CrIS Sensor: Generation of RDRs and SDRs R. Glumb & J. Predina
advertisement

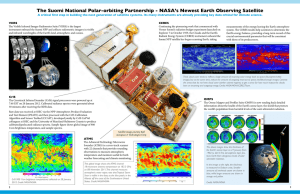
CrIS Sensor: Generation of RDRs and SDRs R. Glumb & J. Predina ITT Industries, ITT Aerospace/Communications, 1919 West Cook Road, P.O. Box 3700, Fort Wayne, IN 46801, USA Contact: ron.glumb@itt.com Contact: joe.predina@itt.com Overall Relationship of RDRs, SDRs and EDRs Sensor Design • 833 km orbit • 98.7° Inclination • CrIS • ATMS 1. 25 -O r RD Rs RDR = Raw Data Record ( Uncalibrated ) SDR = Sensor Data Record (Calibrated) EDR = Environmental Data Record bi t Da ta D um p Context of Discussion Central or Regional Ground Stations 2,200 km Swath Decode Spacecraft Data RDRs to Users Raw Uncalibrated Data Sensor Calibration Algorithms SDRs to Users Calibrated and Geolocated Radiance Data EDR Algorithms EDRs to Users • Temperature Profiles • Moisture Profiles • Pressure Profiles 20 minutes CrIS • ITT INDUSTRIES • AER • BOMEM • BALL • DRS 3-2 Sensor Design Reqmnt ID Requirement SDRP907 Spectral Bands SDRP944 Unapodized Spectral Resolution 1/(2*max OPD) SDRP3546 Spectral Uncertainty SDRP6841 ILS Shape Uncertainty SDRP3481 Radiometric Uncertainty SDRP1033 System NEdN SDRP3696 SDRP3696 FOV FOV - Size (km) 70% width (in/x track) 50% width (in/x track) 10% width (in/x track) 1% width (in/x track) Shape Match (km) 70% width 50% width 10% width 1% width SDRP3628 SDRP3630 Scan Extent SDRP882 SDRP3731 Mapping Uncertainty LOS Jitter CrIS • ITT INDUSTRIES • AER • BOMEM • BALL • DRS CrIS Science Mission Cardinal Requirements LWIR MWIR 650 – 1095 cm 0.625 cm -1 SWIR 1210 – 1750 cm -1 1.25 cm -1 2155 – 2550 cm -1 2.5 cm -1 -1 10 ppm (flight unit 1) 5 ppm (subsequent flight units) 10 ppm (flight unit 1) 5 ppm (subsequent flight units) 10 ppm (flight unit 1) 5 ppm (subsequent flight units) 0.5% FW HM 0.5% FW HM 0.5% FW HM 0.45% 0.58% 0.77% See Chart See Chart See Chart Same as LW IR Same as LW IR 0.3 0.2 0.3 N/A 0.3 0.2 0.3 N/A 11.8/12.7 13.2/14.2 14.9/16.0 16.8/18.0 0.3 0.2 0.3 N/A 30 x-track FORs: +/- 48.333 1.5 km 50 µrad/axis o 30 x-track FORs: +/- 48.333 1.5 km 50 µrad/axis 3-3 o 30 x-track FORs: +/- 48.333 1.5 km 50 µrad/axis o Sensor Design CrIS Science Mission Cardinal Requirements: NEdN NEdN (mW/cm²/sr/cm-1) 1 Tscene = 287K Tscene = 233K 0.1 0.01 0.001 600 1100 1600 Wavenumber (cm-1) CrIS • ITT INDUSTRIES • AER • BOMEM • BALL • DRS 3-4 2100 2600 Signal Flow Earth Radiance • CrIS SDR System Is Comprised of CrIS Optical Hardware CrIS Signal Processing Hardware (RDRs) Ground Calibration Software CrIS CrIS System Functional Partitions for Generation of SDRs • ITT INDUSTRIES • AER • BOMEM • BALL • DRS – Optical Processing Hardware • Converts Scene Radiance to Photons at Detector Surface • 9 separate FOVs with three colors in each – Electronic Signal Processing Hardware • Converts Photons at 27 Detector Surfaces into uncalibrated sampled data streams out of instrument (RDRs) – Ground Calibration Software • Converts Raw Data Records (RDRs) to Calibrated Sensor Data Records (SDRs) – Each FOV Geo-located – 1305 Spectral Channels (colors) per FOV – Radiometrically calibrated – Spectrally calibrated Calibrated Data (SDRs) 3-5 Optical Signal Flow: Earth Scene Interrogated with 3x3 FOV Array Signal Flow CrIS