MSINM001: PROJECT MANAGEMENT 2011/12 Jane Britton Course Leader:
advertisement

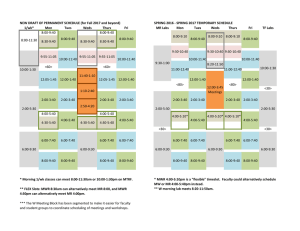
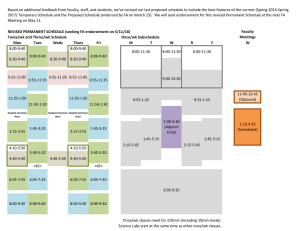
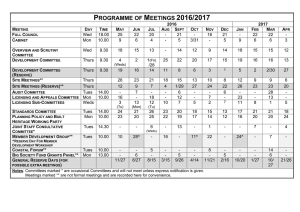
MSINM001: PROJECT MANAGEMENT 2011/12 Jane Britton Course Leader: MSINM001 Project Management Jane has considerable experience as a project manager in BT, both in new product development and change management. She has also worked as a consultant for both private and public sector organisations. Jane is a member of various Association for Project Management (APM) committees and panels on professional development, and is also a Fellow of the APM. Contact Jane in class or E-mail: jane.britton@ucl.ac.uk Matthew Whyndham Lecturer: MSINM001 Project Management Matthew is a practising project manager and research scientist in UCL's Department of Space and Climate Physics (MSSL) where he is a member of the Technology Management Group. Most of his work, both as a scientist and a manager, has been in the instrumentation field (detectors and data systems), and he is also experienced in software-oriented and research projects. He teaches courses in Systems Engineering and Space Systems Technology. Contact Matthew in class or E-mail: m.whyndham@ucl.ac.uk Kevin Kiernan Lecturer: MSINM001 Project Management Kevin has had considerable industry experience leading projects in the Marketing and Customer Service areas. He specialised in launching new products and in the computerisation of order entry systems. As well as his role at UCL, Kevin lectures at both London Metropolitan University and on the Open University’s MBA programme. Contact Kevin in class or E-mail: k.kiernan@ucl.ac.uk This course outline should be read in conjunction with the Department of Management Science and Innovation’s ‘Guidelines for Students’ and other documentation issued to support this course. MSINM001 / Page 1 MSINM001 Project Management Course Outline 2011/12 Why Project Management? Project management is used in both public and private sector organisations to bring about change and manage innovation. Examples of projects include contractual work (e.g. construction, consultancy), the installation of new IT systems, introducing new internal procedures and processes, organising an office move, launching a new product or an advertising campaign, bidding for a major customer contract. You will invariably be involved in projects in your future careers, and you will need to know how to use the tools and techniques of project administration and also understand the environment in which your project is being undertaken - the organisation(s) involved, your customers, politics, power, people and how to get the best from them. Our course aims to introduce you to the range of issues that affect projects, the tools and techniques needed to manage them, and to help you develop the skills, knowledge, attributes and behaviours that the project manager needs. Some comments from previous Project Management students after they had graduated: “I just wanted to say thanks for your lectures on the Project Management course…the concepts you covered on the course have helped me immensely and have ensured I know what’s going on when looking at Gantt charts, process decision designs and work breakdown structures! Pretty much everything you both taught has cropped up at work…the Project Management course has probably been the most applicable subject I studied at university.” (Matthew, under-graduate) “I recently started a new job as a Senior Healthcare Application Analyst (very technical position)…and the first thing they handed me was the company’s project management guide! As I reviewed the manual, I smiled from ear to ear because everything you taught me is in the manual. I’m way ahead of my manager’s expectations.” (Keri, post-graduate) MSINM001 / Page 2 MSINM001 Project Management Course Outline 2011/12 Aims To define the concept of the project in relation to industrial and commercial organisations. To introduce the needs, tools and the success/failure indicators for managing projects. To exemplify project management by