Document 14120866
advertisement
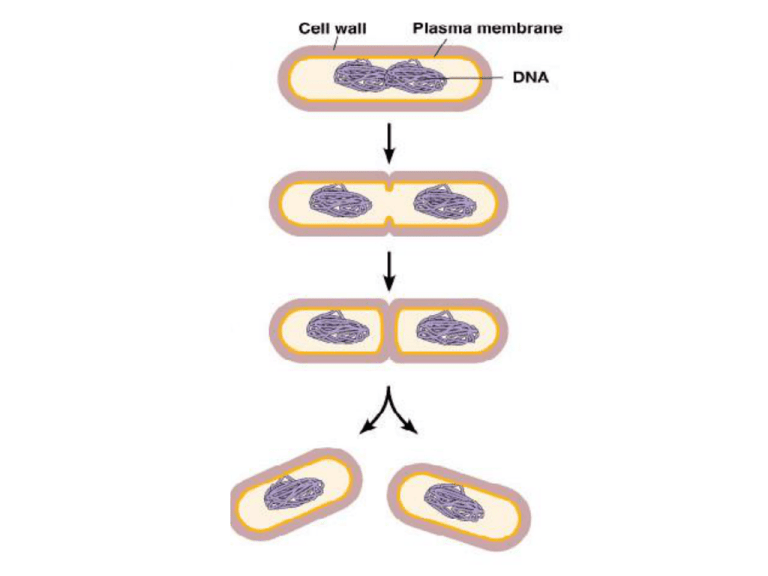
BILL: Identify the structures 1-5 in the prokaryotic cell. 1 2 3 4 5 TYPE OF METABOLISM ENERGY SOURCE CARBON SOURCE EXAMPLE Bacteria that live in the human body (for example E. coli) and all disease causing bacteria. Nitrifying bacteria use nitrogen from the air as their energy source (for example nitrobacter) Rare now, but may have been some of the first life on Earth. Mostly marine prokaryotes. Cyanobacteria live in fresh water, seas, soil and lichen, and use a plant-like photosynthesis which releases oxygen as a byproduct. TYPE OF METABOLISM ENERGY SOURCE Chemoheterotroph Organic compounds Chemoautotroph Inorganic substances such as nitrogen and sulfur Photoheterotroph Photoautotroph Light Light CARBON SOURCE Organic compounds EXAMPLE Bacteria that live in the human body (for example E. coli) and all disease causing bacteria. Nitrifying bacteria use CO2 nitrogen from the air as their energy source (for example nitrobacter) Organic compounds Rare now, but may have been some of the first life on Earth. Mostly marine prokaryotes. CO2 Cyanobacteria live in fresh water, seas, soil and lichen, and use a plant-like photosynthesis which releases oxygen as a byproduct. BILL: WHAT SIMILARITIES DO YOU NOTICE? • Between “photo…” • Between “chemo…” • Between “auto…” • Between “hetero…” Prokaryotic metabolism • How do bacteria acquire their energy & nutrients? – photoautotrophs • photosynthetic bacteria – chemoautotrophs • oxidize inorganic compounds – nitrogen, sulfur, hydrogen… – heterotrophs • live on plant & animal matter • decomposers & pathogens CHEMOHETERTROPH CHEMOAUTOTROPH PHOTOAUTOTROPH Cyanobacteria •A type of prokaryote with much infolding of the cell membrane •Capable of performing photosynthesis, which releases oxygen into the atmosphere CYANOBACTERIA ARE BACTERIA… Which means they have no organelles!!! But, they can do photosynthesis. And, they do have membranes that have folded in. Hmmm… I wonder if this will be important later on in our class…. BILL: Relative to cells without the infolding, how will infolding of the cell membrane change the cells… …Surface area?? …Volume?? …Surface area to volume ratio?? 13