mu ltip lexed link L1 B1 Bos ton
advertisement
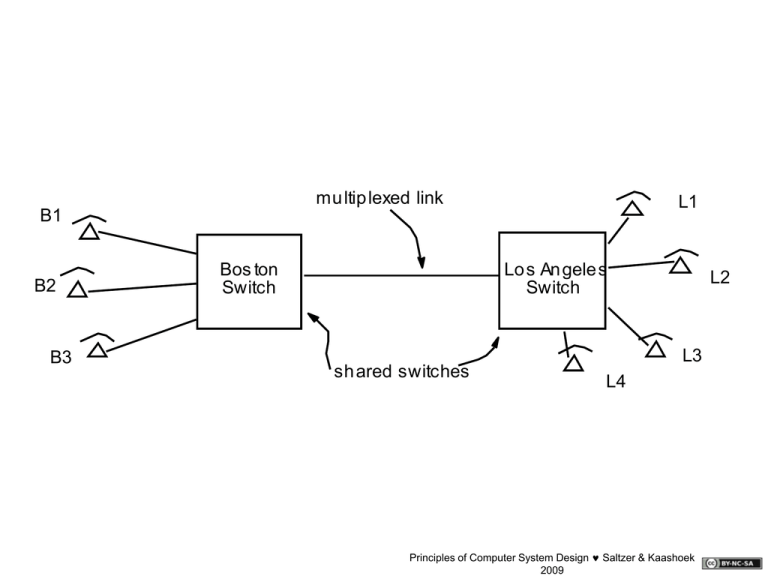
mu ltip lexed link
L1
B1
B2
B3
Bos ton
Switch
Lo s An gele s
Switch
sh ared switches
L2
L3
L4
Principles of Computer System Design Saltzer & Kaashoek
2009
Tim e
5,6 24 b it times
8-bi t fra me
8-bi t fra me
8-bi t fra me
Principles of Computer System Design Saltzer & Kaashoek
2009
D
Pers onal Compu ter
se rvi ce
A
B
mu ltip lexed
li nk
da ta cross es this
li nk in b ursts and
can tolera te vari able del ay
C
Principles of Computer System Design Saltzer & Kaashoek
2009
fra me
Ti me
B
Guid ance
in forma tion
D
40 00 b its
75 0 bi ts
Principles of Computer System Design Saltzer & Kaashoek
2009
pa cket
A
Packe t
Switch
Wo rkstatio n
at netwo rk
attachmen t
po int A
B
1 Packe t
Switch
2 3
Service a t ne twork
attachmen t
po int B
Packe t
Switch
Packe t
Switch
B
Principles of Computer System Design Saltzer & Kaashoek
2009
avera ge
qu euin g
de lay
ma xi mum
to lerab le d elay
1
-----------1 –
1
0
Util izatio n, r
10 0%
rma x
Principles of Computer System Design Saltzer & Kaashoek
2009
A
se nd re ques t,
se t ti mer
B
ti me
req uest 1
res pons e 1
receive respo nse,
res et timer
X
se nd re ques t,
se t ti mer
ti mer e xp ires,
res end reque st,
se t ne w time r
receive respo nse,
res et timer
X
req uest 2
overl oade d
fo rwa rder
di sca rds
req uest
pa cket.