illustrative case studies and practical exercises. To assist students in developing the skills, knowledge, attributes and behaviours of a project manager. Objectives At the end of this course, students will be able to: Define a project, its characteristics and the role of the project manager. Identify the causes of project failure and suggest ways in which these can be overcome. Demonstrate a divergent approach to problem-solving, through the analysis and presentation of views on project problems / situations. Explain the application of the theoretical frameworks within a project environment. Produce a project plan. Identify their own motivations, strengths and weaknesses as members of a project team. Accreditation The Association for Project Management (APM) has accredited the UCL Department of Management Science and Innovation as a provider of courses in Project Management, and this course is aligned to the APM’s Body of Knowledge (5th edition). The benefits to students are: The course provides good grounding and preparation for students wishing to go on and take the APM’s APMP professional qualification. Professional recognition of the course as a good grounding in Project Management subjects suitable for projects in any industry. Students can cite on CVs that the professional association (APM) has attended an accredited provider Project Management course. Subject to availability, MS&I may be able to offer high-achieving project management students the opportunity to convert their knowledge from this course into the APM’s APMP professional qualification, although students may have to pay the APM’s examination fees. For more detail on the APMP qualification see: http://www.apm.org.uk/APMP.asp MSINM001 / Page 3 MSINM001 Project Management Course Outline 2011/12 Syllabus BLOCK ONE - INTRODUCTION Defining a project by differentiating between projects and continuing operations. The project lifecycle - from concept to termination. The factors that necessitate formation of a project team. (Scope, unfamiliarity, complexity of the project and its importance to the organisation). The human resource consequences of project team organisation. The pros and cons of the various project team structures. The conflict between line and project managers. Responsibility exceeding authority. Pitfalls - recognising the environment (technical, financial, political, end user, strategic, human resource and legal) in which a project exists, and the most common reasons for project failure. The necessary competencies of a project manager. BLOCK TWO - THE PROJECT MANAGER AS PROJECT INITIATOR 1. Basing The Project On A Clear Need The unused product delivered to time, cost and performance - a project failure? The importance of understanding the needs and values of the customer, and of project definition. Understanding stakeholders and their different interests and requirements. Understanding a product or completed project from the customer’s viewpoint. Understanding the psychological as well as the technical attributes of a product. The gap between the customer’s perception of a product and its physical features. 2. Putting The Case Projects as the outcome of strategic decisions. Understanding how projects are initiated and selected and why it is important for a PM to be aware of this process. The need to understand the evaluation process before you start. What do decisionmakers want to know? The end result and the fit with the customer’s needs. Benefits and risks. Early exit costs. Plan for logistic support and administration. Past experience of team and organisation. How project proposals are assessed by the organisation: Non-numeric criteria (Strategic objectives, operating necessity, development of new capabilities). Numeric criteria – financial appraisal, probability / risk analysis. How to sell the idea within the organisation. MSINM001 / Page 4 MSINM001 Project Management Course Outline 2011/12 BLOCK THREE - THE SKILLS OF A PROJECT MANAGER 1. Managing People And Leadership Styles The origins of power (physical, resource, position, charismatic, expert and negative). Leadership styles - dependent on task, leader, individuals, team and organisational setting. The importance of motivation. Recognising that different individuals are motivated differently from each other and from the PM. Creating and building teams - characteristics of effective teams; stages in team development. Managing meetings. The danger of wasting time en masse. The importance of effective planning and chairmanship. Phases of a meeting: outlining purpose, ensuring effective discussion, establish conclusions & gaining acceptance. 