cultural Characteristics of North Africa and the Middle
advertisement
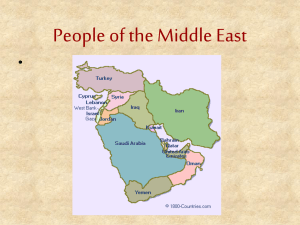
CULTURAL CHARACTERISTICS OF NORTH AFRICA AND THE MIDDLE EAST Francisci WG.4 Palestine and Israel Before 1948, this land was known as Palestine. After intense feelings of nationalism, the Jewish people in Palestine created the country of Israel in 1948. The areas known as West Bank and the Gaza Strip are where most of the Arab Palestinians live today (Muslims). The area known as Golan Heights is a disputed area between Israel and Syria. Modern Day Israel Religion Religion is a divisive force in the Middle East. The Middle East is the birthplace of 3 monotheistic religions – Judaism, Christianity and Islam. Jews, Christians and Muslims all claim the city of Jerusalem as a religious heritage site. Modernization Many people in the Middle East are moving to urban areas (cities) thus resulting in rapid industrialization. The way of life differs greatly in urban areas as opposed to rural areas. Modernization is centered in urban areas while traditional life continues in rural areas. Many people in rural areas are living as nomads – individuals who move from place to place with herds of animals. Population The population is made up of a large percentage of people 15 years or younger. The population pyramid has a wide base and is shaped like a triangle or pyramid. Because of the dry climate and the physical features of the land, the population is not distributed evenly. Population Distribution of Middle East Boundary and Territorial Disputes Western Sahara and Morocco (over resources). Iraq and Kuwait (over oil). Israel and Syria (for Golan Heights). Turks and the Greeks on the island of Cyprus (ethnic differences). Kurdistan Area that includes parts of Iran, Iraq and Turkey, Syria and the former Soviet Union. The Kurds, an ethnic group, lives in this region. The Kurds have strong feelings of nationalism and want their own nation. Arab vs. Non-Arab Countries The main ethnic group in the Middle East is Arab. The language spoken by the Arabs is Arabic. Non-Arab countries in the Middle East include Turkey, Iran and Israel. Political Organizations The League of Arab States: Political organization of over 20 Arab nations. Designed to strengthen ties among the members, coordinate policies, and promote common interests. Art The art of the region reflects the diversity of religions. Stained glass Geometric tiles Calligraphy Mosaics Prayer rugs Architectural Structures Religious buildings: Mosques (Islam) Churches (Christianity) Synagogues (Judaism) Architectural Structures Dwellings: Tents Yurts: a circular tent of felt or skins on a collapsible framework, used by nomads. Architectural Structures Statues and monuments of the region include: Kaaba (Mecca) – Islam Western Wall (Jerusalem) – Islam Dome of the Rock (Jerusalem) – Islam Church of the Holy Sepulcher (Jerusalem) – Christianity Pyramids – Egypt Architectural Structures Mosques and minarets: a tall slender tower attached to a mosque. Hagias Sophia: Museum in Istanbul, Turkey – a church then a mosque. Bazaars and suqs: an outdoor market in an Arab city. Walled Cities Oil Rigs