MPLS: The Magic Behind the Myths Grenville Armitage Lucent Technologies
advertisement

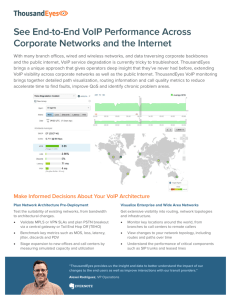
MPLS: The Magic Behind the Myths Grenville Armitage Lucent Technologies Introduction Reviews key differences (and similarities) between IP routing and emerging MPLS approach Article highlights MPLS does not offer much as once portrayed – e.g. gigabit forwarding Fails to point out flaws in vision Contribution related to traffic engineering Scalability Issues MPLS provides traffic engineering capabilities – agreed Benefits of MPLS extend only as far as its deployment End-to-end solution possible only if entire network MPLS enabled MPLS is domain specific! Scalability Issues (contd.) VoIP packet Supports MPLS No MPLS No QoS guarantee MPLS is domain specific!! Stateful Routers LSR (label-switching routers) keep info about different labels Labels correspond to states stored in router Routers that keep information are bad Does not mention how to deal with failures Stateful Routers P 1 4 P 2 ?? 3 Lose label information Loss of Label makes packet Unroutable! Control and Management Unclear how QoS characteristics of each LSP managed Unclear how non-shortest paths for traffic engineering obtained Human intervention required for router configuration Complex and error-prone MPLS not for QoS Domain specificity and scalability issues in deployment No standards to designate Type of Service (TOS) bits MPLS has no end-to-end solution MPLS suffers from static routing problems Static Routing Problem P 4 1 3 P P 2 MPLS offers static routing only! P MPLS not for QoS (contd.) Internet is a significant and rapidly growing carrier of voice traffic Ineffective and impractical for fluctuating demands of VoIP MPLS nothing but domain-specific circuit switching MPLS for VPNs No automatic encryption of data Susceptible to data leak if a connection is disrupted Potential for administrator doing wrong provisioning causing loss of privacy Not clear how MPLS will make use of encryption for security ISPs must manage routing table for each VPN Where does MPLS fit ?? Aims to perform a useful function at the wrong layer – not universally useful LSR, according to IETF specs, expects to speak IP No strategy for evolving an existing ATM network into MPLS network No Application-level Routing Intelligence Need to distinguish different packets on the network QoS requirements statically determined in MPLS Can’t make use of application specific knowledge and requirements MPLS unfit for VoIP MPLS unaware of application requirements No alternate routing to prevent latency, delay, packet loss, jitter Static and domain-specificity hurts in long run Conclusions MPLS static and non-application aware Suited to core of major networks Can be deployed only in single-domain environment where all routers are MPLS enabled No end-to-end solution Guaranteed QoS still elusive MPLS – No Magic, All Myth!!