Functional Biomedical Informatics Research Network (FBIRN) UK E-Science Workshop
advertisement

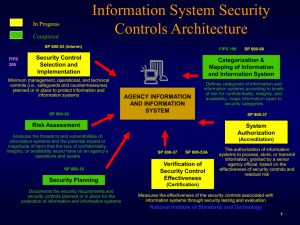
Functional Biomedical Informatics Research Network (FBIRN) David Keator FBIRN NeuroInformatics Working Group Chair University of California, Irvine UK E-Science Workshop October 2, 2006 FBIRN Goals Develop multi-site functional neuroimaging tools. Develop the capability to analyze, as a single data set, data acquired from multiple sites using tools developed from multiple sites Develop a federated data management system to support these multi-site fMRI studies Schizophrenia as a model Schizophrenia • Brain illness with subtle structural and functional changes • Confounds of age/illness duration/treatment effects • Active area of imaging research with many competing theories and approaches Progress hampered by • Inconsistent data & lack of replications • Noncomparable imaging techniques • Small and diverse patient populations This applies to many areas of study FMRI variance and correction How big a problem is it? Traveling Humans Study (Phase I) HIPAA HIPAA HIPAA HIPAA HIPAA Subjects traveled around the country to be scanned at all FBIRN sites Unique dataset: Subject x site interactions can be measured for the first time Measuring Subject and Site Effects ROI – Top 10% of Activated Voxels Variance Source Auditory Hand Visual Subject 18.8 18.3 21.8 Site 43.0 21.0 43.8 Day 0.0 0.0 0.1 Run 0.4 0.1 0.1 Subject X Site 3.6 14.6 10.5 Subject X Site+ 20.7 35.2 20.0 Residual 1.5 4.2 1.5 Calibration Keys Pre-data collection scanner QA Data collection • Effect of different stimuli and response devices Experimental design: • Cognitive task sensitivity, robustness, reliability • Non-neuronal measures of BOLD signal Post-data collection corrections • Use of the breatholding (BH), smoothness, others Data sharing across sites • Data format issues, orientations, provenance, etc. • Data analysis issues Phantom QA methods ave nave SFNR Phantom QA methods Time Series Stability Informatics Tools for Tracking Scanners https://portal.nbirn.net/BIRN/cgi-bin/DataGrid/MRIs/publicMRIStability.cgi Scanner characterization Friedman et al., Neuroimage, In press Calibration methods: Smoothing Smoothing to a common level reduces intersite effects SMOOTHED UNSMOOTHED Site: HARV MINN IOWA NMEX .200 .075 -.075 -.200 Calibration Methods: Non-neuronal measures of BOLD signal Scaling by the breathhold response increases group effect size Group Differences: Uncorrected Corrected Differences between young and old subjects in an fMRI task, before and after correcting for BOLD differences in a separate breathhold task Thomason et al., Human Brain Mapping, 2006 Calibration methods: Grey Matter SFNR Calibrating BOLD signal by SFNR in grey matter reduces intersite effects Intersite effects in 1.5T scanners in eight ROIs, before and after correction Friedman et al., Neuroimage, in press Impact of Calibration Methods Cohen’s f ANOVA Observed Effect Size Remaining challenge None Smooth Smooth, BH Calibrate Smooth, BH Calibrate, BH Screen Phase I Traveling Calibration Subject Dataset Tools delivered since FBIRN inception in 2003 Datasets • Phase I, 10-site traveling subjects dataset • MRI QA datasets Data collection • Phantoms MRI calibration and QA protocol • E-prime programs used in data collection Data management: • XCEDE XML schema Tools for reading and writing XCEDE XML image wrappers • • • • Standardized, general purpose directory hierarchy Data management and “upload” scripts Human Imaging Database schema/Graphical User Interface Code (HID) Clinical Assessment Layout Manager/General Assessment Manager Engine (CALM) • FSL Image Processing Scripts (FIPS) http://www.nbirn.net/downloads/index.shtm Informatics/Analysis Infrastructure Result Images and XML wrapper in Data Grid FMRI Images •Automated image upload to Data Grid/HID for sharing fMRI Scanner Proprietary Scanner Formats, DICOM, NIFTI Data Grid (Local) HID(s) (Local) Clinical Data •Computer aided scale input via clinical data entry interface FIPS: FSL Image Processing Scripts FIPS Results Results with standard descriptions in HID (i.e. data provenance) Multi-Site User Query •Data storage conventions •XML data description (XCEDE) •Image and clinical data held locally •De-identification for public sharing Architecture Overview Subject Management CALM/GAME Assessments Multi-Site Query XCEDE Services Clinical / Demographics Study Protocols Study Data Web Application Core Hierarchy Schema Oracle Database PostgreSQL File System Data Data Grid HID: Community Database Development UCSD: Lead Development UCI: Lead Development MGH: Oracle Specifics UCLA: PostgreSQL Specifics UNM: Clinical Measures UIowa: Performance Duke: XML Data Entry: HID+GUI Clinical Assessment Layout Manager (CALM) Data Management: CALM & GAME Multi-Database Query Detailed Query Information FBIRN Data Federation UMN HID p2 p1 p2 p1 p2 Stanford p1 HID UCLA p2 HID UCI HID UI HID p1 p2 UCSD HID p1 UNM HID = Data Integration Environment = PostgreSQL test site = Phase 1 / Phase 2 data p1 p2 Duke: 67 BWH: 22 MGH: 12 UCLA: 54 UCSD: 6 UCI: 71 UNM: 57 UI: 64 UMN: 57 Yale: 66 p1 MGH BWH HID HID Yale p2 HID p2 p1 419 Subject Visits 3174 Subject Assessments p2 p1 Duke HID Phase II Study: Image Data Volume 21,038 raw image files per subject 9.0 FBIRN Shared Data Files Number of Files (Millions) 8.5 2.4 GB of raw image data per subject 25 GB to 40 GB of processed image data per subject (depending on hypotheses tested) 8.0 7.5 7.0 6.5 6.0 5.5 5.0 July 05 Aug 05 Sept 05 Oct 05 Nov 05 Dec 05 Jan 06 10 million slices of functional imaging data in Phase II 7 Terabytes of image data for all of the Phase II analyses (conservative estimate of 25 GB/subject) Automated Weekly Data Management XML Based Meta-Data Format The XML-Based Clinical and Experimental Data Exchange (XCEDE) XML schema provides an extensive metadata hierarchy for describing and documenting research and clinical human imaging studies. XCEDE XML-Aware Components Image Format Independence INPUTS DICOM Analyze7.5 add XML PROCESSING STEP GE Pfile add XML add XML XML-Aware Applications (e.g., FIPS, BIRN QA) Format X add XML •Readable by humans •Expandable •More efficient and less prone to errors OUTPUTS FIPS Analysis, QA plots, etc. SPM XCEDE XML Toolbox SPM toolbox to capture the results from activation maps using the XML activation schema The toolbox supports both SPM99 and SPM2 statistical structures The toolbox has been used to capture PET and fMRI analysis results and the associated analysis model specifications. Keator et. al., NeuroInformatics 2006. FSL Image Processing Scripts (FIPS) Front end interface for automated image processing and analysis Personnel Time Savings Open source Without FIPS With FIPS 200 subjects 5 subjects 0 200 400 600 Hours 800 1000 Query Atlas The Query Atlas project provides a platform for the development of scientific understanding of experimental research results in the context of neuroanatomy. Interactive 3D and Web-based knowledge management tool that is coupled to the BIRN federated database and links to other data management systems from neuroscience and other fields. BIRN Tools Download http://www.nbirn.net/downloads/index.shtm