APEX III Behavior Support (Tier 2) Team Training Retreat
advertisement

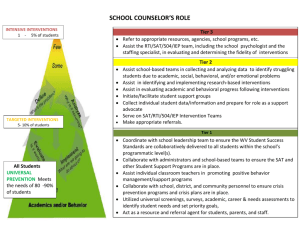
3/11/2014 APEX III Behavior Support (Tier 2) Team Training Retreat Taking Problem Solving to Action Planning March 11, 2014 www.inclusiveed.org 3/11/2014 • This initiative, called Achievement in Dropout Prevention and Excellence (APEX), includes implementation of Positive Behavioral Interventions and Supports (PBIS) combined with an individualized school-to-adult-life transition model developed by the IOD. • The state of New Hampshire has worked with the Institute on Disability since 2002 to implement a Multi-Tiered System of Support (MTSS) focused on behavior in high schools. 3/11/2014 www.inclusiveed.org 2 1 3/11/2014 RENEW is funded by a grant from the Endowment for Health. www.inclusiveed.org 3 3/11/2014 The APEX High School Model: Positive Behavior Interventions & Supports & RENEW Malloy, Agorastou & Drake, 2009 Adapted from Illinois PBIS Network, Revised Sept., 2008 & T. Scott, 2004 Student Progress Tracker; Individual Futures Plan Competing Behavior Pathway, Functional Assessment Interview, Tier 3/Tertiary RENEW and Wraparound Simple Individual Interventions (Brief FBA/BIP, Schedule/ Curriculum Changes, etc) Progress Monitoring (Behavior and Academic Goals) ODRs, Attendance, Tardies, Grades, Credits, Progress Reports, etc. Tier 2 Small Group Interventions (CICO, Social and Academic support groups, Social Skills) Universal: School-Wide Assessment School-Wide Prevention Systems www.inclusiveed.org 2 3/11/2014 Our Expectations Expectations Leadership Team Training Be Responsible Be Respectful Be Prepared Make sure you are comfortable & that your personal needs are met Address question/activity in group time before discussing “other” topics Address your attention to the topic and task Ask questions Turn cell phones, beepers, PDA’s, and pagers off or to vibrate/silent Limit the use of “screens” unless you require them for disability augmentive purposes. Respect and consider every idea Contribute to activities and conversations Bring an open mind Follow through www.inclusiveed.org Agenda for the Day • Team Structure & Processes • Team Activity: Collaborative Team Checklist • Problem-Solving and Data-Based Decision Making • Increasing efficiency around FBA/BIP implementation • Team Activity: BST Checklist • Review Team Goals & Report Out 3/11/2014 www.inclusiveed.org 6 3 3/11/2014 List 3-5 Objectives for the Day www.inclusiveed.org CONTINUUM OF SCHOOL-WIDE POSITIVE BEHAVIOR SUPPORT Tertiary Prevention: Individualized Systems for Students with High-Risk Behavior ~5% ~15% Secondary Prevention: Targeted Systems for Students with At-Risk Behavior Primary Prevention: School-wide/Classroom/ Non-classroom Systems for All Students, Staff, & Settings Today’s focus ~80% of Students www.inclusiveed.org 4 3/11/2014 Tier 2: Basic Team Features & Readiness Features Readiness • • Tier 1 system is in place. • Full administrative and staff support • People & Skills • Understands functioned-based perspective • Develops Tier 2 interventions • Ready to coach staff in Interventions • Distinguish between students needing Tier 2 and Tier 3 Supports Effective & Efficient Team Process • Serve the ‘right’ need • Have group interventions ready and implement with fidelity Use data to evidence success • Use data to drive decisions • Know when supports must be individualized and/or more comprehensive (refer for plan development to folks with expertise) N u m b e r o f R e f e rra ls p e r S t u d e n t www.inclusiveed.org 9 Referrals per Student 20 10 0 Students www.inclusiveed.org 5 3/11/2014 Pyramid of Interventions Level III: Intensive, Individual Interventions •GEDO •PLP •SDA Diploma •MSP •REN EW •Complex FBA/BSP Community Agency Referrals •Community Partners •HUB •North Star Level II: Targeted Interventions • CICO •Social Skills Groups •Simple FBA •Anger Management Groups •Mediation •Adult Ed Classes •Credit Recovery •Truancy Interventions •Drug and Alcohol Counseling • Alt Study Level 1: Universal Interventions and Supports • Differentiated Instruction • Behavior matrix •Parent Contact •Student /Teacher Conference • Parent/teacher Conference •Guidance Support •ELO’s •Extracurricular Activities •RQQP •VLACs •After School Support •Freshman Experience/Academic Skills www.inclusiveed.org * Created by Somersworth High School & NH RESPONDS Facilitator 3-Tiered System of Support at KHS Universal Team Plans school-wide and class supports Child Study Team Intensive Team (Tier II: Behavior Support Team Support Team) (Tier III: Individualized Intensive Support) •Standing team • Uses Process data • Determines overall intervention effectiveness • Uses small group interventions based on function of behavior • Uses Process data •Determines overall intervention effectiveness •Uses Comprehensive FBA/BIP process ALP Check and Connect, Mentoring Comprehensive FBA Other Considerations: Academic Support Universal Supports Apply Universal Classroom Strategies Ed Options, VLACS, Reading /Writing/Math Labs Work Based Learning •Special Ed Referral Reduced Schedule & EA Combo Home Tutoring – (discussion pt) Home Visits (open communication lines) Eagle Academy Mental Health Counseling Group with Individual Feature (JAG) Substance Abuse Counseling Medical Examination Referral Brief FBA * Adapted from Illinois PBIS Network Court Involvement GED Job Corp www.inclusiveed.org Referral to Community Agency Supports 6 3/11/2014 Identify Team Member Roles Team Leader Recorder Time Keeper Administrator Data Specialist Content Specialist Communication Expert PBIS Coach (internal or external) www.inclusiveed.org 13 3/11/2014 Activity: Team Time • Complete Collaborative Team Checklist • Review Team Features & Process • Start Goal Setting 3/11/2014 www.inclusiveed.org 14 7 3/11/2014 Report Out www.inclusiveed.org 15 3/11/2014 Break 3/11/2014 www.inclusiveed.org 16 8 3/11/2014 Features of a Systematic Problem-Solving Model RENEW Facilitator's Training Fall 2013, Copyright Institute on Disability, University of New Hampshire www.inclusiveed.org 17 Problem-Solving Logic • Problem Identification – Is there a problem? What is it? • Problem Analysis – Why is this happening? • Intervention Development and Implementation – What can be done about the problem? • Evaluation: Response to Intervention – Is the intervention working? 3/11/2014 www.inclusiveed.org 18 9 3/11/2014 Data Based Decision-Making • Provides objective viewpoint • Increases efficiency by making need and actions clear • Keeps from “admiring” the problem Question: “What data do we need?” www.inclusiveed.org 19 3/11/2014 Data-based Decision Making 1. Know HOW progress will be assessed. 2. Know WHEN progress will be assessed. 3. Know CRITERIA for fidelity of implementation of the intervention and how fidelity will be assessed. 4. Know CRITERIA for when students are responsive to intervention (it’s working) and non-responsive to intervention (it’s not working). 5. 3/11/2014 Know what to try next along a continuum of support. www.inclusiveed.org 20 10 3/11/2014 A Context for PBIS & Function Based Support • Behavior support is the redesign of environments, not the redesign of individuals • Positive Behavior Support plans define changes in the behavior of those who will implement the plan. A behavior support plan describes what we will do differently. Rob Horner- University of Oregon www.inclusiveed.org Purposes of Functional Behavioral Assessment • Create order out of chaos • Improve the effectiveness and efficiency of behavior support efforts • Professional accountability www.inclusiveed.org 11 3/11/2014 The BIG Idea FUNCTION MATTERS www.inclusiveed.org What is ‘Function of Behavior’? The Function of Behavior refers to what is gained or avoided as a result of a behavior www.inclusiveed.org 12 3/11/2014 Functions of Behavior • Attention – Adult or Peer • Escape – Academics, Adults, Peers, or Environment • Tangible – To gain something • Sensory – To avoid or receive environmental stimuli www.inclusiveed.org Lunch 3/11/2014 www.inclusiveed.org 26 13 3/11/2014 Features of Behavior Pathway Sugai, 2005 Looking at a ‘Behavior Pathway’ helps to develop a “best guess” about function of behavior. www.inclusiveed.org Behavior Pathway: ABC’s of Behavior Setting Events Triggering Antecedents bigger picture; what happened earlier in the day that contributes to behavior what happens right before a behavior occurs Maintaining Consequence Problem Behavior what does the behavior look like what happens right after a behavior occurs; consequences which increase a specific behavior Function? (What is the child getting or avoiding as a result of the behavior)www.inclusiveed.org 14 3/11/2014 When You Can Predict, You Can Prevent Jen: Occurs at 10:30; she meets friend who has a job in the office Chad: Occurs when assigned a writing task; gets sent to ISS where he sits quietly till end of class Joe: Occurs sporadically; spends at least 15 minutes talking with Assistant Principal Could knowing function influence our thinking about discipline practices with these www.inclusiveed.org students? 