Latinos and Native Americans Seek Equality Chapter 23 Section 1 Notes
advertisement

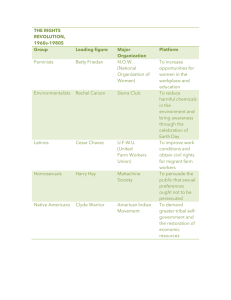
Latinos and Native Americans Seek Equality Chapter 23 Section 1 Notes Objectives • Describe the growth and diversity of the Latino population in the United States during the 1960s. • Summarize the efforts of Latinos to secure civil rights and respect for their cultural heritage. • Explain the efforts of Native Americans to secure reforms in government policies. • Main Idea • During the 1960’s Latinos campaigned for… 1. 2. 3. Improved working conditions/better treatment for farm workers; Educational programs; Political Power • Terms and Names • Cesar Chavez • United Farm Workers Organizing Committee (UFWOC) • La Raza Unida • American Indian Movement (AIM) Latinos fight for improved working conditions: HOW DID THEY GET WHAT THEY WANTED? • Mexican American (largest Latino group in the US) farm workers protested & went on strike due to low wages & poor working conditions; • Barrios (Spanish speaking communities) had higher jobless rates & poverty than whites & other minorities; • Cesar Chavez organized Cal. Farm workers into the Nat’l Farm Workers Assoc. which later became the United Farm Workers Organizing Committee; they used boycotts, labor strikes & hunger strikes & sparked cultural pride inspiring “brown power” movements across the US. FEDERAL LAWS/PROGRAMS THAT ADDRESSED THEIR NEEDS… • By 1970 Union workers were guaranteed higher wages and other benefits they had long been denied. Cesar Chaves…. • Chavez Bio • How can César Chávez be compared to Martin Luther King? • 10 Things you may not know... Improvement in Education • HOW DID THEY GET WHAT THEY WANTED? • Latino politicians began to demand that schools offer Spanish speaking children to be taught using their own language; • Brown Berets – organized by David Sanchez – organized walouts in LA high schools demanding smaller classes, more Latino (Chicano) teachers, Administrators & programs; • Federal Laws/Programs that addressed these needs: • Bilingual Education Act (1968) – provided funds for bilingual & cultural education programs for Spanish speaking children. • High Schools, colleges/universities established Chicano studies programs across the US. Latinos fight for more Political Power • How did they get what they wanted? Federal laws/programs implemented to help? • Mexican American Political Association (MAPA) • Helped elect eight Hispanic Americans to the House of Representatives and one senator • Established in 1970, La Raza Unida (MexicanAmericans United) • Ran Latino candidates in five states • Won races for mayor, school board, and city council. • Some took a confrontational stance – trying to reclaim land the US had taken from Mexican landowners in the 19th century; trying to force recognition of the plight of migrant farmers; most of these confrontations ended with arrests. • What similarities can you ID between the Civil Rights movement & the efforts of Latinos in the 1960’s? Native Americans Struggle for better living conditions, Equality and Greater Autonomy • Native Americans are Culturally diverse; suffer highest rates of poverty, unemployment; disease and death. • Issues: poverty, unemployment , illness (tuberculosis and alcoholism), and shorter life expectancy • 1961 – Declaration of Indian Purpose • Called for end to termination policy & established policies designed to create opportunity for Native Americans • 1968 – LBJ announced the National Council on Indian Opportunity to ensure programs that reflected the needs of Native Americans. Voices of Protest • HOW HAVE THEY TRIED TO GET WHAT THEY WANT? They have organized; protested; confronted the government. • American Indian Movement(AIM) • Dissatisfied young Native Americans • Militant Native American rights organization • began in 1968 as a self-defense group against police brutality • Actively confront the U.S. government to protect the rights of large Native American populations in northern and western states. Confronting the Government • “Trail of Broken Treaties” • Washington DC • March to protest US government’s treaty violations throughout history • Push for end to the Bureau of Indian Affairs due to corruption • Seized building and destroyed records causing $2 million in damage • Wounded Knee, South Dakota • AIM with 200 Sioux to protest tribal leadership and federal policies • Seized town and took hostages • Confrontation with FBI Native American Victories • Federal laws/programs to address their needs: • 1972 - Indian Education Act • 1975 – Indian Self-Determination and Education Assistance Act • Gave tribes greater control over own affairs and children’s education • Alaska Native Claim’s Settlement Act of 1971 • 40 million acres and $962 million to native peoples • Trail of Broken Treaties • Smithsonian "The Indian Problem" 1960’s = ACTIVISM! • Activism & social movements succeed through ORGANIZATION, RESOURCES & STRONG LEADERSHIP. *How well did the 2 groups we discussed today do with those 3 things?