Computation Toolbox
advertisement

Computation Toolbox
Hakki Eres & Graeme Pound
School of Engineering Sciences
University of Southampton, UK
{eres, gep} @soton.ac.uk
© Geodise Project, University of Southampton, 2001-2004.
http://www.geodise.org/
Computation Toolbox
• Access to Globus compute resources from the
Matlab environment
• Proxy certificate management, job submission
and file transfer
• Complex Grid-enabled workflows may be coordinated from Matlab
© Geodise Project, University of Southampton, 2001-2004.
http://www.geodise.org/
Compute Toolbox Functions
Command
Function
Command
Function
gd_certinfo
Returns information about the user's certificate
gd_proxyinfo
Returns information about the user's proxy certificate
gd_chmod
Changes file permissions of a file on a Globus resource
gd_proxyquery
Queries whether a valid proxy certificate exists
gd_condorsubmit
Submits a job through a Globus resource to a Condor
pool
gd_putfile
Puts a remote file using GridFtp
Creates a Globus proxy certificate for the user's
credentials
gd_rmdir
Deletes a remote directory using GridFtp
Destroys the local copy of the user's Globus proxy
certificate
gd_rmfile
Deletes a remote file using GridFtp
Tests the existence of files and directories on a Globus
resource
gd_serverMetrics
Performs a number of tests to Globus resources
gd_testAuthentication
Tests the authentication to a Globus resource
gd_testFileTransfer
Tests file transfer to a Globus resource
gd_testJobSubmission
Tests the job submission to a Globus resource
gd_timeAuthentication
Times authentication to a Globus resource
gd_createproxy
gd_destroyproxy
gd_fileExists
gd_getfile
gd_jobkill
gd_jobpoll
gd_jobstatus
gd_jobsubmit
Retrieves a remote file using GridFtp
Kills a Globus GRAM specified by job handle
Queries the status of a Globus GRAM job until complete
Gets the status of a Globus GRAM job
© Geodise Project, University of Southampton, 2001-2004.
http://www.geodise.org/
gd_timeFileTransfer
Times file transfer to a Globus resource
Submits a compute job to a Globus GRAM job manager
SESC Computation Manager
Graeme Pound, Gang Xue
& Matthew Fairman
{gep, g.xue, m.j.fairman} @soton.ac.uk
© Geodise Project, University of Southampton, 2001-2004.
http://www.geodise.org/
SESC Computation Manager
•
•
•
•
Research by Matthew Fairman and Gang Xue
Web Service interface to Condor
Firewall-friendly
WS-Security provides authentication and
message integrity
• Matlab client
• Deployed over the ISS and SESC Condor pools
© Geodise Project, University of Southampton, 2001-2004.
http://www.geodise.org/
SESC Computation Client
• Geodise Identity Manager
– createIDmanager - Initialises an IDmanager to authenticate with Web
Services
– queryIDmanager - Queries credentials contained within IDmanager
• SESC Computation Client
–
–
–
–
–
–
grid_submit - submits a job to the SESC Computation Manager
grid_platform - creates a job requirements structure
grid_status - Retrieves the status of a job
grid_poll - Polls the status of a job
grid_results - Retrieves the results of a job
sesc_configuration – Utility function to specify configuration file
© Geodise Project, University of Southampton, 2001-2004.
http://www.geodise.org/
Data Management in
Engineering Applications
Jasmin Wason , Zhuoan Jiao, and Simon Cox
School of Engineering Sciences
University of Southampton, UK
{j.l.wason, z.jiao, sjc} @soton.ac.uk
© Geodise Project, University of Southampton, 2001-2004.
http://www.geodise.org/
Challenges
•
Large quantities of data generated at different
locations with different characteristics.
•
Require efficient data management, but low learning
curve for engineers.
•
Integrate data management tools into engineering
application development environments.
•
Secure and reliable data sharing and reuse.
© Geodise Project, University of Southampton, 2001-2004.
http://www.geodise.org/
Geodise Database Toolbox Overview
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Store data with additional descriptive metadata.
Familiar interface for engineers (Matlab).
Central and local databases (shared vs. personal).
Certificate-based authentication and authorisation.
Secure Web service access over SSL.
Query over metadata to easily locate required data.
Data retrieval based on ID rather than on location.
Archive clean-up, controlled deletions of data.
Java API for other components, e.g. Workflow Tool.
