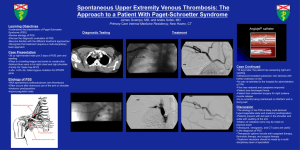
CDF Forecasts: Generation and Verification Wes Wilson Sept. 2003
advertisement

CDF Forecasts: Generation and Verification
Wes Wilson
Sept. 2003
Overview
• Comments on Classical Skill Statistics
• CDF Forecasts
• Statistical Decision Theory
• Application: CDF forecasts for SF Marine Stratus
Skill Scores for Deterministic Forecasts
FORECAST
Scoring Contingency Table
T:
F:
Y:
N:
OBSERVATION
T
F
Y
T
N
A
C
B
D
MY
MN
MT
MF
M
Event happens
Event does not happen
Forecast “YES"
Forecast “NO“
Two Interpretations:
1. Sample estimates
2. Intrinsic statistics
FORECAST
Conditional Probability Contingency Table
OBSERVATION
T
Y
N
P(Y|T) P(T)
P(N|T) P(T)
P(T)
F
P(Y|F) P(F)
P(N|F) P(F)
P(Y)
P(F)
1
P(N)
Skill Statistics for Deterministic Forecasts
• PSS = P(Y|T) – P(Y|F) reflects total benefit
• LR = P(Y|T) / P(Y|F) reflects Benefit-per-Action
PSS Flat Spot:
Different LR:
.9 - .3 = .7 - .1 = .6
.9/.3 = 3 & .7/.1 = 7
Strategy: Maximize LR constrained by “Maintain PSS”
Intro: CDF Forecasts
• Setting:
– Dichotomous outcomes (T or F ) for N trials
– Nested categories whose union fills the outcome space
{[t0,t1], [t0,t2], …, [t0,tm]}
with t1<t2<…<tn
– Probability Forecast : pk(Ti) for the i-th trial, k-th Category
• CDF Forecast: A forecast of probabilities for the
i-th trial, for all categories
1
.5
0
t0
t1
t2
…
tm
Skill Statistics for CDF Forecasts
• Brier Score: (1/N) Σ (pi – oi)2 (Mn.Sq.Error)
= Reliability + Resolution + P(T) ∗ P(F)
.
• For each Category:
– Define P(Y|T) to be the mean probability forecasted when T
– Define P(Y|F) to be the mean probability forecasted when F
–. Define PSS = P(Y|T) – P(Y|F) (Pierce skill for Prob. Fcst.)
• In the limit as a forecast becomes confident,
CDF PSS Æ Deterministic PSS
Decision Theory - Historical
Stream of signals: Dots and Dashes- Discrimination by Length
Separation
Dot
Dash
Decision
Threshold
Miss-identified Dash
Miss-identified Dot
Decision Theory – Probability Forecasts
Stream of Trials: Decisions based on the Probability of events
Separation = PSS
Obs =
False
Obs =
True
0
1
P(Y|F)
P(Y|T)
Decision
Threshold
Missed Opportunity
False Positive
Discrimination by Magnitude of the Probability
Discriminant = # sigma’s to partition equally
Reliability
•
•
Bin data to (k) Probability Classes
Frequency of Occurrence vs. Fcst
•
Discriminating forecast should have
small counts in the middle classes
.
• Numerical estimation of mid-class
frequencies may be problematic
.
Decision
Threshold
Reliability
1.00
0.80
0.80
0.60
0.60
Frequency
Frequency
Reliability
1.00
0.40
0.40
0.20
0.20
0.00
0.00
0.0
0.1 0.2
0.3 0.4
0.5
0.6 0.7
Probability
0.8 0.9
1.0
0.0
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
0.6
Probability Class
0.7
0.8
0.9
1.0
Reliability & Linear Calibration
Reliability | Fcst
1.00
Frequency
0.80
1700
1750
0.60
1800
0.40
1850
1900
0.20
1950
0.00
0.0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.9 1.0
Probability Class
Two Notions of Reliability
1.00
Reliability | Forecast
1.00
0.80
Reliability | Event
0.80
Frequency
1700
1750
0.60
0.60
1800
1850
0.40
P(T)
P(Y)
0.40
Climo
1900
1950
0.20
0.20
2000
0.00
0.0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.9 1.0
Probability Class
0.00
1700
1800
1900
Category Time
2000
SFO Problem
SODAR
Sensor Suite
Oakland
Fort
Funston
S. F. Bay
SFO
Pacific Ocean
Half
Moon
Bay
Surface Weather Observation
SODAR (Acoustic Sounder)
Pyranometer (SW Radiation)
Sonic Anemometer
Radiosonde (Weathe r Balloon)
ARTCC
San Carlos
San Jose
Forecast Algorithms
Regional Stat. Fcst Model
Satellite Stat. Fcst Model
Local Stat. Fcst Model
Generating CDF forecasts
• Goal: Build models that forecast PDF’s for each
of the SFO Marine Stratus Forecasts for CDM TM
models (13z, 15z, 16z, 17z, 18z)
• Climo: Historical Model Performance
• Optimize Five Objective Functions
.
