Middle East Review Global Studies Name
advertisement

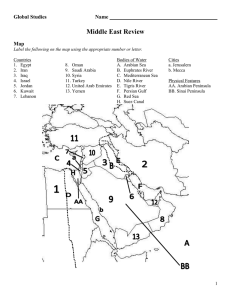
Global Studies Name Middle East Review Map Label the following on the map using the appropriate number or letter. Countries 1. Egypt 2. Iran 3. Iraq 4. Israel 5. Jordan 6. Kuwait 7. Lebanon 8. Oman 9. Saudi Arabia 10. Syria 11. Turkey 12. United Arab Emirates 13. Yemen Bodies of Water A. Arabian Sea B. Euphrates River C. Mediterranean Sea D. Nile River E. Tigris River F. Persian Gulf G. Red Sea H. Suez Canal Cities a. Jerusalem b. Mecca Physical Features AA. Arabian Peninsula BB. Sinai Peninsula 1 General Information Origin of Term Given from a western perspective, it is a name given to group together “Middle East” countries with similar cultural and geographic characteristics Significance of It is where three continents meet (Asia, Africa, Europe); It is where the Region three monotheistic religions began (Judaism, Christianity, Islam); it is the largest course of the World’s oil Common Desert Geographic Feature Most Common Religion Most Common Language Islam Common Government Types Republic and monarchy Arabic Region with Similar Northern Africa Characteristics Monotheism Key Figure Date of Origin Holy Book Holy Day Building of Worship View of Jesus Holidays Judaism Abraham, Moses Jesus Islam Muhammad ~2500 B.C.E. ~100 C.E. ~600 C.E. Torah (613 laws) Bible Koran Friday sundown to Saturday sundown Temple, Synagogue Sunday Friday Church Msoque He is not part of their religion Rosh Hashanah Yom Kippur Passover Lord and savior Prophet Easter Christmas Ramadan Eid al-Fitr Jesus lived, died, was crucified, buried, and rose from here After death, Muhammad ascended Golden Ladder (now Done of the Rock) Importance of Site of 1st & 2nd Jerusalem Temples; capital of Kingdom of Israel Christianity 2 Judaism Made covenant with God to worship one god Abraham Story of the Jewish people escaping slavery in Egypt; led by Moses Exodus King of Israel; established Jerusalem as capital David Sons of David; king of Israel; built first Temple Solomon King of Israel; Built second Temple Herod Western Wall Spreading out of a homogenous people’ it refers to when the Jewish people were scattered around the world Only remaining wall of the Jewish people’s Temple in Jerusalem; it is considered the holiest site for Jewish people Islam Islam Name of the religion Muslim A person who practices Islam Muhammad Jihad Prophet of Islam; received the word of God from the Angel Gabriel who told him to recite it. A turning point for Islam, it was the journey of Muhammad & his followers from Mecca to Median; year 1 in the Muslim calendar Holy war Holy Cities #1 – Mecca, #2 – Medina, #3 - Jerusalem Diaspora Hejira Five Pillars of Islam 1. There is one god, Allah 2. Pray 5 times a day facing Mecca 3. Make a pilgrimage (hajj) to Mecca 4. Fast during holy month of Ramadan 5. Give charity to the poor 3 Arab-Israeli Conflict Terms Homeland of the Jewish people Israel Palestinian West Bank, Gaza Strip, Golan Heights Territories Movement to establish a Jewish homeland Zionism British document stating the need for a Jewish homeland, but not Balfour Declaration at the expense of the Arab people already living there Plan to separate the land into a Jewish Israel and Arab Palestine; UN Partition Plan plan was rejected by the Arabs, but accepted by the Jewish people Palestinian uprising in protest against continued Israeli occupation Intifada of West Bank and Gaza Strip Arab-Israeli Conflict Wars Name Date 1948 War 1948 Suez Crisis/War 1956 Six Day War 1967 Yom Kippur War 1973 Outcome Israel declares itself a country, Arab nations attack, Israel defends itself and gains Arab land Israel, Britain, and France attacked Egypt after Nasser nationalized the Suez Canal; Israel withdrew Israel gains control of the West Bank, Gaza Strip, East Jerusalem, and the Golan Heights Egypt and Syria attacked Israel to regain land lost in Six Day War; Israel successfully defended itself Arab-Israeli Peace Agreements Camp David 1978 Date Egypt, Israel, U.S. Participants Outcome Egypt acknowledged existence of Israel (first Arab nation to do so); Sadat (Egypt) was assassinated for concessions given to Israel Oslo Accords 1993 Israel, Palestinians, U.S. Palestinians received autonomy or self-rule; Rabin (Israel) was assassinated for concession given to the Palestinians Iraq & Persian Gulf War Dictator of Iraq Saddam Hussein 4 US Role in Persian Gulf War Event that Started War Led a coalition force (many countries working together) to get Hussein out of Kuwait Hussein invaded Kuwait Ways it was Hussein was left in power “unfinished” at the time Objective of recent war in Iraq Iraq was suspected of producing weapons of mass destruction; our goal was to remove Hussein from power Iran Leader’s Name When & How Gained Power Shah Pahlavi Monarchy Theocracy Ayatollah Khomeini Ancient Empire Reforms He Promoted Wanted to modernize and westernize 1979 Islamic Created a theocracy and broke off Revolution ties with western nations overthrew the Shah Persian Language & Ethnic Persian (Farsi) language; Persian Ethnicity Group Major Sect of Islam Sh’ia/Shi’ite Iran’s War: Opponent & Years Reason for Current Tension with U.S. OPEC OPEC Largest Oil Producer Egypt Importance of Nile Valley Gamal Abdel Nasser Iraq; 1980-1988 Iran is trying to develop it’s nuclear energy program and we are concerned it is for weapons Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries; influences the amount of oil produced in the world Saudi Arabia It is fertile soil, only place in Egypt that is farmable, and the birthplace of the Ancient Nile Valley Civilization; Leader of Egypt that promoted Arab socialism, and Egyptian nationalism 5 Nasser’s Economic End foreign ownership of resources, modernization Goals Actions Nasser Took Nationalized some of the country’s resources and industries to Achieve Goals Aswan High Dam Suez Crisis Anwar Sadat Major modernization project; it is a hydroelectric dam built along the Nile River When Nasser nationalized the Suez Canal, Israel, France, and Britain attacked Leader of Egypt that recognized the existence of Israel; he was assassinated for giving too much to Israel Turkey Ottoman Empire Former Empire Mustafa Ataturk Ataturk’s Reforms Ways Turkey Differs from Other Middle East Nations Leader of Turkey that promoted Turkish nationalism and its modernization and westernization Created secular government, decreased traditional clothing, simplified alphabet, implemented last names Secular government, similarities to European nations Terrorism Osama bin Laden Al Qaeda 9/11 Attacks Former leader of al Qaeda and organizer of several terrorist attacks on the U.S., including 9/11 Attacks Terrorist organization aimed at the destruction of western nations (especially U.S.); responsible for 9/11 Attacks 4 airplanes were hijacked and used to hit the World Trade Center (NY) and the Pentagon (VA); a 4th plane went down in PA Afghanistan Cold War Conflict Mujahedeen Taliban Reason for US Military Action Soviet Union invaded 9179 to “help” Afghan communists; the U.S. helped the Afghanis repel this invasion Group, which included Osama bin Laden, that the U.S. helped train to fight against the Soviet invasion Conservative Islamic group that has controlled large portions of Afghanistan; opposes any Westernization Osama bin Laden organized 9/11 Attack from Afghanistan; Taliban would not turn him over to U.S., so we attacked 6