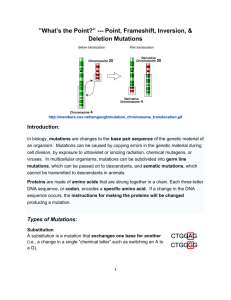
Lecture #20 – 10/22/01 – Dr. Wormington X
advertisement

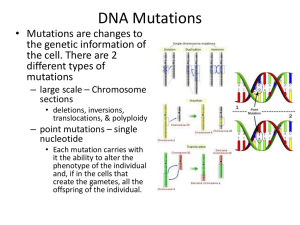
Lecture #20 – 10/22/01 – Dr. Wormington When Bad Things Happen to Good DNA! "Small Scale" Genetic Mutations Lose H-bond donor X Lose H-bond acceptor Gain H-bond donor Imino Now pairs with A Amino tautomer normally Pairs w/ G Fig. 12.19 has an Error! Delete this extraneous bond! Even mutations don't generate pentavalent Carbon atoms! More Bad Things That Can Happen to Good DNA! "Small Scale" Genetic Mutations Vegens & Wine Aficionados Beware! Bisulfite used as anti-oxidant in wine & To prevent veggies from wilting in salad bars Nearly as potent a mutagen as Nitrous Acid Lose H bond donor HSO3 Gain H bond acceptor Generated by Breakdown Of Nitrites Consumed as Preservatives In Smoked Meats, Hot dogs etc. Now pairs with A Proofreading or Mismatch Repair Eliminate Mutation CG Base Pair Converted to TA Base Pair Pairs w/ A During Replication Deaminated C Mismatch not corrected Cytosine is Not the Only Base Which Can be Mutated Potent Mutagen Used in Laboratory To Generate Mutants GC Base Pair Converted to AT Base Pair Carcinogens (Chemicals Which Cause Cancer) = Mutagens React Directly w/ DNA Must 1st Be Metabolized Before Reacting w/ DNA Dry Cleaning Cigarettes Exotic Food Spice Moldy Peanuts Change 1 amino acid to another Phe to Leu is a Conservative Substitution Introduces a Premature Stop Codon Generates a truncated protein. ~30% of all human genetic diseases due to nonsense mutations Extra nucleotide incorporated during replication 4 nucleotides deleted during replication Frameshift mutations most deleterious as resultant protein is almost always nonfunctional •Some Final Thoughts on "Small" Mutations •Not Every Mutation Has an Effect Mutations in 3rd Position of Degenerate Codons Often Don't Change Amino Acid Synonym Codons Encode Similar Amino Acids Not Every Nucleotide Is Present Within a Coding Region (or even a Gene!) •Can Mutations Map Outside of Coding Regions? Mutations Within Transcription Promoters Can Affect Gene Expression "Up" Mutations Increase Amount of mRNA/Protein Product "Down" Mutations Decrease Amount of mRNA/Protein Product •Is There Anything You Can Do To Avoid Mutations? •Don't Eat, Drink, Breath •Don't Go Outside or Work Inside •Mutations Drive Evolution! •Without Mutations We'd Still be Amoebae •Now Onto "Large Scale" Mutations "Large" Scale Chromosomal Mutations DNA molecule broken at 2 sites by ionizing radiation & rejoins w/o middle fragment Gamete will lack C&D Homologous chromosomes break at 2 different sites & reattach at wrong places "Nonreciprocal recombination" Gamete has duplicated C&D Zygote will be functionally triploid for these 2 genes DNA molecule broken at 2 sites by ionizing radiation & rejoins w/ middle fragment reversed "Nonhomologous" chromosomes recombine common in many cancers Viruses – Molecular Parasites • Causal Agents of Numerous Human Diseases Spanning the Cold to Cancer Incl. Hepatitis, Flu, Ebola, Smallpox, Measles, Herpes, HIV, Polio, West Nile • Relatively Small Genomes (DNA or RNA) Amenable to Genetic Analyses • Relatively Simple Bipartite Gene Expression Program “Early” Genes Expressed Before Viral Genome Replication “Late” Genes Expressed After Viral Genome Replication • Utilize Host Cell Biosynthetic Processes During Infection Provide Excellent Models to Study Basic Molecular & Cellular Events • Typically Proliferate By 1 of 2 Life Cycles – Some Viruses Exhibit Both “Lytic” or “Productive” Infection Lyses & Usually Kills Infected Cell Cells supporting Lytic Cycle Termed “Permissive” • “Lysogenic” or “Nonproductive” Infection Results in Integration of Viral DNA Into Host Cell Genome “Provirus” Infectious Viral Progeny Usually Not Generated Cells supporting Lysogenic Cycle Termed “Nonpermissive” • Viruses Can Be Inhibited by Anti-viral Therapies or Vaccines, but not Antibiotics!