Requirements engineering Contents
advertisement

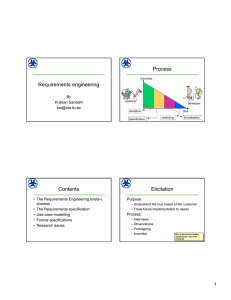
Requirements engineering By Kristian Sandahl krs@ida.liu.se Contents • The Requirements Engineering (meta-) process • The Requirements specification • Use-case modelling • Validation of requirements: Inspections 1 Process fuzziness customer developer time elicitation modelling specification formalisation Elicitation Purpose: – Understand the true needs of the customer – Trace future implementation to needs Process: – Interviews – Observations – Prototyping – Invention OF TELECOMMUNICATION REQUIREMENTS COME FROM STANDARDS 2 Requirements specification 1(3) • Requirements are specified in natural, but domain-specific language • Should not consider design solutions • A contract between customer and developer • Starting point for the vendor’s: • developers • testers • tech writers • managers • marketing people • software acquisition people Requirements specification 2(3) Requirements are: • Numbered • Inspected • Prioritised • Unambiguous • Testable • Complete • Consistent • • • • Traceable Feasible Modifiable Useful for: – – – – – operation maintenance customer developer …. 3 Requirements specification 3(3) Introduction Relationship to other services General Global product information requirements User External perspective interfaces Critical success Network factors management Network plan Maintenance Functional design criteria Downstream inpact Conversion System architecture Test procedures Electric environment Work flows Features Modelling • Representation in semi-formal notation • Often diagrammatic representation • Examples: – Object-orientation – Data flow diagrams – Decision tree – Entity-relationship models 2EQUIRES A PARADIGM car Is a VOLVO Is a SAAB SHIFT TO GIVE FULL ADVANTAGE 4 Formalisation • Represents requirements in a mathematical notation • Interpretation with logic gives possibilities: – Consistency check – Proof of correctness – System simulation – Unambiguity • Examples: Z, VDM, NP-tool,... 2EQUIRES THOROUGH EDUCATION Use-case modelling 1(4) A use-case is: A PARTICULAR FORM OR PATTERN OR EXEMPLAR OF USAGE A SCENARIO THAT BEGINS WITH SOME USER OF THE SYSTEM INITIATING SOME TRANSACTION OF SEQUENCE OF INTERRELATED EVENTS Jacobson, m fl 1992: Object-oriented software engineering. Addison-Wesley 5 Use-case modelling 2(4) Use-case (check ID) Notation: Uses Use-case (withdraw money) Actor (bank client) Use-case modelling 3(4) The interaction diagram: Client Insert card response Terminal Database PIN question response response 6 Use-case modelling 4(4) • • • • • • Often written in natural language Notation allows nesting, sub-routines,.. Easy to understand Can be a basis for test-cases Starting point for identifying objects Two schools: – formalise and detail – keep as an overview Inspections 1(7) • Purpose = detect defects • More formal that other review methods: – Well-defined process – Goal – Rules – Roles – Data to be collected 7 Inspections 2(7) • Cost of defects is higher the later they are detected • Inspections can be used early Internal defect costs Cost of defects External defect costs Cost of quality Detection costs Cost to achieve quality Prevention costs Inspections 3(7) Initialisation: Finalisation: • entry • follow-up • exit Reflection: RCA and • Planning • kick-off, briefing Execution: process improvement • inspection, preparation • collection, inspection 8 Inspections 4(7) Moderator: • Inspection leader • Control: all do what they are supposed to on time • Process adherence : speed, roles, entry and exit • Follow-up: action list, data collection Inspections 5(7) Author: • Creates the product • Decides that the product can be inspected • Gives the group information about the product in all phases. • Responsible for product repair • (The author is not the moderator) 9 Inspections 6(7) Inspector: • Finds defects • Inspects according to instructions • Inspects also according to own ideas • Report all defects found • Report any problems to the moderator • All in the groups are inspectors Inspections 7(7) Scribe: • Documents all items in the protocol in such a way that the author can understand which part of the product that is affected in which way. • (The moderator is not scribe) • (The author is not scribe) 10