Field of Regard (FOR) Definition • 1 FOR = 9 FOVs • 1 FOV = 3 IR bands Single CrIS Scan Line (full sweep, 30 FORs) 3.33 degree steps Nadir 48.33 degree Edge 0.963 degree (14.0 km) Anti-sun S/C Velocity 3 1.100 degree 1100 km (16.0 km) 2 1 6 5 4 9 8 7 1.024 degree (14.9 km) 0.897 degree (13.0 km) Three Successive CrIS Scan Lines (nadir to edge sweep) CrIS • ITT INDUSTRIES • AER • BOMEM • BALL • DRS 3-6 Signal Flow Instrument Converts Scene Photons to Packetized Bits (RDRs) Optical Signal Flow: Entrance Pupil to Exit Pupil Electrical Signal Flow: Exit Pupil to Packetized Bits CrIS • ITT INDUSTRIES • AER • BOMEM • BALL • DRS 3-7 Optical Signal Flow Optical Signal Flow: Entrance Pupil to Exit Pupil • Partially unfolded CrIS optical system shows flow of signal radiance to detectors. Interferometer Cooler Telescope Detector Optics Scene Radiance SSM CrIS • ITT INDUSTRIES • AER • BOMEM • BALL • DRS 3-8 Optical Signal Flow Detector Active Area Plane Located at Exit Pupil Electrical Signal Flow: Pupil Image Photons to Packetized Bits Detector P/A Exit Pupil Image RDR Consists of: - Engineering Data - Science TLM Data - Signal ID/QC Data ADC Digital Signal Processing RDR Interferograms Calibration Data Downlinked to Earth CrIS • ITT INDUSTRIES • AER • BOMEM • BALL • DRS 3-9 Optical Signal Flow Interferogram Generated by Interferometer With +/- 0.8 cm OPD Sweep Two Sided Double-sided Interferograms Baselined for CrIS LW MW SW –0.8 –0.4 –0.2 0.0 0.2 0.4 OPD [cm] Double-Sided Interferogram Benefits: • Better phase calibration of instrument (and consequent treatment of channelization effects) • Less sensitive to sweep asymmetries of hardware (vs Single-sided interferograms) CrIS • ITT INDUSTRIES • AER • BOMEM • BALL • DRS 3 - 10 0.8 Electrical Signal Flow Filters Optimized for Low Gain and Phase Distortion Dedicated A/D on Each Channel Minimizes Noise CrIS Electronic Signal Processing: Key Features (1 of 2) • 27 Channel Interferogram Signal Processing – Anti-alias analog filter • 5 pole low pass (51.7 kHz) • 2 pole high pass (300 Hz) – 14-bit ADC • 13.4 effective bits on each detector channel @ 128 ksps – Oversampled to prevent cut-off effects of anti-aliasing filter (gain/phase slope) from encroaching IR signal passband • Metrology delay matched sampling, commandable Digital Processing Techniques Significantly Reduce Data Transmission Rate Extensive On-orbit Programmable Flexibility CrIS • ITT INDUSTRIES • AER • BOMEM • BALL • DRS – Programmable electronic gain • Optimizes each CrIS IR channel dynamic range • 40 dB range, 0.156 dB increments, commandable – Impulse noise suppression • Reduces impulse noise energy over 60 times, programmable – 255 tap decimating digital FIR filter (fully programmable) • Decimation reduces bandwidth & data rate • 69 dB stopband, +/-2.5 dB In-band ripple, sharp transition • 9 channel ASIC implementation for low power & speed – Bit trim encoding to reduce data rate • Removes unneeded leading zeros of interferogram data samples • Implemented by Flight computer, commandable reconfigure 3 - 11 Electrical Signal Flow CrIS Formats All Data into CCSDS Packets CrIS Electronic Signal Processing: Key Features (2 of 2) • Data transmitted in Packets with Unique IDs • Science Data Channel (packets per 