req uest 2’
res pons e 2’
X
Principles of Computer System Design Saltzer & Kaashoek
2009
B
A
req uest 3
se nd re ques t,
se t ti mer
X
ti mer e xp ires,
res end reque st,
se t ne w time r
receive respo nse,
res et timer
req uest 3’
X
overl oade d fo rwa rder
di sca rds re spon se 3
du plicate arrives at B
B s ends resp onse 3’
res pons e 3’
Principles of Computer System Design Saltzer & Kaashoek
2009
B
A
se nd re ques t,
se t ti mer
req uest 4
res pons e 4
ti mer e xp ires,
res end
receive
res pons e,
res et timer
req uest 4’
X
res pons e 4’
pa cket containi ng re spon se
ge ts d elayed
du plicate arrives at B
B s ends resp onse 4’
receive
du plicate
res pons e
Principles of Computer System Design Saltzer & Kaashoek
2009
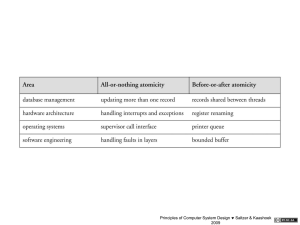
Ap plicati on chara cte risti cs
Continuo us
stream
(e.g., inte ractive
voice)
is och ronou s
(e.g., tele phon e
ne twork)
go od m atch
Burs ts o f da ta
(mo st
compu ter-to compu ter d ata)
Resp onse
to loa d
varia tion s
wastes
capacity
(ha rd-edg ed)
ei ther accepts
or blocks ca ll
go od m atch
(gra dual )
1 va riabl e de lay
2 discards data
3 rate adap tati on
Network
Type
as yn chro nous
(e.g., Inte rnet)
varia ble late ncy
up sets
ap plicati on
Principles of Computer System Design Saltzer & Kaashoek
2009
Networks encounter a avst range of
D ata rate s
Prop agati on, trans mis si on, qu euin g, and proce ss ing d elay s.
Loads
Num bers o f use rs
Networks traverse hostile envir
onments
Noi se d amag es d ata
Links sto p working
Best-effort networks have
Varia ble d elay s
Varia ble tran smi ss ion rate s
D is carde d pac kets
D upl ica te pac kets
Maxi mum p ack et len gth
Reo rd ered de live ry
Principles of Computer System Design Saltzer & Kaashoek
2009
resu lt
FIR E
(#, target, ac tion)
Client stub
request:
Prepare
request
mes sage.
Send to
service
Wait for
res pons e.
proc: FIRE
args:
3
type: integer
value: 2
type: string
value: “Lucifer”
type: pro ced ure
value: EV ADE
proc edureFIR E (nmi ss, where, reac t)
...
retur n resu lt
Service stub
Receiv e
request
mes sage.
Call
requested
procedure.
Prepare
res pons e
mes sage.
Send to client.
res pons e:
acknowledgment
type: string
value: “dest royed”
Principles of Computer System Design Saltzer & Kaashoek
2009
Main prog ram
ap plicati on p rotocol
calle d pro ced ure
RPC cl ient stu b
pre sentatio n pro tocol
RPC service s tub
Principles of Computer System Design Saltzer & Kaashoek
2009
Main prog ram
fi re
(return)
RPC cl ient stu b
se nd_
me ssag e
ap plicati on p rotocol
fi re
pre sentatio n pro tocol
(return)
RPC service s tub
se nd_
me ssag e
receive_
me ssag e
Clie nt n etwork
p ackage
calle d pro ced ure
tra nspo rt pro tocol
receive_
me ssag e
Service n etwork
pa ckage
Principles of Computer System Design Saltzer & Kaashoek
2009
La ye r One
A
La ye r Two
La ye r Thre e
B
J
X
C
K
D
L
Y
Z
Principles of Computer System Design Saltzer & Kaashoek
2009
DATA
L INK _SEND
NETW ORK _HA NDLE
B
A
Li nk
La ye r
(pk t, link2)
li nk 1
li nk
pro tocol
C
Li nk
La ye r
li nk 2
LT DATA LH
li nk
pro tocol
Li nk
La ye r
Principles of Computer System Design Saltzer & Kaashoek
2009
DATA
NETW ORK_ SEND
(s egme nt, “IP”, na p_11 97)
ne twork
Netw ork
La yer
Netw ork
La yer
pro tocol
NT DATA NH
lINK_SE ND (pa cke t, link 2)
Link
La yer
LT NT DATA NH LH
li nk 2
li nk
pro tocol
L INK _SEND
(pa cke t, link 5)
NETWOR K_HANDL E
Link
La yer
Link
La yer
li nk5
Principles of Computer System Design Saltzer & Kaashoek
2009
FIR E
(7, “Lu cife r”, eva de)
FIR E
DATA
End-to-End
Layer
(RPC)
end -to-en d
End-to-End
Layer
(RPC)
(7, “Lu cife r”, eva de)
protoco l
ET DATA EH
Netw ork
Layer
Netw ork
Layer
Netw ork
Layer
NT ET DATA EH NH
Link
Layer
Link
Layer
Link
Layer
Link
Layer
LT NT ET DATA EH NH LH
Principles of Computer System Design Saltzer & Kaashoek
2009
The end-to-end argument
Th e app lication knows best.
