Cell Transport Define HOMEOSTASIS. How does the plasma membrane maintain homeostasis?
advertisement

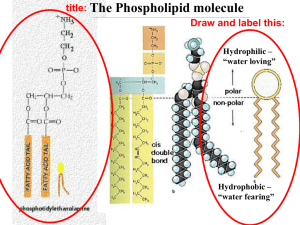
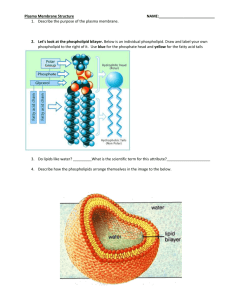
Cell Transport Define HOMEOSTASIS. How does the plasma membrane maintain homeostasis? Cell Transport Define HOMEOSTASIS. Maintaining a relatively constant or stable internal environment, even when external conditions change dramatically How does the plasma membrane maintain homeostasis? Cell membranes help organisms maintain homeostasis by controlling what substances may enter or leave cells Structure of the Cell Membrane What type of organic compound is shown? Label each of the following: • Glycerol • Phosphate • Saturated Fatty Acid • Unsaturated Fatty Acid Structure of the Cell Membrane Phospholipid molecules make up the cell membrane. The head of the phospholipid is polar • What is a polar molecule? • The polar head is hydrophilic (they can mix with water). Structure of the Cell Membrane The tails of the phospholipid is nonpolar • The nonpolar tail is hydrophobic (they can’t mix with water). Phospholipid Bilayer: the tails face inward to avoid contact with water, the heads face outward to be in contact with water.