2. Commercial Negotiation The nature of trade: a transaction which two or more parties each perceive as being to their own advantage. Negotiation as the process of dividing the benefits of trade. The types of negotiation likely to be encountered by a PM, both within and external to the organisation. Recognising the opportunities for win-win situations. Stages of negotiations: preparation, meeting, settlement and implementation. Principles of effective negotiation. 4. Commercial Contracts Reasons for a contract: definition of agreement, reduction of risk to supply of resources. Types of contract and contractor / supplier reimbursement options. The issues that should be covered in a contract. BLOCK FOUR - PROJECT PLANNING, MONITORING AND EVALUATION 1. Planning The need for planning. Setting an appropriate level of planning. Identifying the means, resources and actions necessary to accomplish one or more objectives. Knowledge of the broad planning required to implement a project of medium sized complexity. Knowledge of the main planning and presentation techniques. Experience of preparing a Project Plan for a medium-sized project. 2. The Project In Context The importance of quality and safety. Quality Systems – their role in project organisations. 3. Work Definition Definition of the product. Product and Work breakdown structures. Task responsibility matrices. 4. Resources Understanding the resources at the disposal of the project. Understanding the ways a cost estimate may be prepared, appreciation of estimating accuracy and of the use of contingency funds. Experience in preparing estimates. MSINM001 / Page 5 MSINM001 Project Management Course Outline 2011/12 5. Scheduling Determining the best means of achieving project objectives. Coping with changes. Knowledge of scheduling techniques, especially of networks. Networks and Gantt charts. Critical Path Analysis. Knowledge and experience of computer-based planning tools. 6. Dealing With Risk The nature of risk. Methods for evaluating and dealing with project risk. Use of a risk register. 7. Project Monitoring And Control Monitoring tools and control tools. Familiarity with budget management and progress evaluation. 8. Project Performance Measurement Relating physical progress with cost status. Measures of cost and schedule performance. Understanding of Earned Value concepts. 9. Managing Complexity Sources of complexity, and why it can be a problem. Use of processes. Knowledge of change control process. Course Hours: Lectures, including Small group work (20 x 2 hours) Assignments Reading Revision/examinations Total Student hours 40 50 48 50 188 MSINM001 / Page 6 MSINM001 Project Management Course Outline 2011/12 Lecture Programme This course will be offered in 5 versions. See timetables below. The under-graduate (3001). M-Level (M001) and post-graduate (G001) versions are run together with mixed groups of students (U-G, M-Level and P-G). Attendance at all timetabled lectures is compulsory Timetables AUTUMN 2011 MSIN3001/M001/G001 (A) GROUP A TIME TUESDAY 11:00 - 13:00 LECTURE THURSDAY 09:00 – 11:00 LECTURE Group A places are primarily for Management Joint Study Programme students with some places available to others on a ‘wait list’ basis via Moodle. AUTUMN 2011 MSIN3001/M001/G001 (C) GROUP C TIME TUESDAY 14:00 – 16:00 LECTURE THURSDAY 14:00 – 16:00 LECTURE Group C is reserved for Mechanical Engineering. No ’wait list’ places available to other students. AUTUMN 2011 MSIN3001/M001/G001 (E) GROUP E TIME WEDNESDAY 11:00 - 13:00 LECTURE FRIDAY 09:00 – 11:00 LECTURE Group E is primarily for IMB students