Principles of Computer System Design Saltzer & Kaashoek
2009
Fil e Tra nsfe r Progra m (en d-to-e nd l ayer)
Fil e tra nsfe r syste m
Gnute lla (network la ye r)
Tran sport Proto col (end -to-en d la ye r)
Internet Proto col (netwo rk l ayer)
Internet
(lin k
layer)
dia led con nection (end -to-en d la ye r)
tel epho ne s wi tch (netwo rk l ayer) (lin k
layer)
physi cal wire (l ink layer)
dia l-up
tel epho ne
netwo rk
Principles of Computer System Design Saltzer & Kaashoek
2009
data
A
ready
B
acknowl edge
Principles of Computer System Design Saltzer & Kaashoek
2009
V
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
ti me
Principles of Computer System Design Saltzer & Kaashoek
2009
A
B
Principles of Computer System Design Saltzer & Kaashoek
2009
pr ocedureFRAME _ TO_ BIT (frame _data, le ngth)
on es_ in_a _row= 0
for i from 1 to le ngth do
// Firs t sen d frame c onte nts
SEND _BIT (frame _data[i]);
if frame _data[i] = 1 then
on es_ in_a _rowon es_ in_a _row +1;
if on es_ in_a _row= 6 then
SEND _BIT (0);
// Stuff a zero so that da ta doe sn’ t
on es_ in_a _row 0;
// look like a framin g marke r
else
on es_ in_a _row 0;
for i from 1 to 7 do
// Now sen d framin g marke r.
SEND _BIT (1)
Principles of Computer System Design Saltzer & Kaashoek
2009
pr ocedureBIT _ TO _FRAME (rcv d_bit)
on es_ in_a _rowintegerinitially 0
if on es_ in_a _row< 6 then
bits_in_frame bits_in_frame + 1
frame _data[bits_in_frame] rcv d_bit
if rcv d_bit = 1 then on es_ in_a _row on es_ in_a _row+ 1
else on es_ in_a _row 0
else
// This may be a s eve nth on e-bit in a row, che ck i t out.
if rcv d_bit = 0 then
on es_ in_a _row 0
// Stuffed b it, don 't us e it.
else
// This is the en d-of-fra me ma rk er
LINK _R EC EIVE (frame _data, (bits_in_frame - 6), link_id)
bits_in_frame 0
on es_ in_a _row 0
Principles of Computer System Design Saltzer & Kaashoek
2009
Network La ye r
Network pro tocol
Sta ndard
pro tocol
High
rob ustn ess
pro tocol
Experi mental
pro tocol
Li nk Layer
Principles of Computer System Design Saltzer & Kaashoek
2009
Ad dress
In terne t Reso luti on Ap pletalk
Protoco l Protoco l Protoco l
Sta ndard
pro tocol
High
rob ustn ess
pro tocol
Path
Ve cto r
Exch ange
Protoco l
Experi mental
pro tocol
Network La ye r
Li nk Layer
Principles of Computer System Design Saltzer & Kaashoek
2009
str uctureframe
str ucturec hec ked_ con tents
bit_string ne t_protoc ol
bit_string pa yloa d
bit_stringc hec ksu m
// multi plex ing p aramete r
// payl oad d ata
pr ocedureLINK _SEND (da ta_bu ffer, link_identifier, lin k_proto col, network_p ro toco
) l
frame instance ou tgoin g_frame
ou tgoin g_frame .che cke d_c onten ts.pa yloa
d da ta_bu ffer
ou tgoin g_frame .che cke d_c onten ts.ne t_protoc
ol da ta_bu ffer.network_p ro toco l
frame _len gth LENGTH (da ta_bu ffer) + he ader_length
ou tgoin g_frame .che cks um C HECK SUM (frame .che cke d_c onten ts
, frame _len gth)
s endp ro c link_p ro toco[tha
l
t_lin k.protoc ol]
// Selec t lin k protoc ol.
s endp ro c(ou tgoin g_frame, frame _len gth, link_identifier
) // Send fram e.