8 second scan) – – – – – Yields 1.44 Mbps Data Rate Packets Tagged with Unique APIDs to Speed Sorting and Ground Processing • Other Data Packets for C&DH, Diagnostics Up to 128 Unique APID Packet Assignments CrIS Earth scene packets (810 = 27 detectors x 30 scenes) ICT calibration packets (54 = 27 detectors x 2 looks) DS calibration packets (54 = 27 detectors x 2 looks) Science telemetry packet (1) Engineering packet (once every 30 scans, 4 minutes) • ITT INDUSTRIES • AER • BOMEM • BALL • DRS – – – – – – – – Time of Day (TOD) & navigation packet (once/sec) Housekeeping telemetry (2 kbps) LEO&A telemetry (0.256 kbps) Command packets Test packets Memory load/memory dump packets Diagnostic interferogram data packets Telemetry dwell packets (diagnostic telemetry) 3 - 12 Electrical Signal Flow CrIS On-board Signal Processing Builds RDRs 13.4 A/D PV HgCdTe 21 038 samples 24 18 Decimate 24 18 Trim....54% Bit Bit Trim…63.1% 5-Pole Butterworth LPF 51.7 kHz 866 samples Trim....63% BitBitTrim…73.4% Decimate eff 530 samples Trim....60% BitBit Trim…61.7% 1% Sweep Velocity Error FOV #1 255 Tap FIR BPF 650 - 1095 cm -1 Longwave Impulse Noise Suppression 10 cm/sec OPD Sweep Velocity 202 samples PV HgCdTe 2155 -2550 cm -1 Shortwave IR to Metrology Delay Matching PV HgCdTe 10854 samples Decimate 20 12.1 - 17.5 kHz 5-Pole Butterworth LPF 51.7 kHz A/D 13.4 5 506 samples Impulse Noise Suppressed Decimate 26 15 Decimate 26 15 21.55 - 25.5 kHz 1550 Laser Low Data Rate CrIS 17 17 255 Tap FIR BPF Laser Metrology Driven Sampling 13.4 A/D Decimate 20 255 Tap FIR BPF 5-Pole Butterworth LPF 51.7 kHz Impulse Noise Suppression 1210 - 1750 cm Midwave Impulse Noise Suppression 160 msec Integration Time • ITT INDUSTRIES • AER • BOMEM • BALL • DRS 160 kHz LPF Delay Equalize Sample Pulses 128,906 Hz +/-1% Metrology Reference 3 - 13 2 kbps TLM CCSDS Data Packet & FOV#1 through #9, TLM, F i li i d 6.5 - 10.95 kHz -1 1.5 Mbps Electrical Signal Flow Impulse Noise Detection/Suppression is Important in a Space Environment • CrIS Detectors Can Be Subject to Impulse Noise – Sensor charging/arc discharge – High energy particle (space radiation environment) bombardment of detector – Impulse will span two undecimated interferogram samples I(x) – Frequency of occurrence expected to be very low Impulse Noise Interferogram x real IGM • Impulse Noise Clipping Reduces Noise Susceptibility – – – – CrIS Factor of 60 or more suppression improvement CrIS uses bit trim mask to detect impulse noise prior to digital FIR filter/decimation Substitute a zero value in place of the measured impulse noise value. Number of impulse noise hits is counted and reported for each interferogram to aid in data quality assessment. • ITT INDUSTRIES • AER • BOMEM • BALL • DRS 3 - 14 255 Tap Digital FIR Filter & Optical Filter Overlay Long Wave Band Electrical Signal Flow Cascade of Two Optical Filters Plus Sharp Cutoff Digital FIR Filter Provide High Out-of-Band Rejection LW Band: 650 cm-1 1095 cm-1 1 10 0 10 FIR FIRFilter Filter Passband PassbandRipple Ripple -1 Excellent Robustness to EMI Aliasing Enables Use of Large Decimation Factor In-band Ripple Removed by Calibration CrIS Gain 10 Cascaded Cascaded Optical OpticalFilter Filter Response Response -2 10 FIR FIRFilter Filter