with a small number of places available to others on a ’wait list’ basis via Moodle. SPRING 2012 MSIN3001/M001/G001 (B) GROUP B TIME TUESDAY 11:00 - 13:00 LECTURE THURSDAY 09:00 – 11:00 LECTURE Group B is available to all students. Places are allocated on a first come, first served basis via Moodle. SPRING 2012 MSIN3001/M001/G001 (D) GROUP D TIME MONDAY 11:00 – 13: 00 LECTURE WEDNESDAY 09:00 – 11:00 LECTURE Group D is available to all students. Places are allocated on a first come, first served basis via Moodle. Students should select on Moodle which version of this course they will attend. Students are not allowed to swap versions after registration without prior agreement of the course leader (Jane Britton). Each group has different assessments, some of which are done in teams, so you may not ‘mix and match’ your attendance at different groups. MSINM001 / Page 7 MSINM001 Project Management Course Outline 2011/12 Office Hours Students who wish to have individual or small group tutorial meetings to discuss aspects of the course with course lecturers should e-mail the lecturer concerned for an appointment. Office hours for lecturers will normally be on their course teaching days. The student reception for Management courses is on the First Floor of the Engineering Front Building (EFB), on the corner of Malet Place. Course lecturers are based in the Henry Morley building. Assessment Details of the coursework assessments will be provided in a separate coursework pack for each of the tutor groups (A, B, C, D, E). Each tutor group has different assessments, one of which is done in a team, so students must make sure that they have the correct pack for their particular tutor group. A summary overview: 1 x report: case study analysis (individual) 1 x project planning assignment (team and individual) 1 x two hour examination (unseen) 10% 40% 50% Revision Sessions Due to space constraints there will be more than one version of the revision session. See Moodle for details of the scheduled sessions, you can choose which one you attend. Coursework Hand-in dates Term 1 (Tutor Groups A and C) Assignment 1: Before 1.30pm, Friday 28 October 2011 Assignment 2 (Pts 1 and 2): Before 1.30pm, Wednesday 14 December 2011 Assignment 2 (Pt 3): Before 1.30pm, Wednesday 21 December 2011 Term 1 (Tutor Group E) Assignment 1: Assignment 2 (Pts 1 and 2): Assignment 2 (Pt 3): Before 1.30pm, Monday 31 October 2011 Before 1.30pm, Thursday 15 December 2011 Before 1.30pm, Thursday 22 December 2011 Term 2 (Tutor Group B) Assignment 1: Assignment 2 (Pts 1 and 2): Assignment 2 (Pt 3): Before 1.30pm, Friday 3 February 2012 Before 1.30pm, Wednesday 21 March 2012 Before 1.30pm, Wednesday 28 March 2012 Term 2 (Tutor Group D) Assignment 1: Assignment 2 (Pts 1 and 2): Assignment 2 (Pt 3): Before 1.30pm, Thursday 2 February 2012 Before 1.30pm, Tuesday 20 March 2012 Before 1.30pm, Tuesday 27 March 2012 Marks are aggregated across all of the assessment components (coursework and exam) to calculate your final grade for the course. In order to be eligible for a pass you must submit work for ALL components. Failure to submit all required coursework assessments and sit the examination will result in students being marked as not complete for the module, ie they will fail. The M-Level Pass mark for the course is 50% overall (across all components). Important Note: The Department of Management Science and Innovation (MS&I) operates a late penalty system for coursework submissions that are handed in after the deadline. Please see MS&I Student Guidelines for full details. MSINM001 / Page 8 MSINM001 Project Management Course Outline 2011/12 MSIN 3001 / M001 / G001 PROJECT MANAGEMENT: SESSIONS 2011/12 Teachin g Week 1 2 3 4 5 Session 1: The Project Game Session 2: Project Characteristics Tues 4 Oct (A&C) Weds 5 Oct (E) Mon 9 Jan (D) Tues 10 Jan (B) Thurs 6 Oct (A&C) Fri 7 Oct (E) Weds 11 Jan (D) Thurs 12 Jan (B) Session 3: Project Planning Session 4: Why Projects Fail Tues 11 Oct (A&C) Weds 12 Oct (E) Mon 16 Jan (D) Tues 17 Jan (B) Thurs 13 Oct (A&C) Fri 14 Oct (E) Weds 18 Jan (D) Thurs 19 Jan (B) Session 5: Defining