Principles of Computer System Design Saltzer & Kaashoek
2009
pr ocedureLINK _R EC EIVE (rec eive d_frame
, le ngth, link_id)
frame instance rec eive d_frame
if C HECK SUM (rec eive d_frame .che cke d_c onten,ts
le ngth) =
rec eive d_frame .che cks um
then
// Pas s go od pa cke ts up to nex t laye r.
go od_fram e_c ountgo od_fram e_c ount+ 1;
GIVE _TO _NETWORK _HANDLER (rec eive d_frame .che cke d_c onten ts.pa yloa
, d
rec eive d_frame .che cke d_c onten ts.ne t_protoc
);ol
else ba d_frame _co untba d_frame _co unt+ 1 // Ju st c ount d amag ed frame .
// Eac h network l ayer proto col hand ler mus t caSET
ll _HANDLER be fore the fi rs t pac ket
// for that proto col arri ves …
pr ocedureSET _HANDLER (ha ndle r_ proce dure
, ha ndle r_ protoc ol
)
ne t_han dler[ha ndle r_ protoc ol
] ha ndle r_ proce dure
pr ocedureGIVE _TO _NETWORK _HANDLER (rec eive d_pa cke,tne two rk _protoc ol
)
ha ndle r ne t_han dler[ne two rk _protoc ol]
if (ha ndle r ° NULL ) call ha ndle r(rec eive d_pa cke,tne two rk _protoc ol
)
else un expe cted _protoc ol_ cou nt un expe cted _protoc ol_ cou nt+ 1
Principles of Computer System Design Saltzer & Kaashoek
2009
35
netwo rk
attach ment
poi nt
01
07
24
33
Network
11
40
41
16
39
42
netwo rk
add ress
Principles of Computer System Design Saltzer & Kaashoek
2009
struc tur epac ket
bit_string so urce
bit_string des tina tion
bit_string end _protoc ol
bit_string pay load
proc edureNETWOR K _ SEND (se gmen t_buffe r, des tina tion,
network_ protoc ol, end _protoc ol)
pac ket instance outg oing _pac ket
outg oing _pac ket.p aylo ad se gmen t_buffe r
outg oing _pac ket.e nd_p ro tocoend
l
_protoc ol
outg oing _pac ket.s ourc e MY _ NETWOR K _ADDRESS
outg oing _pac ket.d estinatio n des tina tion
NETWOR K _HANDLE (outg oing _pac ket
, net_ protoc ol)
Principles of Computer System Design Saltzer & Kaashoek
2009
proc edureNETWOR K _ HANDLE (net_ pac ket, net_ protoc ol)
pac ket instance net_ pac ket
if net_ pac ket.de stin ation° MY _NETWOR K _ADDRESS then
nex t_hop LOOKUP (net_ pac ket.de stin ation, forwarding _table)
LINK _ SEND (net_ pac ket, nex t_hop, lin k_proto col, net_ protoc ol)
else
GIVE _TO _END _LAYER (net_ pac ket.pa yloa d
,
net_ pac ket.en d_proto col
, net_ pac ket.so urce)
Principles of Computer System Design Saltzer & Kaashoek
2009
Segm ent prese nted to
the netwo rk l ayer
DATA
Packet pres ente d to
the lin k l ayer
sourc e &
destination
end
protocol
DATA
Fram e
app earin g
on the link
frame netw ork sourc e &
mark protocol destination
end
protocol
DATA
chec k frame
sum mark
Exampl e
1111111
RPC
“Fire”
97142 1111111
55316
IP
41 —> 24
Principles of Computer System Design Saltzer & Kaashoek
2009
B
C
1
A
1
1
G
sou rce
1
H
3
4
1
