India Modern History Review Sheet
advertisement
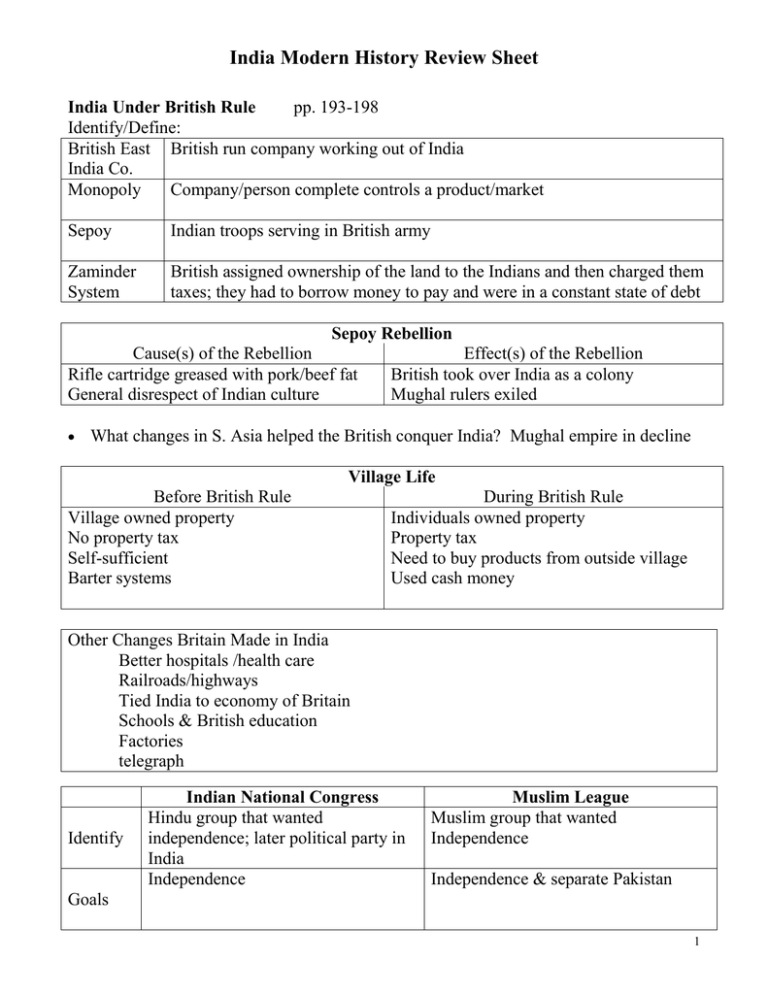
India Modern History Review Sheet India Under British Rule pp. 193-198 Identify/Define: British East British run company working out of India India Co. Monopoly Company/person complete controls a product/market Sepoy Indian troops serving in British army Zaminder System British assigned ownership of the land to the Indians and then charged them taxes; they had to borrow money to pay and were in a constant state of debt Sepoy Rebellion Cause(s) of the Rebellion Rifle cartridge greased with pork/beef fat General disrespect of Indian culture Effect(s) of the Rebellion British took over India as a colony Mughal rulers exiled What changes in S. Asia helped the British conquer India? Mughal empire in decline Village Life Before British Rule Village owned property No property tax Self-sufficient Barter systems During British Rule Individuals owned property Property tax Need to buy products from outside village Used cash money Other Changes Britain Made in India Better hospitals /health care Railroads/highways Tied India to economy of Britain Schools & British education Factories telegraph Identify Indian National Congress Hindu group that wanted independence; later political party in India Independence Muslim League Muslim group that wanted Independence Independence & separate Pakistan Goals 1 Road to Freedom pp. 201-204 Identify/Define: Civil disobedience (peace protest) Satyagraha non-violence Ahimsa Civil Refusal to obey unjust laws disobedience Salt March Gandhi marched to the sea and made salt to protest the law against making salt Amritsar Massacre Peaceful protesters were attacked by British soldiers Muhammad Ali Jinnah Muslim League; first leader of Pakistan Jawaharlal Nehru Indian National Congress; first leader of India “Mahatma” “Great Soul” What name does Gandhi give to the “Untouchables?” Children of god What was Gandhi’s early life like? What was his family like? What did he do for a living? middle class family; studied law in Britain; started fighting for Indian rights in S. Africa first What object was used to symbolize Gandhi’s efforts? spinning wheel How does Gandhi die? Who was responsible? assassinated by a Hindu extremist 2 Goals Independence Peace between Hindus and Muslims Eliminate Untouchable caste Mohandas Gandhi Methods satyagraha ahimsa fasting Reasons Methods Worked no way to win with force Many Indians v. few British Used moral values of British British looked like fools Guilt of the British People willing to suffer India gained independence in 1947. Why were the British willing to leave India? Weak from WWII, British people didn’t support keeping India, Indian nationalism high Political Challenges pp. 205-209 Identify/Define: Sikh Religion that is a blend of Hinduism and Islam Indira Gandhi Prime minister that was assassinated Rajiv Gandhi Opened India to foreign investments, increased private ownership Parliamentary people vote for political parties to represent them in Parliament (like democracy Congress) Coalition When there is not clear majority in Parliament, some parties join together to form a majority What type of government does India have? Federal republic/parliamentary democracy How has religion created divisions and bonds in the Indian government? The religions have argued for centuries and continue to do so What are some of the goals of Nehru? Self sufficient, modernization, government guidance of development Economic Development pp. 209-213 Identify/Define: Green Movement to improve farming techniques Revolution Tenant Farmer rents land from large land owner and pays % of crop as rent farmer Land reform When land is redistributed more equally among the people What is the chief goal of Nehru’s economic planning? Self-sufficient How do natural resources help India industrialize? coal 3 Three programs to help farmers 1) irrigation – improved irrigation and damning techniques 2) Green Revolution – improved farming technology 3) land reform – redistributing land to the people so land is more evenly distributed and production increases How economic development effects the environment -Poor soil conditions -people forced to move due to conditions -Contaminated water -erosion and flooding due to poor drainage -Toxic waste Changing Patterns of Life pp. 214-217 Identify/Define: Cottage Small business conducted out of the home industry Infant Number of babies that die mortality How has the government emphasized education and how has this emphasis caused problems? Not everyone is receiving the same education Where do most people live in India: cities, villages or towns? villages Effect of modernization on Indian families Infant mortality dropped & nuclear family became more common Regional and Global Issues pp. 223-227 Why are India and Pakistan fighting over Kashmir?: For the Indus river, and fertile soil How did the Cold War affect India & Pakistan? US & USSR gave India money – India maintained non-alignment (picked no side) Soviet Invasion of Afghanistan – USSR invaded Afghanistan to “help”it become communist; Afghans Soviets out. 4