PAPER 7B STRATEGIC MANAGEMENT QUESTION 1 IS COMPULSORY.
advertisement

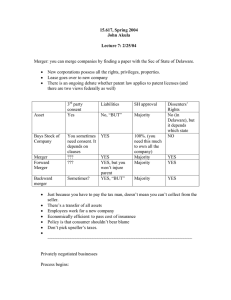
PAPER 7B STRATEGIC MANAGEMENT QUESTION 1 IS COMPULSORY. ATTEMPT ANY TWO QUESTIONS FROM THE REMAINING. 21st October 2015 50 MARKS Q 1. Answer the following questions – 1. 2. 3. 4. (5 MARKS EACH) Explain in brief the steps necessary to implement BPR. Why do companies feel it necessary to deviate towards globalization? What are the objectives of SWOT analysis? Define network structure in brief. Q 2. (A) State with reasons which of the following questions are correct/incorrect :- (2 MARKS EACH) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Portfolio analysis involves comparison of various functional areas of business. Strategic management is a bundle of tricks and magic. SWOT analysis presents a comparative account. Focus strategies are most effective with consumers having similar preferences. TQM is a people-focused management system that aims employee’s satisfaction. (B) How is ‘Strategic Business Unit’ beneficial for improving the competitive advantage of a firm? (5 MARKS) Q 3. Differentiate between the following:- (5 MARKS EACH) 1. Synchro marketing and De-marketing 2. Divestment strategy and Liquidation strategy 3. Logistic management and Supply chain management Q 4. (A) Briefly explain the different types of merger. (B) Briefly explain the four strategies as discussed by Glueck and Jaunch. Page 1 of 5 (8) (7) SUGGESTED ANSWERS to SM Mock Test of 21st October 2015 Q1. A1. Companies begin business process re-engineering by creating a plan of action based on the gap between the current and proposed processes, technologies and structures. Steps involved in implementing BPR are as follows:1. Determining objectives and framework – objectives are the desired results of the redesign process which the management attempts to achieve. It helps in building a comprehensive foundation for the re-engineering process. 2. Identify customers and determine their needs – the designers have to understand customers since the purpose to redesign a process is to add value to customers. 3. Study the existing process – existing process provides an important base for the redesigners. 4. Formulate a redesign process plan – this is the real crux of the re-engineering efforts. 5. Implement the process – the process should be applied over the organization to achieve a dramatic improvement in achieving the objectives. A2. Reasons necessary for the globalization of companies are as follows :1. Due to rapid shrinking of time and distance across the globe resulting in faster communication, transportation, growing financial flows and rapid technological changes. 2. Domestic market is not large enough to absorb whatever is produced. 3. Justification of foreign investment keeping in view the size of foreign market. 4. Securing a reliable and cheaper source of raw-materials. 5. Reducing high transportation costs by setting up over-seas plants. A3. The basic objectives of conducting SWOT analysis are as follows :1. To exploit the strengths of the company to achieve its objectives. 2. To identify the shortcoming in the company’s present skills and resources and to take necessary corrective steps so that the overall interest of the organization is protected. 3. To focus on profit making opportunities in the business environment and for identifying threats. 4. To highlight areas within the company, which are strong and might be exploited more and weaknesses, where some defensive planning might be required to prevent the company from downfall. Page 2 of 5 A4. Network structure is a newer and somewhat more radical organizational change design. The network structure could be termed as non-structure as it virtually eliminates in-house business functions and outsource many of them. A corporation organized in this manner is a virtual organization because it is composed of a series of project groups or collaboration linked by constantly changing non-hierarchical , cobweblike networks. Q2(A) 1. Incorrect – portfolio analysis can be defined as a set of technologies that help strategies in taking strategic decisions with regard to individual products or businesses in a firm’s portfolio. 2. Incorrect – strategic management is not a bundle of tricks and magic. It involves systematic and analytical thinking and action. 3. Correct – SWOT analysis presents the information about both external and internal environment in a structured form so as to compare strength, weakness, opportunity and threats. 4. Incorrect – Focus strategies are most effective when customers have distinctive preferences or requirements and when rival firms are not attempting to specialize in the same segment. 5. Incorrect – TQM is a people-focused management system that aims at continual increase in customer satisfaction at lower real cost. Q2(B) A Strategic Business Unit is beneficial for improving the competitive advantage of a firm in the following ways – 1. A scientific way of grouping the businesses of a multi-business corporations to enable strategic planning. 