everywhere… What was the status of Japanese – American soldiers? • • • • Also fought in segregated units Fought in European theater Served as interpreters in U.S. 442d regiment fought in France and Italy Objectives…. • Explain American strategy to counter Japanese successes in the Pacific • Describe Allied effort to defeat Hitler • Discuss the final military efforts that brought Allied victory in Europe and Asia The Atlantic Charter – August, 1941 • Self determination • Equal trading rights • System of general security War in the Pacific Japanese victories • Philippines • Malaya • Thailand • Hong Kong • Guam • Wake Island • Gilbert Islands • Manila • Singapore • Dutch East Indies Bataan Death March – April, 1942 Camp O’Donnel – Death camp – 1,600 Americans died here as well as 10,000 Filipinos Battle of Coral Sea Battle of Coral Sea • Japanese goals …… • Outcome of the battle …. • Significance …. Battle of Midway 1942 • Japanese goals… • Results of the battle: 4 Japanese aircraft carriers were destroyed • Significance: Turning point of WWII in the Pacific Yorktown is abandoned Japanese torpedo planes attack the USS Yorktown Battle of Guadalcanal • Situation in the Pacific • Strategy of island hopping Early Danger • Allies decide to concentrate on defeating Hitler and use defensive action against the Japanese in the Pacific • Hitler was seen as the greater threat • June 22, 1941 – Germany attacked the Soviet Union Siege of Leningrad – 900 days Battle of Stalingrad • 300,000 German troops • 4 months • More Russians died than Americans in the entire war • Turning point of the war in Europe North Africa • German and Italian forces were fighting in North Africa • Field Marshal Erwin Rommel – the “Desert Fox” • Target – Suez Canal and oil • Germans invaded Egypt and came within 70 miles from Alexandria • Soviet Union wanted a second major front in France Operation Torch • November, 1942 • Eisenhower invaded Morocco • Montgomery drove from Egypt • Rommel caught in between – Lost – 250,000 Germans surrendered Invasion of Sicily - 1943 • • • • Soft underbelly of Europe Italy surrendered Sept. Mussolini rescued by Germans Allies fought their way north against the Germans • 1944 Allies landed at Anzio • Six months later Allies took Rome Mussolini and his mistress were dragged through the streets of Rome and hung upside down in humiliation. Battle of the Atlantic • 1943-1944 • Characterized by the contributions of science and technology • Radar and sonar – depth charges • RAF and USAF – strategic bombing – night and day – incendiary bombing – • Hamburg – 60,000 dead • Dresden – incendiary bombing Aftermath of firebombing in Dresden Germany Dresden Soviet Offensive-1943 • Reclaimed Russian cities • Poland – established a puppet government at Lublin • Romania • Bulgaria • Helped Marshal Tito in Yugoslavia Casablanca-1943 • Roosevelt • Churchill • Unconditional surrender • Resolve to attack Italy before France Election 1944 • Democrats – FDR and Truman • Republicans – Thomas Dewey and John Bricker • Issue – FDR’s failing health • Outcome – FDR wins an unprecedented fourth term – Strength for FDR in urban vote – Congress is increasingly conservative and Republican Tehran Conference • Churchill, Stalin, and FDR • Agreed to invasion across English Channel • Began air strikes to soften Germany Operation Overlord • • • • • D-Day – June 6, 1944 Eisenhower - commander 150,000 Allied soldiers 5 beaches Goal? Liberation of Paris • Pushed through to Paris • Rapid Allied advance • Germans retreated rapidly Battle of the Bulge • German counter –offensive • Bulged into the Allied lines • Total surprise to the Allies • Month long battle • American losses – 75 to 80,000 Yalta Conference – February, 1945 • • • • • Roosevelt, Stalin, Churchill Germany divided into 4 Berlin divided into 4 “friendly gov’t in Poland” S.U. to get ½ reparations Yalta • S.U. will enter war against Japan • UN decided upon • Agreed to try German and Japanese criminals of war Defeat of Germany • Allies attacked from the west with Eisenhower • Allies stopped 50 miles west of Berlin • Soviets took Berlin • Russians and U.S. met at Elbe River • May 8 - terms Discovery of the Holocaust • 1942 – “Final Solution” – systematic campaign to liquidate European Jews • Extermination camps in Poland • 6 million Jews – over 1 million children • 5 million Slavs, Gypsies and enemies of the German State April 12, 1945 • Death of FDR • Harry Truman – Vice President – From Missouri – Not in the inner circle – No – nonsense approach with Soviets – Plain speaker Deterioration of Soviet-American relations • Truman had no patience with S.U. • Wanted free elections in Poland • Told S.U. to keep promises of Yalta • Wanted Soviet help in defeating Japan and creating U.N. • Met at Potsdam Defeat of Japan • Iwo Jima – 700 miles from Japan-base to bomb Japan – 5 miles square – 6 weeks and 26,000 marine casualties • Okinawa – 350 miles from Japan – 7,600 Am. Deaths/110,000 Japanese deaths – Kamikaze attacks • Naval Blockade and aerial bombing of Japan Marines at Iwo Jima Potsdam Conference – July, 1945 • Truman, Stalin, Attlee, Churchill • Truman informed Stalin of bomb • Issued order that bomb be used if Japan did not surrender by Aug. 3 Decision to drop the bomb • Interim Committee • Would cost 1,000,000 Am. Lives to invade Japan • Drop on a deserted island – might work • Japan near surrender – wanted to keep Emperor VJ Day – August 14 • Cost of war: –292,000 Americans died –18 million Russians –4 million Germans –2 million Japanese –Total: 60 million people