3 Key Strategies • Identify how to intervene early in an escalation. • Identify environmental factors that can be manipulated. • Identify replacement behaviors that can be taught & serve similar function www.inclusiveed.org 15 3/11/2014 Simple Behavior Pathway is the basic working unit of an FBA Setting Events Homework not done Triggering Antecedents Teacher Gives Writing Assignment Can I Impact the antecedent so student is less likely to need to escape (or…less likely to need to gain attention…) thru inappropriate behavior ….? Maintaining Consequence Problem Behavior Repeated loud talking disrupting others from their work Replacement Behavior: What could we teach student to do so he could achieve function in a prosocial way? Teacher requests quiet then removes to hallway; gives zero on assignment Function? (What is the child getting or avoiding as a result of the behavior) www.inclusiveed.org Jack gets into arguments with his math teacher if she asks him to correct his mistakes. As a result of this behavior Jack often avoids work and gains the teacher’s attention. This is more likely to happen if he has had difficulty with another subject prior to coming to math. Setting Events Triggering Antecedents Problem Behavior Maintaining Consequences www.inclusiveed.org 16 3/11/2014 Jack gets into arguments with his math teacher if she asks him to correct his mistakes. As a result of this behavior Jack often avoids work and gains the teacher’s attention. This is more likely to happen if he has had difficulty with another subject prior to coming to math. Setting Events Difficulty with another subject before math Triggering Antecedents Problem Behavior Maintaining Consequences Asked to correct his mistakes argues Avoids work www.inclusiveed.org Setting Event Modifications Antecedent Modifications Behavior Modifications (Skills to Teach) Consequence Manipulations www.inclusiveed.org 17 3/11/2014 The Final Word • It is not fair to expect anyone to exhibit a behavior which has never been taught • The key to changing inappropriate behaviors is replacing them with appropriate behaviors that serve the same function www.inclusiveed.org Goal Setting Activity Based upon the data: By June of 2014, we will have accomplished: • Specific measures: www.inclusiveed.org 18 3/11/2014 NEXT STEPS • Next Team Meeting (date and time): • Agenda items: • Roles (facilitator, note taker, timekeeper): • Location www.inclusiveed.org Suggested Timeline for 2013-14 • Use the APEX Benchmarks Tool to complete a plan. www.inclusiveed.org 19 3/11/2014 Report Out www.inclusiveed.org 39 3/11/2014 Upcoming Workshops & Retreats The 2014 Conference on School Culture, Climate, and Positive Behavior Support will take place on August 20-21, 2014 at the SERESC Event & Conference Center in Bedford, NH. PBIS Universal Team Training Retreat March 27th, 2014 8:00 – 2:30 pm Holiday Inn 172 N Main St. Concord, NH 03833 3/11/2014 www.inclusiveed.org 40 20 3/11/2014 Some other Research Articles Hawken, L. S. & Horner R. H., (2003) Implementing a Targeted Group Intervention Within a SchoolWide System of Behavior Support. Journal of Behavioral Education, 12, 225-240. March, R. E. & Horner, R. H. (2002) Feasibility and contributions of functional behavioral assessment in schools. Journal of Emotional and Behavioral Disorders, 10, 158-70. www.inclusiveed.org Resources • Iod.unh.edu – APEX project page • pbis.org (high school pages) www.inclusiveed.org 21 3/11/2014 Thank You! Kathy Francoeur, Research Associate Institute on Disability University of New Hampshire 10 West Edge Drive Durham, NH 03824 603-863-0318 Kathryn.francoeur@unh.edu 3/11/2014 www.inclusiveed.org 43 22