the Work Session 6: Project Proposals Tues 18 Oct (A&C) Weds 19 Oct (E) Mon 23 Jan (D) Tues 24 Jan (B) Thurs 20 Oct (A&C) Fri 21 Oct (E) Weds 25 Jan (D) Thurs 26 Jan (B) Session 7: Scheduling Session 8: Managing Stakeholders Tues 25 Oct (A&C) Weds 26 (E) Mon 30 Jan (D) Tues 31 Jan (B) Thurs 27 Oct (A&C) Fri 28 Oct (E) Weds 1 Feb (D) Thurs 2 Feb (B) Session 9: Risk Session 10: Resource Management Tues 1 Nov (A&C) Weds 2 Nov (E) Mon 6 Feb (D) Tues 7 Feb (B) Thurs 3 Nov (A&C) Fri 4 Nov (E) Weds 8 Feb (D) Thurs 9 Feb (B) 6 Week commencing Monday 7 Nov 11 & 13 Feb 12: Reading Week 7 8 Session 11: Introduction to project planning software Session 12: Teamwork & Project Plan Cwk Tutorial Session 11: Introduction to project planning software Session 12: Teamwork & Project Plan Cwk Tutorial Tues 15 Nov (A&C) Weds 16 Nov (E) Mon 20 Feb (D) Tues 21 Feb (B) Thurs 17 Nov (A&C) Fri 18 Nov (E) Weds 22 Feb (D) Thurs 23 Feb (B) Session 13: Configuration Mgmt Session 14: Projects in Organisations Tues 22 Nov (A&C) Weds 23 Nov (E) Mon 27 Feb (D) Tues 28 Feb (B) 9 Thurs 24 Nov (A&C) Fri 25 Nov (E) Weds 29 Feb (D) Thurs 1 Mar (B) Session 15: Monitoring and Control Tues 29 Nov (A&C) Weds 30 Nov (E) Mon 5 Mar (D) Tues 6 Mar (B) 10 11 Session 16: Motivation & Leadership Thurs 1 Dec (A&C) Fri 2 Dec (E) Weds 7 Mar (D) Thurs 8 Mar (B) Session 17: Earned Value Session 18: Negotiation & Contracts Tues 6 Dec (A&C) Weds 7 Dec (E) Mon 12 Mar (D) Tues 13 Mar (B) Thurs 8 Dec (A&C) Fri 9 Dec (E) Weds 14 Mar (D) Thurs 15 Mar (B) Session 19: Quality & Closure Session 20: Exam Briefing Tues 13 Dec (A&C) Weds 14 Dec (E) Mon 19 Mar (D) Tues 20 Mar (B) Thurs 15 Dec (A&C) Fri 16 Dec (E) Weds 21 Mar (D) Thurs 22 Mar (B) MSINM001 / Page 9 MSINM001 Project Management Course Outline 2011/12 Reading List Essential MSIN3001/M001/G001 Project Management Session Notes - set of notes relating to the issues covered in each lecture, available on the course Moodle site. Title Project Management: Planning & Control (5th edition)1 Authors Albert Lester Pub ButterworthHeinemann Year 2007 ISBN 0-7506-6956-X Additional Reading Recommended readings (generally book chapters) are provided in each set of session notes; See also the Session Plan on Moodle which summarises the recommended readings by lecture / topic. In addition, the following are useful supplementary reading: BS6079-1: 2010. Project Management – Part 1: principles and guidelines for the management of projects BSI 2010 BS6079-2: Part 2: Vocabulary BSI 2000 APM Body Of Knowledge (5th Edition) APM 2006 1-903494-13-3 The Noah Project Ralph A Kliem & Irwin S Ludin 1993 0-566-07469-9 Project Management (7th ed.) J. R. Meredith, S. J. Mantel 2010 978-0-470-40026-5 2007 0-9582-833-5-9 Project Management Leadership R Burke and S Barron The Project Workout (3rd ed.) R. Buttrick 2005 0-273-68181-8 Other British Standards Relating to Project Management BS6079-3: Part 3: Guide to the Management of Business Related Project Risk BSI 2000 BS ISO10006: 2003. Quality Management Systems - Guidelines for Quality in Project Management BSI 2003 1 Also available via UCL library e-books MSINM001 / Page 10 MSINM001 Project Management Course Outline 2011/12 UCL members can access British Standards on-line at no charge. Go to the library online databases at: http://www.ucl.ac.uk/Library/database/index.shtml If you are using the UCL system you should be able to go straight to BS, but if you are offcampus you should be prompted to login with your UCL username and password. There are a wide range of project management texts in the management collection (in DMS Watson library), and these are all excellent reference / background reading sources. Reference-only copies of some texts can also be obtained from the library desk. Specific books and articles, as they relate to each topic, are noted in the session plan. MAP The Department of Management Science & Innovation (MS&I) is located on the first floor of Engineering Front Building in Malet Place, opposite Waterstones. Teaching Staff are based in the Henry Morley Building at the rear of Foster Court/Medawar buildings. MSINM001 / Page 11