The Groundwater Reservoir Hydrologic Cycle Atmosphere
advertisement

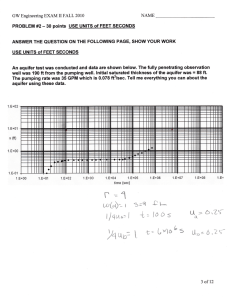
The Groundwater Reservoir Atmosphere Evaporation Eva Evaporation iratio n ( ) = Storage potr Liquid Flow ansp Vapor Precipitation (water vapor) The Hydrologic Cycle surface Land Streams Lakes etc. Surface Oceans Infiltration Overland flow = Direct Runoff (Surface water) (Seawater) Volcanic outgassing Interflow Vadose Zone (Soil moisture) Runoff = Streamflow Infiltration Groundwater flow and Baseflow (Ground water) Subduction Subsea outflow Water Table Seafloor vents Gravity drainage Hydrologic Cycle (Ice, snow, depression storage) Water Table •Follows the slope of the land •Meets the surface at wetlands Stream Water Table Groundwater Flow •Flow from high to low water table •Flow exits the subsurface at streams = discharge •Baseflow = groundwater flow feeding streams •Gaining / perennial stream = fed by groundwater Gaining Stream Groundwater Flow Recharge Area • Streams • Swamps • Lakes • Springs • Seeps Discharge Area Drought •Water no longer infiltrates from the surface •Flow continues underground •Water table drops Gaining Stream Drought •Water no longer infiltrates from the surface •Flow continues underground •Water table drops Gaining Stream Drought •Water no longer infiltrates from the surface •Flow continues underground •Water table drops Gaining Stream Drought •Water no longer infiltrates from the surface •Flow continues underground •Water table drops Gaining Stream Drought •Water no longer infiltrates from the surface •Flow continues underground •Water table drops Gaining Stream Drought •Water no longer infiltrates from the surface •Flow stops underground •Water table flattens Drought •Water no longer infiltrates from the surface •Flow reverses underground •Stream becomes a losing or ephemeral stream. Losing Stream Losing Stream Subsea outflow • discharge of freshwater along shoreline Discharge Area saltwater Low Tide freshwater outflow face Cape Ann, Mass. My charming wife. Aquifer - geologic unit that can store and transmit water in amounts and at rates high enough to supply usable wells. Aquifuge - absolutely impermeable layer. Aquiclude - low permeability unit that forms upper or lower boundary. Aquitard - low permeability unit that can store and slowly transmit water. Confining Units - leaky / impermeable Porosity • percentage of open spaces in rock and sediment that can hold water. • Grain size does not affect porosity. primary secondary Permeability • The ease with which water flows through porosity. • Most important variable is grain / pore size. Pendular water Porosity Permeability Gravel 20% Very high Aquifer Sand 20% High Aquifer Clay 50% Very low Confining unit Three types of Aquifers • Unconfined (water table aquifer open to recharge from the surface) • Confined (artesian aquifer - capped by a confining layer) • Perched (small aquifer above main water table) Perched Water Table Unconfined aquifer (water table aquifer) • open to recharge directly from the surface • water table - upper limit of saturation •recharges directly from precipitation recharge water tab le unconfined Well in unconfined aquifer Confining layer (clay) Confined aquifer (artesian aquifer) • NOT open to the surface - topped by a confining layer • no water table - aquifer is fully saturated • recharges slowly by leakage across the confining layer recharge unconfined confined Confining layer (clay)