INTRODUCTION- Cells things.
advertisement

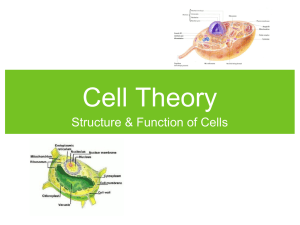
CHAPTER 3: CELLS INTRODUCTION- Cells The cell is the ________________________ in living things. Cells vary in their ____________________________ All cells have similar ____________________________ Typical animal cell contains 4 parts: The CELL (or plasma) ________________________________. The ________________________________________ The CELLULAR ________________________________ _______________________ The ___________________________________ Membrane Structure = Fluid Mosaic Model (page 67) Composed of a double _____________________;many __________ The surfaces of the membrane are ______________ due to the __________________________; The internal portion of the membrane is _____________ due to the _________________________ Membrane Proteins ________________________________ into and extend across the lipid bilayer. Most are ____________________ They serve as either _______________________________ 3-1 CHAPTER 3: CELLS ________________________________________ ___________________________________________ of the cell membrane. They serve as _________________________ Intercellular Junctions ____________________ cell membranes together (Glue) Tight Junctions ________________________________ Desmosomes are _______________________________ Gap Junctions allow ____________________________ A COMPOSITE CELL & Its Organelles Membrane Structure Phospholipid ____________ Cytoplasm (cytosol) = ____________________ that holds the cellular organelles inside the cell Ribosomes Make _________________; found on _________ __________________ Rough ER ______________________________ to other parts of the cell via _________________________ Smooth ER _________________________ 3-2 CHAPTER 3: CELLS Golgi Apparatus Found close to ER. Takes _____________ ________________________; then sends them on their way (____________________) Mitochondrion ______________________. Takes in food; ___________________, which is broken down ______________. Some cells have more mitochondria than others Cristae ________________________ to increase surface area Nucleus _________________________________. Contains _______________ DNA converted to ________ and stored in ____________. RNA sent out to cell as a ________________ Surrounded by __________________________ Nuclear pores allow_____________________________ Cytoskeleton _________________________ cell shape Microfilaments Used for ______________________ Microtubules Thicker __________________________ Cilia and Flagella Help some cells __________________ Lining of _____________________ Lysosomes Contain _______________________; breaks down _____________; can _______________________ Nuclear Membrane Surrounds ____________________ 3-3 CHAPTER 3: CELLS CentriolesSet of microtubules that ______________________ Plasma Membrane Selective __________________________ Plant Cell Organelles Cell Wall Protects ___________________________ Vacuoles Storage for ________________________________ Chloroplasts Found only in _______________. Used to trap the ______________________ Structure of Plasma Membrane & Movement Through Cell Selectively Permeable allows ________________________ _________________________ Phospholipid Bilayer Polar heads ___________________of cell; ___________________________________ Polar = ________________________________ Nonpolar = ____________________________ Why is there this arrangement of lipids? Cytoplasm and outside of cell is _________________ Molecules on the Plasma Membrane 3-4 CHAPTER 3: CELLS Carbohydrates Act as _____________________________ Cholesterol Gives membrane _______________________ Receptor Proteins bind ___________________________ _______________________________________ Recognition Proteins proteins on membrane that are used for ______________________________________ Adhesion Proteins help cells of a certain type _________ ________________________________ What gets in and out of the cell membrane? How do some substances pass through the membrane while others stay out? Materials moves across the membrane in two ways 1. _________________________ 2. _________________________ Passive Transport 1. Diffusion movement of molecules from _____________ _____________________________________ ________________________________________ pass through the membrane by diffusion Equilibrium Cells in equilibrium have ________________ 3-5 CHAPTER 3: CELLS ____________________________________ Facilitated Diffusion molecules bind to _____________ across the _________________ Diffusion through channels specific passageways _______________________________________________ Water, Diffusion and the Plasma Membrane Osmosis Diffusion ______________ Isotonic Cells at ________________________________ Hypertonic Cell in a solution that has a ___________ _________________________Water rushes out of the cell Hypotonic Cell in a solution that has a ___________ ____________________________Water rushes into the cell Active Transport Using __________________________ into the cell against their concentration gradients 1. Cell Membrane Pumps carrier proteins pump ions _______________________________________ 2. Endocytosis _____________________________ or liquids by plasma membrane Cells take in _________________________ from bloodstream 3-6 CHAPTER 3: CELLS Pinocytosis Endocytosis of _______________ 3. Exocytosis vesicle contents ______________________ _________________are transported by exocytosis DNA in the Cell Inside the nucleus are ________________________________ Chromosome made from ___________________. Coils _____ so it can fit into a cell Each chromosome consists of ___________________________ Center of the chromosome is __________________________ Number & Types of Chromosomes Sex chromosomes determine the sex of an organism ___ = female ___ = Male All other chromosomes are called __________________ Homologous Chromosomes Each organism gets ____________ of each autosome; __ from mom and __ from dad (___total chromosomes; __ pairs in humans) 3-7 CHAPTER 3: CELLS Each 2 paired chromosomes are called ____________________ Homologous chromosomes _________________________ Diploid & Haploid Cells Diploid Cells Cells with _________ of each chromosome Haploid Cells Cells with __________ of each chromosome Most cells in the body are __________ Sex cells (sperm & egg) are _____________ Why do cells divide? 1. Get _______________ 2. _______________________ 3. Surface ________________________________________ When do cells divide? Depends on the type of cell (days, weeks, months, some never divide) Cell Cycle Cells will ________________________ Stages of Cell Cycle in Eukaryotes Interphase ________________ G1 ___________________ S ________________________ 3-8 CHAPTER 3: CELLS G2 -> ________________ Mitosis DNA, which has been replicated needs to be ________ _________________________________ Stages of Mitosis Prophase 1. Chromatin _________________________________________ 2. Spindle fibers _______________________________________ Metaphase 1. Spindles align chromosomes in the ______________________ Anaphase 1. Centromeres _________________________________ 2. Chromatids move _____________________________ Telophase 1. Chromosomes ____________________________ 2. Nucleus _________________ 3. Spindle ________________________ 4. Cell __________________________ Cytokinesis (Cell Division) Animal Cell cleavage furrow _________________________ Plant Cell cell plate ________________________________ 3-9 CHAPTER 3: CELLS 3-10