BS, MLE, PSS, LR|PSS, RL&PSS
– 15 min. Nested Categories
– Predictors: SFO deterministic forecasts LSF, RSF, SSF, CF
– Develop a Forecast Model for the probability that the event
will occur in each category
– Obs: Times that SFO initiated Side-by approaches
15z Climo Forecast
Skill Metrics
1.00
0.80
PSS
BS
0.60
POD
PFP
0.40
Tsig
Fsig
0.20
1.00
0.80
1750
1800
1850
1900
Category Tim e
1950
1700
2000
Frequency
0.00
1700
Reliability
Dscr
1750
0.60
1800
1850
0.40
1900
1950
0.20
2000
0.00
0.0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.9 1.0
Probability Class
15z BS Forecast
Reliability
1.00
Skill Metrics
1.00
0.80
0.80
PSS
BS
0.60
Frequency
1700
1750
0.60
1800
1850
0.40
1900
POD
PFP
0.40
2000
Tsig
Fsig
0.00
0.0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.9 1.0
DISC
0.20
0.00
1700
1950
0.20
Probability Class
Reliability | Event
1.00
1750
1800
1850
1900
1950
2000
Category Tim e
0.80
Rel_F
Rel_E
avgPSS
0.06
0.01
0.40
0.60
P(T)
P(Y)
0.40
Clim
0.20
0.00
1700
1800
1900
Category Time
2000
15z PSS Forecast
Reliability
1.00
Skill Metrics
1.00
0.80
1700
PSS
BS
0.60
Frequency
0.80
1750
0.60
1800
1850
0.40
1900
POD
PFP
0.40
2000
Tsig
Fsig
0.00
0.0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.9 1.0
DISC
0.20
0.00
1700
1950
0.20
Probability Class
Reliability | Event
1750
1800
1850
1900
1950
2000
1.00
Category Tim e
0.80
Rel_F
Rel_E
avgPSS
0.23
0.14
0.60
0.60
P(T)
P(Y)
0.40
Clim
0.20
0.00
1700
1800
1900
Category Time
2000
15z PSS-cal Forecast
1.00
Reliability | Forecast
Skill Metrics
1.00
0.80
0.80
PSS
BS
POD
PFP
Tsig
Fsig
DISC
0.60
0.40
0.20
Frequency
1700
1750
0.60
1800
1850
0.40
1900
1950
0.20
2000
0.00
0.0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.9 1.0
Probability Class
0.00
1700
Reliability | Event
1750
1800
1850
1900
1950
1.00
2000
Category Time
0.80
Rel_F
Rel_E
avgPSS
0.10
0.07
0.38
0.60
P(T)
P(Y)
0.40
Climo
0.20
0.00
1700
1800
1900
Category Time
2000
15z PSS&RL Forecast
Reliability | Fcst
1.00
Skill Metrics
1.00
0.80
PSS
BS
POD
PFP
Tsig
Fsig
DISC
0.60
0.40
0.20
Frequency
1750
0.80
0.00
1700
1700
0.60
1800
1850
0.40
1900
1950
0.20
2000
0.00
0.0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.9 1.0
Probability Class
Reliability | Event
1.00
1750
1800
1850
1900
1950
2000
Category Time
Rel_F
Rel_E
avgPSS
0.80
0.06
0.03
0.43
0.60
P(T)
P(Y)
0.40
Clim
0.20
0.00
1700
1800
1900
Category Time
2000
Forecast Comparisons
15z
PSS
sqrtREL
16z
PSS
sqrtREL
17z
PSS
sqrtREL
18z
PSS
sqrtREL
DET
0.51
0.42
DETc
0.31
0.24
CLIMO
0.38
0.22
BS
0.40
0.24
PSS
0.60
0.48
PSSc
0.38
0.32
PSS&RL
0.43
0.24
0.54
0.41
0.35
0.22
0.39
0.22
0.45
0.22
0.59
0.40
0.41
0.32
0.48
0.24
0.55
0.40
0.34
0.22
0.40
0.20
0.43
0.24
0.56
0.32
0.43
0.28
0.43
0.22
0.53
0.41
0.32
0.22
0.34
0.14
0.35
0.24
0.54
0.32
0.35
0.24
0.40
0.28
Summary
• We have developed several viable methods for
generating CDF forecasts
• The deterministic forecasts developed by the SFO
Marine Stratus project are useful predictors for
modeling CDF forecasts
• Some CDF forecasts have much better Pierce
Skill than the deterministic Consensus forecasts
• There is a trade-off between PSS and Reliability
What’s Next?
• Understand PSS/Rel balance
• Tune forecasts to needs of TM models
• CDF forecasts for other Airports & CDM Needs
– SFO forecasts from Met. Data
– Other airports:
Convert deterministic Forecasts to CDF’s
Forecasts from archived NWS data
.
.
.