Mutations Fantasy Reality
advertisement

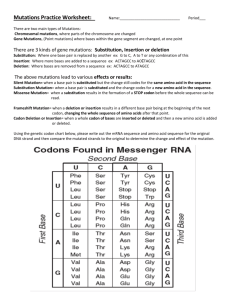
Mutations Fantasy Reality Mutations Mutations: a permanent and heritable change in the nucleotide sequence of a gene. Are caused by mutagens (x-rays and UV light) • Substitution Mutation: One base is substituted for a different base. – Also known as a point mutation Mutations Point or Substitution mutations can affect the protein in various ways. •Silent Mutation: – The mutated codon still codes for the same amino acid. – Since there are 64 different codons but only 20 different amino acids – more than one codon can code for the same amino acid. – What affect do silent mutation have on the protein. Example – What happens to the protein when the DNA sequence AGA is mutated to become AGC? Mutations • Missense Mutation: – The mutated DNA nucleotide changes the amino acid in the protein. – How is the protein affected? Example: – Sickle cell disease: the sixth codon in the protein hemoglobin, GAG, is mutated to GTG. – How does this mutation change the amino sequence in hemoglobin? Mutations • Nonsense Mutations – the mutation changes a codon for an amino acid to one of the STOP codons (TAA, TAG, or TGA). – How is the protein affected? Example – Cystic Fibrosis is caused by a mutation in the gene that codes for the CFTR gene which is made of 1408 amino acids. – the substitution of a T for a C at nucleotide 1609 converted a glutamine codon (CAG) to a STOP codon (TAG). – The protein produced by this patient had only the first 493 amino acids of the normal chain of 1480 and could not function properly. Mutations • Insertions and Deletions: One base is inserted or removed from a DNA sequence. – Also called a Frameshift mutation: nucleotides are read 3 nucleotides at a time (the reading frame). Removing or adding 1 or 2 nucleotides will change the grouping of the nucleotides. – How does a frameshift mutation affect the protein? Mutations Mutagens: chemicals or physical agents that cause mutations. • Examples: X-rays and UV light • Mutations are random; some are beneficial and some are harmful. Translation Genetic Code – the sequence of A, C, G and U used to read the mRNA sequence. • The genetic code is read three letters at a time. • Each group of three mRNA nucleotides is called a codon. • Each codon corresponds to a single amino acid. Chromosomal Mutations • Chromosomal mutation: mutation that changes the number or structure of chromosomes. – Deletion: The loss of all or part of a chromosome – Duplication: A segment is repeated – Inversion: part of the chromosome is reverse from its usual direction. – Translocation: one chromosome breaks off an attaches to another chromosome.