Stopband StopbandRipple Ripple -3 10 -4 10 -5 10 • ITT INDUSTRIES • AER • BOMEM • BALL • DRS 0 500 1000 1500 2000 2500 Wavenumber (cm-1) 3 - 15 3000 3500 4000 Electrical Signal Flow Filtering and Decimation Order of Magnitude Reduction of Samples via Signal Processing CrIS Interferogram Measurements Double Sided IGMs LW MW SW –0.8 Overscan Samples Taken to Fill Digital FIR Filter Pipeline 127 • ITT INDUSTRIES • AER • BOMEM • BALL • DRS 0.0 0.2 0.4 0.8 LW Band MW Band SW Band ± 0.8035 cm OPD ± 0.4092 cm OPD ± 0.2015 cm OPD 26 26 20,736 real 1 CrIS –0.2 OPD [cm] 24 One Decimated Overscan Sample for ZPD Uncertainty –0.4 24 20 127 127 10,560 real FIR Filter & Decimate 24 FIR Filter & Decimate 20 complex complex 1 864 3 - 16 20 1 528 127 5,200 127 127 real FIR Filter & Decimate 26 complex 1 1 200 1 Bit Trimming Performed By CrIS Flight Computer Electrical Signal Flow Bits Above Mask Are Discarded No Loss of Information On-orbit Programmable Mask Interferogram Envelope 407 Bits Bitsabove abovemask mask are discarded are discarded 460 15 [Output Bits/Sample - 1] (complex) Bit Trimming Allows CrIS to Meet Bandwidth Requirements (LW example for a pre-trimmed 17 bit word width) 353 10 31 515 299 138 568 729 836 1 866 5 0 -5 -10 Data After Trim: -15 63.1% in the LW -0.8 -0.6 -0.4 -0.2 0 0.2 73.4% in the MW Optical Path Difference (cm) 61.7% in the SW 866 decimated complex samples CrIS • ITT INDUSTRIES • AER • BOMEM • BALL • DRS 3 - 17 0.4 0.6 0.8 Electrical Signal Flow Space Segment Processing: Functional Flow SPACE SEGMENT - CrIS Sensor Detector DS ADC I (x ) Interferogram Interferometer (photons) 255 Tap FIR I (x ) L(σ ) ES: Earth Scene DS: Deep Space ICT: Internal Calibration Target Filtering & Decimation Reduces data rate ~ I ( x ) complex Engineering Data (three different types) Must be done first real ICT Observed scene Impulse Noise Clipping Once per 4 minutes éBit trim format data élaser frequency info: NNe, NL éICT emissivity tables & model éPolarization correction tbl (if needed) éILS parameters for 54 channels éCrIS mounting angles éLOS angles for each FOV Signal ID/QC Data éIGM start time (UTC) éFOR index (0-31) éBand ID (LW,MW,SW) éFOV ID (1-9) éSweep direction éZPD min, max & position éQuality control flags éImpulse noise count Bit Trimming Downlinked to Earth RDR Packet Encoding Interferograms Calibration Data Once per 8 seconds éLaser diode temperature/current éICT, BS, Scan mirror temperatures éAll optic temperature telemetry éSSM pointing errors Science TLM Data Only Processing of Science Data Shown CrIS • ITT INDUSTRIES • AER • BOMEM • BALL • DRS 3 - 18 Electrical Signal Flow RDR Content (1/3) • Interferogram Data Packets (27 packets/FOR) Comprises Bulk of Data Auxiliary Data Contained in Each Interferogram Data Packet Used for Identification Purposes Contaminated Data Detected by CrIS Sensor & Flagged CrIS • ITT INDUSTRIES • AER • BOMEM • BALL • DRS – Interferograms – Interferogram Identifiers • Spacecraft ID tag • CrIS Sensor ID or serial number • FOR index (1 - 30 = Earth scenes, 0 = ICT, 31 = DS) • FOV number (1-9) • Band designator (LW, MW, SW) • Interferometer sweep direction (forward, reverse) • UTC stamp (Instant when FOV footprint frozen) • ZPD magnitude and fringe count – Data Quality