Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology
advertisement

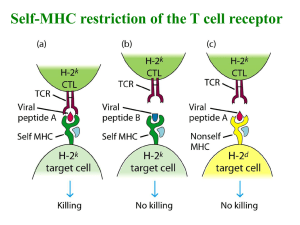
Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.176: Cellular and Molecular Immunology Course Director: Dr. Shiv Pillai AICD Naive Activated Activated Effector Memory Effector AICD Naive Activated • INNOCUOUS ANTIGEN Memory • PATHOGEN • No Danger- very low • Danger induces expression of costimulatory ligands costimulatory ligands • Signal One + Signal • Signal One Only Two – Non-responsiveness – Tolerance (anergy) – Lymphocyte Activation INNOCUOUS ANTIGENS • Commensal microbes • Food antigens • Host cell proteins that have not induced thymic deletion • Fetal antigens? Choices during T cell activation • INITIALLY: – Anergy OR – Activation into Effector state • RESTIMULATION OF EFFECTORS – Activation Induced Cell death OR – Memory – Differentiation e.g.Th1 versus Th2 – Other regulatory subsets Issues in T cell activation - I • Crosslinking versus Coreceptors • Is the Affinity of the TCR for MHC Too Low? • Lipid rafts and the need for Immunological Synapse generation • Interfering with Signal Oneimmunosuppression and how it works Issues in T cell Activation -II • Anergy versus Activation • How is the quality of an immune response modulated - Th1 versus Th2 for instance? α γ ε β ε δ ζζ ITAM α2 β2 α1 β1 MHC class II peptide α γ ε β ε T cell receptor δ ζζ polysaccharide monosaccharide antigen receptor NO SIGNAL SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION TCR α CD4 γ ε β ε δ ζζ Fyn Lck Zap-70 TCR-MHC interactions • 1. Few MHC-peptide complexes on an APC specific for a given TCR • 2. Affinity of TCR for specific MHCpeptide combo is pretty low - 10-4 to 10-6 M • 3. How then does a T cell receive specific signals? It Takes Two to Tango…..? • SLC (secondary lymphoid chemokine) draws naïve T cells and activated dendritic cells through the HEV into lymph nodes • Signaling through CCR7 activates integrins for adhesion but also induces T cell polarization via cytoskeletal rearrangements • “Leading edge” of T cell slides alongside any dendritic cell it sees and a dance begins Just a brief romance……..? • Adhesion molecules on T cell bind to their counterparts on the DC; LFA-1 to ICAM1,VLA-4 to VCAM-1 (LFA-1 and VLA-4 are integrins), CD2 to CD48 and so on • CCR7 mediated adhesion is brief….minutes The TCR knows….. • The right TCR-MHC/peptide interaction sustains a long term relationship…. For a few hours • True synapse formation is initiated Lipid rafts and Immunological Synapses • Signaling initiated from specialized membrane microdomains- lipid rafts aka DIG domains or GEMs (these contain acylated proteins, GPI anchored proteins, PIP2 etc). • Signaling through TCR induces cytoskeletal rearrangements and fusion of lipid rafts forming immunological synapses. ~40 nm 15 nm CD28 T B-7 CD4 TCR MHC class II CD2AP CD48/CD58 APC CD2 LFA-1 ICAM-1 Outer ring "Quiescent" APC Low levels of B7-2/CD86 MHC class-II CD4 Co-receptor γ ε ε δ ζζ ITAM CD28 Signal One T cell Minimal IL-2 Transcription No activation Induction of anergy "Activated" APC High levels of B7-1/CD80and B7-2/CD86 MHC class-II CD4 Co-receptor γ ε ε δ ζζ ITAM CD28 Signal One T cell Signal Two IL-2 transcription Also induction of IL-2R, CD40L, FasL, and CTLA-4 Some of the events turned on by Signals One and Two • Induction of IL-2R and IL-2 expression • Induction of cyclins D2 and D3 and CDK4 and degradation of p27 CDK inhibitor cells divide • Induction of CD40L • Induction of FasL and of higher levels of CTLA-4 B7 costimulation III: terminating responses High levels of B7.1 and B7.2 MHC class-II CD4 coreceptor δ ε ε γ ζζ ITAM CD28 CTLA-4 High levels of CTLA-4 induced by TCR, CD28, and IL-2R signals Signal Two T cell Signal One CD4 CD28 TCR Lck Fyn ZAP-70 LAT PI3 Kinase Vav PLCγ1 Cleaves PIP2 DAG Grb2 SOS Ras/Raf/ERK IP3 Ca++ Rac/SEK/JNK Nil-2-a Cytoplasmic NFAT Calcineurin (phosphatase) Nuclear NFAT ERK P JNK IL-2 transcription Fos/Jun (AP-1) (Repressor of IL-2 transcription) ACTIVATED P P P P P P P P P P IL-2 A NF-AT AP-1 Oct-1 NFκB/ AP-1 NFAT AP-1 NFAT AP-1 Oct-1 NFAT NFκB/ AP-1 c-Rel p65 Nil-2-a Egr-1/ HMGI/Y SP-1 Egr-1/ SP-1 TATA ANERGIZED X A NF-AT AP-1 Oct-1 NFκB/ AP-1 p65 Egr-1/ SP-1 NFκB/ AP-1 NFAT AP-1 c-Rel HMGI/Y -285 -275 -250 -220 -205 -180 NFAT AP-1 Oct-1 Nil-2-a NFAT TATA