5
2
2 3
des tina tion
1
F
1
5
K
4
2
3
4
3
4
2
E
1
5
J
1
1
D
2
Principles of Computer System Design Saltzer & Kaashoek
2009
B
C
1
A
1
1
G
sou rce
1
3
4
1
5
2
H
2 3
des tina tion
1
F
1
5
K
4
2
3
4
3
4
2
E
1
5
J
1
1
D
2
de stin atio n
li nk
A
al l other
en d-layer
1
Principles of Computer System Design Saltzer & Kaashoek
2009
B
C
1
A
1
1
G
sou rce
1
3
4
1
5
2
H
2 3
des tina tion
1
F
1
5
K
4
2
3
4
3
4
2
E
1
5
J
1
1
D
2
des tina tion
lin k
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
J
K
1
2
2
3
4
4
end -layer
2
3
4
Principles of Computer System Design Saltzer & Kaashoek
2009
B
C
1
A
1
1
G
sou rce
1
3
4
1
5
2
H
2 3
des tina tion
1
F
1
5
K
4
2
3
4
3
4
2
E
1
5
J
1
1
D
2
to
pa th
G
<>
Principles of Computer System Design Saltzer & Kaashoek
2009
B
C
1
A
1
1
G
sou rce
1
3
4
1
5
2
H
2 3
des tina tion
1
F
1
5
K
4
2
3
4
3
4
2
E
1
5
J
1
1
D
2
Fro m A,
via link 1
to
pa th
Fro m H,
via link 2:
to
pa th
Fro m J,
via link 3:
to
pa th
Fro m K,
via link 4:
to
pa th
A
H
J
K
<>
<>
<>
<>
Principles of Computer System Design Saltzer & Kaashoek
2009
B
C
1
A
1
1
G
sou rce
1
3
4
1
5
2
H
2 3
des tina tion
1
F
1
5
K
2
3
4
3
4
2
path vector
4
E
1
5
J
1
1
D
2
forward ing tabl e
to
path
to
lin k
A
G
H
J
K
<A>
<>
<H>
<J>
<K>
A
G
H
J
K
1
end -layer
2
3
4
Principles of Computer System Design Saltzer & Kaashoek
2009
B
C
1
A
1
1
G
sou rce
1
3
4
1
5
2
H
2 3
des tina tion
1
F
1
5
K
4
2
3
4
3
J
4
2
E
1
5
1
1
D
2
From A,
via l ink 1
From H,
via l ink 2:
From J,
via l ink 3:
From K,
via l ink 4:
to
path
to
path
to
path
to
path
A
G
<>
<G>
B
C
G
H
J
K
<B>
<C>
<G>
<>
<J>
<K>
D
E
G
H
J
K
<D>
<E>
<G>
<H>
<>
<K>
E
F
G
H
J
K
<E>
<F>
<G>
<H>
<J>
<>
Principles of Computer System Design Saltzer & Kaashoek
2009
B
C
1
A
1
1
G
sou rce
1
3
4
1
5
2
H
2 3
des tina tion
1
F
1
5
K
2
3
4
3
2
E
1
5
J
4
pa th vector
4
1
1
D
2
fo rwa rding tab le
to
pa th
to
li nk
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
J
K
<A>
<H, B>
<H, C>
<J, D>
<J, E>
<K, F>
<>
<H>
<J>
<K>
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
J
K
1
2
2
3
3
4
en d-layer
2
3
4
Principles of Computer System Design Saltzer & Kaashoek
2009
// Ma intai n routin g and forwa rd ing ta bles .
ve ctorass ociative arr ay
// ve ctor[d_ addr] co ntain s pa th to de stin ation
d_ addr
ne ighb or_vec tor
instance of
ve ctor // A path v ecto r rec eiv ed from s ome neig hbor
my _vec torinstance ofve ctor // My current p ath ve ctor.
ad dr ass ociative arr ay
// ad dr[ j] is the ad dress of the network atta chm ent
// poin t at the o ther end of lin
j. k
// my _add ris add re ss of my n etwork attac hme nt poi nt.
// A pa th is a pa rs abl e lis t of ad dress es , e.g. {a ,b,c,d }
pr ocedure
ma in()
// In itial ize , then s tart adv ertisi ng.