Indicators • Fringe count error and fail bit trim flags • Impulse noise count (0-127) • Invalid interferogram data flag (Saturated channel, failed detector) 3 - 19 Electrical Signal Flow Engineering Data Embedded in RDRs Eliminates Need for Sensor Unique Calibration Handbooks Allows Remote Terminals to Seamlessly Synchronize with Any CrIS Sensor Downlink Anytime CrIS • ITT INDUSTRIES • AER • BOMEM • BALL • DRS RDR Content (2/3) • Engineering Data Packet (once per 4 minutes) – Metrology Wavelength Data • Neon fringe count (from last calibration) – ICT Calibration Data • Emissivity versus wavenumber • ICT radiometric model parameters – ILS Model Parameters for Each CrIS Detector • FOV to LOS offset angles • FOV size (angular) – Polarization Correction Data vs. Scan Angle & Wavenumber – Mapping Data • CrIS to S/C alignment cube • CrIS LOS to CrIS cube reference angles • CrIS scanner to interferometer alignment data – Coefficients to convert data to engineering units – Bit trim parameters & other format decoding data 3 - 20 Electrical Signal Flow RDR Content (3/3) • Science Telemetry Data Packet (once per 8 seconds) Science Telemetry Packets Only Contain Dynamic Data Supporting Science Mission Calibration and Geolocation More Complete and General Telemetry/House keeping Data Sent to Spacecraft Operations Control Center Over Different Channel CrIS – Metrology Wavelength Data • Laser diode case temperature, current and model parameters – Temperatures • Beamsplitter, Scan mirror, Scan Baffle, Telescope, Aft optics, Detector – SSM servo pointing errors • From each of 30 previous earth scenes • In-track • Cross-track • Normal Telemetry Data Packets (once per second) • ITT INDUSTRIES • AER • BOMEM • BALL • DRS – Rotation of 8 fixed format packets • 2 kbps maximum data rate • Recent FT1394 requirement – Contents • Temperatures, secondary voltages, PCE status, command status, heater currents, IFM status, SSM status 3 - 21 SDR System Design Description: Ground Software Element SDR Algorithm Ground Calibration Software Is Partitioned into 9 Modular Groups • Initialization • Radiometric Calibration – Initialize software – Initialize RDR reading pointers – – – – – – – – • Data Input – Low level data handling – Configuration data handling – Calibration data handling • Ingest sensor unique cal data • Monitor calibration data • Compute spectrum correction matrix – Science data handling • Geolocation – Map FOV to latitude & longitude – Calculate view angles/ footprint geometry • Preprocessing – Perform bit trim decoding – Convert interferograms to spectra Average warm target spectra Average cold target spectra Subtract sensor background radiance Calibrate sensor gain Remove phase dispersion Compute ICT radiance Isolate/reject orthogonal noise Apply spectrum correction matrix • Remove ILS errors • Apply user selectable apodization • Map channels to fixed wavenumber grid • Quality Control – – – – Identify/exclude bad data Detect/correct fringe count error Estimate NEdN (bin by bin) Flag bad FOVs • Post-processing • Spectral Calibration – Perform spectral calibration – Compute laser WL from neon lamp – Compute laser WL from diode parameters – Select user required spectral bins – Format data for EDRs – Archive data • Data