Document 14118576
advertisement

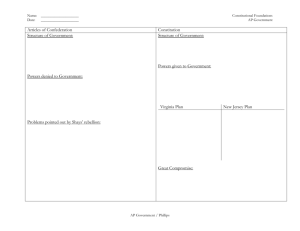
THE ROAD TO RATIFICATION: 1787 Hamilton, proposed another convention after Annapolis, 1787. All states but Rhode Island sent delegates to Phila, beginning on th May 25 1787. Major point of concern: Virginia Plan vs. New Jersey Plan. (proportionality of representation.) “The Great Compromise” House and Senate. 3/5 Compromise: slavery question. Do slaves count towards popular vote? Federalists vs. Anti-­‐Federalists. Federalists -­‐wanted orderly and efficient gov. -­‐usually aristocratic. -­‐not anti-­‐freedom, but preferred central authority. -­‐Example: James Madison Anti-­‐Federalists -­‐usually small farmers. -­‐most interested in individual freedoms. -­‐Example: George Mason THE ROAD TO RATIFICATION: 1787 Approach to the writing of the Constitution was pragmatic and not theoretical. -­‐Economic issues were less debated, in other words most Federalists and Anti-­‐Federalists supported the economic reasons for centralization. -­‐Delaware ratified 1st, dec 2nd 1787, PA was second dec 7th. -­‐Mass and NH were the closest ratification votes, but both still approved. -­‐NH was the 9th state to approve, making the Constitution operable. -­‐VA, APPROVED 89-­‐79 NY 30-­‐27, Hamilton led the way, Federalist Papers (Madison as well) Washington elected president, 1789