SET_TYPE_HANDLER (HANDLE _ADVERTISEMENT , ex cha nge_ protoc)ol
clearmy _vec tor;
// Lis ten fo r a dvertis eme nts
do occ asionally
// and a dvertis e my paths
for eac hj in link_idsdo
// to all of my n eigh bors.
s tatus SEND _PATH _VECTOR (j, my _add,r my _vec tor
, ex ch_ protoc)ol
if s tatus ° 0 then
// If th e lin k was d own,
clearne w_ vec tor
// forget ab out an y path s
FLUSH _AND _R EBUILD (j)
// that s tart wi th that l ink.
Principles of Computer System Design Saltzer & Kaashoek
2009
pr ocedure
HANDLE _ADVERTISEMENT (ad vt, li nk_i d)
// Ca lled wh en an advt a rriv es.
ad dr[li nk_i d] GET _SOU RC E (ad vt)
// Extrac t neig hbor’s add re ss
ne ighb or_vec tor
GET _PATH _VECTOR (ad vt)
// an d path vec tor.
for eac h
ne ighb or_vec tor
.d_ addrdo
// Loo k for bette r p aths .
ne w_ pathad dr[li nk_i d], ne ighb or_vec tor
[d_ addr]}
// Build poten tial p ath.
if my _add ris not inne w_ paththen
// Skip i t if I’m in it.
if my _vec tor
[d_ addr] = NULL) then
// Is it a n ew des tinati on?
my _vec tor
[d_ addr] ne w_ path
// Yes , add th is o ne.
else
// Not new; if be tter, use it.
my _vec tor
[d_ addr] SELEC T _PATH (ne w_ path
, my _vec tor
[d_ addr])
FLUSH_AND _R EBU ILD (li nk_i d)
Principles of Computer System Design Saltzer & Kaashoek
2009
pr ocedure
SELEC T _PATH (ne w, ol d)
// De cid e if ne w p ath is bette r th an ol d one .
if firs t_hop(ne w) = firs t_hop(ol d) then retur n
ne w // Update any p ath we were
// alread y us ing.
elseif le ngth(ne w) •le ngth(ol d) then retur n
ol d // We kn ow a sh orter path, k eep
elser etur nne w
// OK, th e new on e loo ks b etter.
pr ocedure
FLUSH _AND _R EBUILD (li nk_i d)
// Flu sh o ut sta le pa ths from this neig hbor.
for eac h
my _vec tor,d_a ddr
if firs t_hop(my _vec tor
[d_ addr] ) = ad dr[li nk_i d] and ne w_ vec tor
[d_ addr] = NULL
then
deletemy _vec tor
[d_ addr]
// De lete p aths that are n ot sti ll ad vertis ed.
R EBUILD_FOR WARDING _TABLE (my _vec tor
, ad dr)
// Pas s in fo to forwarder.
Principles of Computer System Design Saltzer & Kaashoek
2009
regi on R1
R1.B 1
R1.A
2 3
regi on R2
forward ing tabl e in R1.B
regi on forwardin g
sectio n
R1.C R1.D
R3.C
to
lin k
R1
R2
R3
R4
local
1
1
3
local forwardi ng
sectio n
to
lin k
R1.A
1
R1.B end -layer
R1.C
2
R1.D
3
regi on R3
regi on R4
Principles of Computer System Design Saltzer & Kaashoek
2009
receiver
sen der
sen d fi rst s egme nt
seg ment 1
tim e
accep t se gmen t 1
receive ACK,
sen d se con d se gmen t
ACK 1
seg ment 2
accep t se gmen t 2
receive ACK,
sen d th ird s egme nt
ACK 2
3
(repe at N times )
•
•
•
N
accep t se gmen t N
ACK N
Done.
Principles of Computer System Design Saltzer & Kaashoek
2009
sen der
sen d se gmen t 1
sen d se gmen t 2
sen d se gmen t 3
receive ACK 1
receive ACK 2
receiver
seg ment 1
2
3
ack 1
ack 2
(repe at N times )
•
•
•
tim e
ackno wl edge seg ment 1
ackno wl edge seg ment 2
N
ackno wl edge seg ment N
ack N
receive ACK N, don e.
