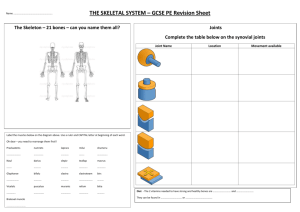
Name______________________________________________________________Section___ __ The five functions of the skeletal system are
advertisement

Name______________________________________________________________Section___ __ Unit 4 ­ Skeletal System Review The five functions of the skeletal system are ­ 1. Support 2. Protection 3. Movement 4. Mineral Storage 5. Hematopoiesis (blood cell formation) List the four shapes of bones and give an example of each ­ 1. Short ­ carpals, tarsals, calcaneus 2. Long ­ humerus, tibia, fibula 3. Flat ­ skull, sternum, ribs, scapula 4. Irregular ­ vertebrae, mandible, sacrum, pelvis (sesamoid ­ special short bone ­ patella) This type of bone is a special type of short bone that forms within tendons.___sesamoid_______ List and describe the parts of a long bone. 1. Diaphysis ­ the long part 2. Epiphysis ­ the ends, covered in articular cartilage, articulate with other bones 3. Metaphysis ­ where the diaphysis and epiphysis meet What type of cartilage makes up a fetal skeleton and can be found on the ends of long bones? ____articular (hyaline) cartilage______________ Compact bone is found on the outside of the bone while spongy bone is found on the interior of the bone and contains ____marrow_____________. Which body cavities do the axial skeleton support and protect? _______Ventral cavity________ Cranial Bones Frontal Parietal Temporal Occipital Sphenoid Ethmoid Lambdoid Sagittal Coronal Squamous Hyoid _Frontal______ 1. Forms the anterior portion of the cranium and roof of eye sockets __Temporal___ 2. Form part of both the lateral walls of the cranium _Sphenoid____ 3. Butterfly shaped bone that forms part of the floor of the cranium _Parietal______ 4. Forms most of the superior and lateral aspects of the skull _Ethmoid_____ 5. Most deep of the skull bones; lies between the sphenoid and nasal bones __Parietal_____6. These are the paired bones of the cranium __Temporal___ _Lambdoid____7. These are the sutures of the cranium __Sagittal_____ ____Coronal_____ ___Squamous____ __Hyoid______ 8. This is inferior to the mandible and does not articulate with any other bones Vertebral Bones Thoracic Sacrum Altas Axis Cervical Lumbar Coccyx __Atlas_______ 1. The C1 is called this. __Axis________ 2. The C2 is called this. __Atlas_______ 3. This is the only vertebrae that does not have a body. __Cervical____ 4. Starting with the most superior, the vertebral column consists of the following vertebrae. ___Thoracic__ ___Lumbar____ ___Sacrum____ __Coccyx____ __Thoracic____ 5. These vertebrae articulate with the ribs. What is the difference between the true ribs and the false ribs? True ribs attach directly to the sternum. False ribs have an indirect connection. Appendicular Skeleton Ulna Radius Clavicle Scapula Ilium Tibia ___Tiabia_____ 1. The large medial bone of the lower leg ___Ulna______ 2. The bones that support the forearm ___Radius____ ___Clavicle___ 3. The bones that make up the pectoral girdle __Scapula____ __Clavicle____ 4. The bone that is intermediate to the sternum and humerus ___Radius____ 5. The bone in the forearm that articulates with the wrist __Ilium_______ 6. These bones make up the pelvic girdle Ischium Pubis __Ischium____ ____Pubis_____ Describe the differences between the pelvis of a male versus a female. Female ­ tilted forward, cavity is broad and shallow Male ­ Tilted less forward, cavity is narrow and deep Joints List the six types of synovial joints and where they can be found in the body. 1. Gliding ­ wrist, ankles, sacroiliac joints, ribs 2 ­ 7 with sternum 2. Hinge ­ elbow, joints of the phalanges, knee, jaw 3. Pivot ­ joint between the proximal ends of the radius and ulna, the arch of the atlas rotates around the dens of the axis 4. Condylar/Ellipsoidal ­ joints between the metacarpals and phalanges 5. Saddle/Sellar ­ joint between the carpal and metacarpal of the thumb 6. Ball and Socket ­ hips and shoulder Adipose tissue that protects articular cartilage and acts as packing tissue for the joint is called ____fat pads_________________. Fractures This fracture occurs when one side of the bone is broken and the other side is bent. ____Green Stick______________ This fracture projects through the skin. ______Open or Compound_______ This type of fracture is produced by twisting. _____Spiral________________________ This type of fracture results in shattered pieces. __________Comminuted______________ Describe what is happening in each picture as it relates to bone fractures healing. Step 1 ­ Extensive bleeding, fracture hematoma forms, dead bone extends along the shaft Step 2 ­ Cell division occurs and migrates to the fracture area, hard skin forms, internal callus organizes, broken ends are temporarily stabilized Step 3 ­ Osteoblasts replace central cartilage with spongy bone, calluses form a brace at the fracture site, if there was a cast, it can be removed at this stage Step 4 ­ Osteoclasts and osteoblasts continue to remodel the bone, the bone could be slightly thicker and stronger than normal at the fracture site Disorders & Diseases Scoliosis Osteoporosis Osteomalacia Osteoarthritis _Osteoporosis___ 1. A reduction in bones mass that would compromise normal function _Scoliosis_______ 2. Curvature of the spine _Osteomalacia___ 3. Softening of the bones due to lack of Vitamin D __Osteoarthritis__ 4. Degenerative joint disease, mostly in weight bearing joints __Osteoarthritis______ __Scoliosis_________ _Osteomalacia____