Egr-1/ SP-1 -160 -150 -135 -125-105 - 9 0 - 8 5 - 7 5 - 6 0 - 4 5 -30 No Activation Anergy TCR Naive CD4 Activation induced cell death Activated Effector TCR/CD28 Restimulation Chronic stimulation and phenotypic differentiation IL-12 IL-18 No restimulation IL-4 Memory Th1 Th2 Receptor clustering Activation of Src-family kinases ITAM tyrosine phosphorylation Recruitment of Syk family tyrosine kinases to ITAMs and activation of these kinases Recruitment of adaptors to the membrane Tyrosine phosphorylation of adaptor proteins and activation of downstream pathways SOS 1, 2 (Guanine nucleotide exchange factors) Inactive GDP Ras Active Ras GTP Effectors p120GAP Neurofibromin (RasGAPs) c-Raf ERK activation 1. Crosslink receptor YP YP YP 2. Activate tyrosine kinase GDP GTP 3. Phosphorylate tyrosines on ITAMs and other adaptors MAPKKK (Raf) 4. Recruit signal effectors such as GEFs 5. Convert G protein from inactive GDP bound form to active GTP bound form MAPKK (MEK) 6. Recruit and activate MAP Kinase Kinase Kinase (sometimes referred to as a MEK kinase) MAPK (ERK) 7. MAPKKK is a serine/threonine kinase which activates a MAP Kinase Kinase 8. MAPKK is a dual specificity kinase which phosphorylates MAP Kinases on threonine and tyrosine residues. MAPK translocated to the nucleus TP YP 9. MAPK phosphorylates targets in nucleus which may regulate transcription or message stability Nucleus CTLA-4 CD4 CD28 TCR Lck Fyn ZAP-70 X LAT PI3 Kinase Vav PLCγ1 Cleaves PIP2 DAG FK506 Ras/Raf/ERK IP3 Ca++ Cyclosporin Grb2 SOS X Rac/SEK/JNK Nil-2-a Cytoplasmic NFAT Calcineurin (phosphatase) Nuclear NFAT ERK P P JNK Fos/Jun (AP-1) IL-2 transcription (Repressor of IL-2 transcription) IL-12 Thp Inflammation IL-1 TNF IL-6 Fever Acute phase response Th1 IFN-γ IL-2 Lymphotoxin Th1/Th2 1. TCR Signal strength - nature of antigen and amount 2. Route of immunization and cytokine milieu 3. Signals induce transcriptional patterns that influence differentiation The lists of transcription factors on the next image are included to paint the picture more completely - you do NOT need to memorize them IL-4R CD28 TCR IL-12R IL-18R SLAM JNK1 JNK2, p38 JNK1 STAT6 c-Maf GATA-3 NIP-45 NFATc JunB NF-IL6 etc Th2 phenotype 1. Transcriptional Induction of IL-4, IL-5, IL-6, IL-9, IL-10, IL-13 NFATp NFAT4 Bcl-6 JNK2, p38 T-bet STAT4 ? ATF-2 Th1 phenotype 1. Transcriptional induction of IFN-γ, IL-2, LT 2. Shut off of IL-12Rβ2 2. Synthesis of IL-12Rβ2 3. Expression of CCR3 3. Expression of CCR5 Cytokine receptor Cytokine Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Jak SH2 domain STAT Y STAT dimer Transcription of target gene Y STAT site IL-7Rα CC CC CC CC γc WSXWS Src family kinases Jak3 PI3Kinase Accessibility for V(D)J recombination Survival/proliferation Induction of Bcl-2 in pro-T cells γc and X-linked SCID γc or the common gamma chain is a component of the IL-2, IL-4, IL-7, IL-9, and IL-15 receptors The γc gene is encoded on the Xchromosome IL-2Rα IL-2Rβ γc CC CC "sushi" WSXWS Box 1 Box 2 Syk Jak1 c-myc mTOR/ FRAP Jak3 Lck Shc Ras/ Raf/ERK PI3K Y STAT dimer (STAT 5 and STAT 3 are activated) Bcl-2 Activated B and Th2 cells Th1 cells S S S S S S High affinity receptor IL-12Rβ1 (binding subunit in mouse; low affinity receptor in man) IL-12Rβ2 (signaling subunit) IL-12Rβ1 Jak2 Tyk2 Y STAT 4 dimer Igα YY Src-family kinase YY Igβ ITAM Igα YY YY YY Activated Syk YY Igβ ITAM Inactive Syk Btk is recruited to the membrane by PI3K PH TH PI3K generates PIP3 PR YP(223) SH3 SH3 SH2 Autophosphorylation site PR SH2 TH KINASE PH YP(551) KINASE Y551 Activation segment tyrosine phosphorylated by Src family kinases CR2/CD21 is a coreceptor and positive regulator of BCR signaling Receptor for EBV CR2/CD21 YYYY Immune complex BCR CD19 β α CD81 Lyn Fyn Syk Vav PI3K CD22 is a negative regulator of BCR signaling Sia α2-6Gal β1-4GlcNAc CD22 Igβ Igα Lyn SHP-1 BCR Y Ιgβ Y immune complex Y YY FcγRIIB1 Ιgα ITIM PI3K SHIP ITAM Btk, Akt, PLC γ1, etc Ca++ activated TCR T CD4 gp 39/CD40L YBCR CD40 MHC class II (loaded) Y B CD40 TRAF-N Ring TRAF2 TRAF3 TRAF5 TRAF6 Zn finger TRAF-C JNK/SAPK activation Activation of IKK complex IκB degradation NF-κB nuclear translocation CD8+cell IL-2 CD28 CD8 CD4+ cell MHC class II B7 CD4 MHC classI APC CD8+cell CD4+ cell CD28 CD40L CD8 CD4 MHC class II MHC class I B7 B7 CD40 "Unlicensed APC "Licensed APC"