Principles of Computer System Design Saltzer & Kaashoek
2009
se nder
receiver
ma y I se nd?
receive permi ssio n,
se nd s egme nt 1
se nd s egme nt 2
se nd s egme nt 3
se nd s egme nt 4
receive ACK 1
receive ACK 2
receive ACK 3
receive ACK 4,
wait
…
receive permi ssio n,
se nd s egme nt 5
se nd s egme nt 6
ti me
yes, 4 s egme nts
receive reque st,
op en a 4-se gmen t
wind ow
se gmen t #1
ack # 1
ack # 2
ack # 3
ack # 4
#2
#3
#4
bu ffer
bu ffer
bu ffer
bu ffer
se nd 4 more
se gmen t #5
#6
•
•
•
segm ent 1
segm ent 2
segm ent 3
segm ent 4
fi nish ed p roce ssin g
se gmen ts 1 –4, reope n
th e wind ow
bu ffer segm ent 5
bu ffer segm ent 6
Principles of Computer System Design Saltzer & Kaashoek
2009
unl imited re source
ca pacity
of a li mite d
reso urce
use ful
work
don e
lim ited reso urce
with no was te
co nges tion
co llap se
offered load
Principles of Computer System Design Saltzer & Kaashoek
2009
duplic ate acknow ledgment
rec eived
multiplic ative
decreas e
additive
increas e
delay
Window
size
slow s tart,
again
timer
ex pires ,
stop sending
slow s tart
Time
Principles of Computer System Design Saltzer & Kaashoek
2009
le ader
64 bits
de stin atio n
48 bits
so urce
48 bits
type
16 bits
da ta
36 8 to 12,000 bits
checksu m
32 bits
Principles of Computer System Design Saltzer & Kaashoek
2009
17
24
12
05
19
Sta tion
Id enti fier
(Eth ernet
Ad dress )
Principles of Computer System Design Saltzer & Kaashoek
2009
pr ocedureETHERNET _HANDLE (ne t_packet, le ngth)
de stin ation ne t_packet.targe t_id
if de stin ation = my _sta tion_ idor de stin ation =
GIVE _TO _END _LAYER (ne t_packet.d ata
,
ne t_packet.e nd_p ro toco, l
ne t_packet.source_id
)
else
ig nore pa cke t
BROADC AST
_ID then
Principles of Computer System Design Saltzer & Kaashoek
2009
L
work
statio n
up per-la ye r netwo rk a ddres s
li nk iden tifi er
M
N
P
Q
work
work
work
statio n se rve r
statio n statio n
1
1
17
1
15
18
1
1
14
22
G
K
rou ter
…
6
19
1
2
3
4
5
H
J
E
F
Eth ernet
Eth ernet sta tion ide ntifier
Principles of Computer System Design Saltzer & Kaashoek
2009
L
work
statio n
up per-la ye r netwo rk a ddres s
li nk iden tifi er
M
N
P
Q
work
work
work
statio n se rve r
statio n statio n
1
1
17
1
15
18
1
1
14
22
G
K
rou ter
…
6
19
1
2
3
4
5
H
J
E
F
Eth ernet
Eth ernet sta tion ide ntifier
in terne t
ad dress
Eth ernet/
statio n
M
N
P
Q
K
E
en et/1 5
en et/1 8
en et/1 4
en et/2 2
en et/1 9
en et/1 9
Principles of Computer System Design Saltzer & Kaashoek
2009
L
work
statio n
up per-la ye r netwo rk a ddres s
li nk iden tifi er
M
N
P
Q
work
work
work
statio n se rve r
statio n statio n
1
1
17
1
15
18
1
1
14
22
G
K
rou ter
…
6
19
1
2
3
4
5
H
J
E
F
Eth ernet
Eth ernet sta tion ide ntifier
internet
add ress
M
Ethe rnet/
sta tion
ene t/15
in terne t
ad dress
M
E
Eth ernet/
statio n
en et/1 5
en et/1 9
Principles of Computer System Design Saltzer & Kaashoek
2009