Output CrIS • ITT INDUSTRIES • AER • BOMEM • BALL • DRS 3 - 23 Signal Flow Through Ground Calibration Algorithm SDR Algorithm ~ I ( x) ES (88%) ~ S es [n] Scene FCE Handling Radiometric Calibration (complex) Compute Spectrum L(σ ) Process Calibration References N ma = 30 ~ S (σ ) Health Monitoring ~ L (σ ) L [r.u.] Metrology Monitoring DS (6%) ~ S ds [n] Calibration FCE Handling Moving Average N ma = 30 ICT (6%) ~ S ict [n] Calibration FCE Handling Moving Average Spectrum Correction mean cold reference ~ S ds Spectral Resampling ILS Correction mean hot reference ~ S ict User Defined Apodization L [r.u.] T ict σ0 CrIS • ITT INDUSTRIES • AER • BOMEM • BALL • DRS 3 - 24 σ1 σ L(σ ) NEdN CrIS Interferograms to Calibrated Spectra: Signal Processing Progression SDR Algorithm Interferogram Samples from CrIS A/D 24 127 LW Band MW Band SW Band ± 0.8035 cm OPD ± 0.4092 cm OPD ± 0.2015 cm OPD 26 26 20,736 real 24 20 127 127 10,560 real FIR Filter & Decimate 24 Interferogram Samples in RDRs complex 1 1 1 864 SDR Algorithm Spectral Samples After SDR Algorithm Calibration Spectral Channels Retained 76 20 127 5,200 127 real FIR Filter & Decimate 20 FIR Filter & Decimate 26 complex complex 528 1 1 SDR Algorithm 75 48 • ITT INDUSTRIES • AER • BOMEM • BALL • DRS 47 20 21 433 real 159 Discard Guard Band Discard Guard Band Discard Guard Band 433 real 3 - 25 1 SDR Algorithm 1305 Total CrIS Spectral Channels CrIS 200 713 real 713 real 127 159 SDR Algorithm Calibrated Radiance in 1305 Channels Noise Estimates in Each Channel SDR Content At SDR Algorithm Output (1 of 2) • Calibrated Data – Real part of the spectra after Spectral Correction • LW 713 bins @ 0.625cm-1 (650-1095) • MW 433 bins @ 1.25cm-1 (1210-1750) • SW 159 bins @ 2.5cm-1 (2155-2550) – Imaginary part of the spectra before Spectral Correction (LW 713 bins, MW 433 bins, SW 159 bins) – NEdN estimates (LW 713 bins, MW 433 bins, SW 159 bins) • Geolocation Data Mapping Data CrIS • ITT INDUSTRIES • AER • BOMEM • BALL • DRS – Latitude/longitude @ sea level for each FOV center – Major and minor elliptical footprint size for each FOV – Elevation & azimuth angle from each FOV center to satellite 3 - 26 SDR Content At SDR Algorithm Output SDR Algorithm (2 of 2) • Identifiers Identifiers Help in the Archiving of Data – Spacecraft ID, CrIS sensor ID, Sensor flight software version number, SDR algorithm version number, Apodization tag – FOR number, FOV number – Band designator (LW,MW,SW), FOV longitude and latitude, Slant angle, Viewing angle, Size of FOV on ground • Quality Control Quality of Data Is Assessed and Tagged CrIS • ITT INDUSTRIES • AER • BOMEM • BALL • DRS – – – – ZPD reset, Fail bit trim, Impulse noise count (0-127) Invalid data (RDR and SDR) and invalid geolocation flags FCE detected and corrected in SDR algorithm Excess NEdN, Excess Sensor Thermal drift 3 - 27 Web Site Further Information • This presentation of CrIS data record generation and processing is a summary of more detailed information available at: http://npoesslib.ipo.noaa.gov CrIS • ITT INDUSTRIES • AER • BOMEM • BALL • DRS 3 - 28


![Appointments: Manual Booking using [ALT-M] in conjunction](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/007588400_2-a89991296ab31df74067d7b72cd8b787-300x300.png)