© Geodise Project, University of Southampton, 2001-2004.
http://www.geodise.org/
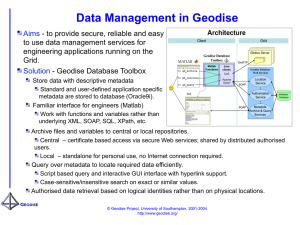
Architecture
Client
Grid
Geodise Database
Toolbox
Matlab
Functions
Globus Server
GridFTP
Java
clients
CoG
Geodise Database
Web Services
Apache
SOAP
Location
Service
SOAP
Authorisation
Service
GUI
SOAP
Metadata
Archive & Query
Services
© Geodise Project, University of Southampton, 2001-2004.
http://www.geodise.org/
Metadata
Database
Secure Archiving
•
•
•
Store data with additional descriptive information.
– Data sources: files, variables, datagroups, workflows.
– Standard metadata (e.g. name, size, format, archive date…)
– User-defined application specific metadata.
Transactional data archiving.
– Store files via GridFTP to Globus server.
– Store the metadata as relational and XML data in Oracle 9i.
Certificate-based authentication and authorisation.
– Requests signed with proxy certificate and sent over SSL.
– Certificate subject mapped to user ID for authorisation.
© Geodise Project, University of Southampton, 2001-2004.
http://www.geodise.org/
Flexible Data Management for Engineers
•
•
Familiar interface for engineers.
– Wrap database services as Matlab functions and
metadata as Matlab structures.
– XML Toolbox (developed by Geodise and GEM
projects): converts Matlab variables and structures
to/from XML behind the scenes.
Central and local archives provide more flexibility.
– Central: secure Web service access; central
administration.
– Local: no web access needed, personal edition.
– Switch between local and central archive by setting
parameter in configuration file.
© Geodise Project, University of Southampton, 2001-2004.
http://www.geodise.org/
Query and Retrieve
•
•
•
Query over metadata to locate required data.
– Simple query syntax for ease of use in scripts.
– GUI with hyperlink for data navigation and download.
– Case-sensitive/insensitive and similarity search.
– Wildcard support in search condition descriptions.
Retrieve data based on logical data identities.
– Data identities can be obtained from querying
metadata.
Only authorised users can query/retrieve data.
– Access granted to others by data owner.
© Geodise Project, University of Southampton, 2001-2004.
http://www.geodise.org/
OptionsMatlab
Design Search and Optimisation Package
Graeme Pound
School of Engineering Sciences
University of Southampton, UK
gep@soton.ac.uk
© Geodise Project, University of Southampton, 2001-2004.
http://www.geodise.org/
OptionsMatlab
• Matlab interface to
Options design search
package
• Objective and constraint
functions defined as
Matlab functions
• Access to Geodise
functions allows Gridenabled optimisation
Matlab environment
OptionsMatlab.MEX
optjob
optfun
optcon
optjob.m
optfun.m
© Geodise Project, University of Southampton, 2001-2004.
http://www.geodise.org/
optcon.m
OptionsMatlab Plots
Objective function
surfaces
Optimisation trace
© Geodise Project, University of Southampton, 2001-2004.
http://www.geodise.org/
Multi-Dimensional Plots
4D objective function,
constraints & data points
Interactive tiles
© Geodise Project, University of Southampton, 2001-2004.
http://www.geodise.org/
Accessing Condor via Globus 2.4
Hakki Eres
School of Engineering Sciences
University of Southampton, UK
eres@soton.ac.uk
© Geodise Project, University of Southampton, 2001-2004.
http://www.geodise.org/
Accessing Condor Through Globus Servers
Firewall
CEDC LAN
ISS LAN
Condor Pool
Client with Geodise
(utp-25)
Globus
Globus Server
Condor Node
(blue07.iridis)
Central Manager
(blue06.iridis)
Dedicated Node
(isstrain-01)
Dedicated Node
(isstrain-02)
© Geodise Project, University of Southampton, 2001-2004.
http://www.geodise.org/
Dedicated Node
(isstrain-03)
gd_condorsubmit Command
Submits a job through a Globus resource to a Condor pool
• Syntax
handle = gd_condorsubmit(classAD_Structure, RSL_Structure,…
resourceManagerContact,
filesystemType)
• Inputs
– classAD_Structure: A structure describing Condor submit description
file
– RSL_Structure: A structure describing Globus resource specification
– resourceManagerContact: A string describing the Grid resource
– filesystemType: 'NFS' for a shared filesystem. (Optional)
• Output:
– handle: A string showing the handle for a successfully submitted job.
© Geodise Project, University of Southampton, 2001-2004.
http://www.geodise.org/
Using gd_condorsubmit
1. Define your
ClassAD as a
Matlab
structure.
2. Define your
RSL as a
Matlab
structure.
3. Make a job
submission to
the Globus
server.
