change. You must also tell us the unique chemical and... Name: ____________________________ Chemical and Physical Changes Lab
advertisement

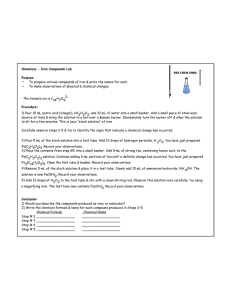
Name: ____________________________ Chemical and Physical Changes Lab Directions: Use your pre lab information to determine if the reaction at each station is a physical or chemical change. You must also tell us the unique chemical and physical properties of each substance used. After completing each station, fill out the information on the corresponding data table. Warning: Many of the substances used in this lab are VERY DANGEROUS. Many are corrosive the skin, and full attention to detail is required during the entire lab. Please do not remove your safety goggles for any reason! Follow all direction EXACTLY and ask questions if you are unsure of the procedures. Station 1 Procedure: Mg and HCl *Caution: HCl is a very strong acid Place a 1/2 inch piece of magnesium ribbon in a test tube. Add 10 drops of the HCl and observe for 30 seconds. Record data in your data table. Dump the excess HCl and Mg in the waste container, and rinse the test tube using the water from the Water Beakers (NOT THE SINKS!). Station 2 Procedure: Heating Sucrose *Caution: beaker and hot plate will get very hot Put half a spoonful of sucrose in small beaker. Place on hot plate for about 2 minutes and observe. Remove the beaker from hot plate with tongs, and clean out the beaker. Station 3 Procedure: Silver nitrate and Hydrochloric acid *Caution: HCl is a very strong acid Place 5 drops AgNO3 into test tube. Replace cap to the AgNO3 dropper container. Add 5 drops HCl and observe. Record Data. Rinse out the test tube in sink and place back on the rack. Station 4 Procedure: Heating a Crayon *Caution: beaker and hot plate will get very hot Place a piece of the crayon in a beaker. Use a hotplate to heat the crayon for about 1 min. Let cool for a minute. Remove the contents and place in the waste bucket. Record Data Page 1 of 6 Station 5 Procedure: Citric Acid plus Baking Soda *Caution: Citric acid is a very strong acid Pipette out 10 mL (10 full squirts from a pipette) of citric acid solution into a test tube and then place the tube in a ring stand with a clamp. Place the thermometer into the citric acid solution, and record the initial temperature. Weigh out 3.000 g of solid baking soda Add the baking soda to the citric acid solution, while leaving the thermometer in place. Gently stir the solution with a stir rod (NOT the thermometer) to ensure good mixing. Don’t worry if the reaction foams over and out of the test tube! When the reaction begins to slow, remove the thermometer and record the new temperature. Dispose of the reaction products down the sink at your lab station, using lots of water. Put the clean test tube back on the rack. Station 6 Procedure: H2SO4 and antacid *Caution: sulfuric acid is a very strong acid Place a bit of Rolaids in test tube. Add 5 drops of sulfuric acid. Dump waste in sink and rinse test tube and replace back on rack. Station 7 Procedure Copper(II) chloride and Aluminum foil: *Caution: CuCl2 is toxic Place a small piece of aluminum foil in test tube. Using the dropper, add about 15 drops of CuCl2 to the foil. Observe for 30 seconds. Using tweezers, lift out foil and put in the trash can. Dump excess CuCl2 in waste container and rinse test tube in sink and put back on test tube rack. Page 2 of 6 Physical and Chemical Changes Data Table Station Any unique physical # or chemical properties. 1 Observations during Reaction Observations of materials after rxn. (may include temp) Chemical or Physical Change? Justification 2 3 4 5 6 7 Page 3 of 6 Physical and Chemical Changes Post Lab 1) When we make observations in chemistry class, we describe certain physical properties of objects or chemicals. List the 5 different kinds of physical properties and 5 different chemical properties that we have learned. Physical Properties: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Physical Properties: 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 2) What is a physical change? 3) What is a chemical change? What are the types of “evidence” for a chemical change? 4) In your own words, what is the difference between a chemical change and a physical change? 5) Under each sentence, identify each of the following as a physical or a chemical change. Then, explain why each is a chemical or physical change under the sentence. a. You leave your bicycle out in the rain and it rusts. b. A sugar cube dissolves in water. c. Pure potassium is normally stored in oil. When the oil is removed, a flame is produced because the potassium can now react with oxygen in the air. d. Sand is mixed with water. Page 4 of 6 e. Scientists break up water (called hydrolysis) up by separating it into O2 and H2 f. You are cleaning your bathroom and you accidentally mix bleach and ammonia, which produces a toxic gas, which makes you pass out. g. Burning coal for a barbecue. h. Chewing up a bite of hamburger. i. You take a shower and your wet hair begins to dry. j. Silver nitrate and sodium chloride mix to form a grey-violet precipitate. k. Trimming a plant because it has grown too high. l. Mashing up potatoes to make mashed potatoes. m. Sodium polyacrylate and water mix in a bowl to form a gel. When the water evaporates, the sodium polyacrylate remains in the bowl. n. Hydrogen peroxide is poured on some liver the liver begins to break down. o. Write your own example of a chemical or physical change Page 5 of 6 6) Identify each statement as being true or false to the left of the sentence. Then briefly explain why for each. a. A change in size or shape is a physical change. b. A chemical change means a new substance with new properties was formed c. An example of a chemical change is when water freezes. d. When platinum is heated, then cooled to its original state, we say this is a physical change. e. When milk turns sour, this is a physical change because a change in odor does not indicate a chemical change. f. When magnesium is burned, ash forms. We say this is a physical change because the magnesium looks different. g. Every substance has physical properties. h. Every substance has chemical properties. i. Write your own true false question here and answer it yourself. Page 6 of 6