2. An improvement over the territorial grouping of businesses and strategic planning based on it. 3. Products that are related from the standpoint of function are assembled together. 4. Each SBU will have its own set of competitors. 5. Each SBU will have its own CEO. 6. Each SBU shall have its own distinct strategy for improving performance. Q3. 1. Synchro marketing – when the demand for any product is irregular due to season, some parts of the day, hour basis, synchro marketing can be used to find ways to alter the same pattern of demand through flexible pricing, promotion, and other incentives. For example, movie tickets can be sold at a lower cost over weekdays to generate demand. Demarketing – marketing strategies to reduce demand temporarily or permanently – the aim is not to destroy demand but only to reduce or shift it. This happens when there is overfull demand. For example, buses are overloaded in the morning and evening, roads are busy for most of the times, parks are crowded on weekends, etc. Here demarketing can be applied to regulate demand. Page 3 of 5 2. Divestment strategy – it involves the sale or liquidation of a portion of business or a major division, profit centre or SBU. It is usually a part of rehabilitation or restructuring plan and is adopted when a turnaround has been attempted but has proved to be unsuccessful. The option of a turnaround may even be ignored if it is obvious that divestment is the only answer. Liquidation strategy – Liquidation as a form of retrenchment strategy is considered as the most extremeand unattractive. It involves closing down a firm and selling its assets. It is considered as the last resort because it leads to serious consequences such as a loss of employment for workers, termination of opportunities a firm could pursue and the stigma of failure. 3. Supply chain management is an extension of logistics management. However, there are differences between the two. Logistic management includes management of inbound logistics, outbound logistics, transportation, warehousing, ordering and handling material and inventory management. It is related to planning, implementing and controlling movement and storage of goods. Supply chain management is an integrating function of all major activities within the organization. it is a system review of linkages in the chain consisting of different partners – suppliers, intermediaries, third parties and customers. It involves delivering the right product at the right time at the right place in a right way. Q4(A) Merger is a process of combining two or more organizations together. The different forms of mergers are as follows – 1. Horizontal merger – they are combination of firms engaged in the same industry. It is a merger with a direct competitor. The principle objective behind this is to achieve economies of scale in the production process by shedding duplication of functions. For example, formation of Brook Bond Lipton India Ltd. through merger of Lipton India and Brook Bond. 2. Vertical merger – it is a merger of two organizations that are operating in the same line of industry but at different stages of production and distribution system. This leads to increased synergies with the merging firms. If an organization takes over its supplier, it is known as backward integration. If an organization takes over its distribution channel, it is termed as forward integration. 3. Co-generic merger – in co-generic merger, two or more merging organizations are associated in some way or the other related to production, technologies, etc. it helps businesses to diversify around the same set of resources and strategic requirements. 4. Conglomerate merger – it is a combination of organizations that are not related to each other. There are no linkages and no common factors between the merging organizations. Page 4 of 5 Q4(B) According to Glueck and Jaunch there are four ways in which generic strategiescan be considered which are as follows – 1. Stability strategies – one of the important goals of a business is stability to safeguard its existing interests and strengths to pursue well established and tested objectives, to continue in the chosen pat, to maintain operational efficiency on a sustained basis, to consolidate the commanding position already reached, etc. 2. Expansion strategy –it is implemented by redefining the business by adding the scope of business substantially increasing the efforts of the current business. It is a promising and popular strategy that tends to be equated with dynamism, vigor, promise and success. 3. Retrenchment strategy – a business organization can redefine its business by divesting a major product line or market. It becomes necessary or expedient for coping with particularly hostile and adverse situations in the environment. 4. Combination strategies – stability, expansion or retrenchment strategies are not mutually exclusive. It is possible to adopt a mix to suit particular situations. Such a mixture f strategies is termed as combination strategies. Page 5 of 5