© Geodise Project, University of Southampton, 2001-2004.
http://www.geodise.org/
Grid Support Functions and Tools
Hakki Eres
School of Engineering Sciences
University of Southampton, UK
eres@soton.ac.uk
© Geodise Project, University of Southampton, 2001-2004.
http://www.geodise.org/
Grid Support Functions and Tools
• Support functions and tools allow end users to
– Verify that the specific Grid resources they require are available
by checking basic functionality such as authentication, file
transfer, and job submission,
– Check that their applications and files exist on the Grid resource,
– Make sure that user security settings are configured correctly.
• Matlab functions are available.
• They are also integrated to the workflow editor.
© Geodise Project, University of Southampton, 2001-2004.
http://www.geodise.org/
Available Matlab Functions
Command
Function
gd_fileExists
Tests the existence of files and directories on a Globus resource
gd_testAuthentication
Tests the authentication to a Globus resource
gd_testFileTransfer
Tests file transfer to a Globus resource
gd_testJobSubmission
Tests the job submission to a Globus resource
gd_timeAuthentication
Times authentication to a Globus resource
gd_timeFileTransfer
Times file transfer to a Globus resource
gd_timeJobSubmission
Times job submission to a Globus resource
© Geodise Project, University of Southampton, 2001-2004.
http://www.geodise.org/
Matlab Environment
© Geodise Project, University of Southampton, 2001-2004.
http://www.geodise.org/
Example Matlab Scripts
…
if ~testAuthentication('escience-dept2')
error('You are not authorized to use escience-dept2');
end
…
if ~fileExists('escience-dept2','/usr/local/bin/gambit')
error('/usr/local/bin/gambit does not exist on escience-dept2');
end
…
server(1).name='escience-dept2';
server(2).name=‘artemis';
for i=1:size(server,2)
if gd_testJobSubmission(server(i).name,'/home/eres')
server(i).status='on'
else
server(i).status='off'
end
end
…
© Geodise Project, University of Southampton, 2001-2004.
http://www.geodise.org/
Workflow Editor
•
•
•
The resources are loaded from an initial XML configuration file which can be modified by either
manually editing the resource configuration file, or directly within the Grid tool.
The tool menu provides a full set of functions to verify authentication, job submission, and file
transfer operations from the client to different Grid resources.
A Grid resource is specified by a host name, executable directory,and work directory. The
resource checking process measures the time required for authenticating the user on the remote
Grid resource, running a test job, and transferring a file to (or from) it. Additionally, it verifies that
the executable and work directory exist on the Grid resource.
© Geodise Project, University of Southampton, 2001-2004.
http://www.geodise.org/
Checking All Resources
© Geodise Project, University of Southampton, 2001-2004.
http://www.geodise.org/
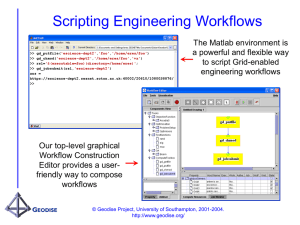
Geodise Workflow Construction
Environment
Fenglian Xu and Hakki Eres
School of Engineering Sciences
University of Southampton, UK
{f.xu, eres} @soton.ac.uk
© Geodise Project, University of Southampton, 2001-2004.
http://www.geodise.org/
WCE Architecture
Workflow Construction Environment
Globus
Web
Services
Knowledge
Matlab
Geodise
Compute Toolbox Workflow Components
library
library
Legacy Code
© Geodise Project, University of Southampton, 2001-2004.
http://www.geodise.org/
Grid Enabled Configure Model
Grid Enabled Tool
Globus Client
Java CoG
RSL
Matlab Server
Globus Client and Server
Java CoG
Matlab with Geodise Toolkits
RSL
RSL
RSL
Grid Resource
Grid Resource
Grid Resource
Globus Server
Globus Server
Globus Server
Executable Code
Executable Code
Executable Code
© Geodise Project, University of Southampton, 2001-2004.
http://www.geodise.org/
Geodise Workflow Construct Environment (WCE)
Workflow work space
--Mapping data flows
Components
tree
-- Load from an
xml file/instance
store
Knowledge support--
Provide advisor information for
next/previous possible
candidates
Resources management--enable to
deploy workflows to be run on the Grids
© Geodise Project, University of Southampton, 2001-2004.
http://www.geodise.org/
Features -- I
• Compose workflows by the following nodes:
•
•
•
•
•
task nodes – Matlab functions
condition nodes – if else type
loop nodes – for, while
join nodes – marks the end of condition nodes
connection nodes – specify the sequential of the nodes in a
workflow and data flows between two non-connection nodes
• Configure workflows by configuring each node
property sheet ( see Fig.1 )
© Geodise Project, University of Southampton, 2001-2004.
http://www.geodise.org/
Fig.1 Connection Property Sheet
© Geodise Project, University of Southampton, 2001-2004.
http://www.geodise.org/
Features -- II
• Validate a workflow– to a particular Matlab server under
the specified working directory
• Check Grid resources
• Submit a workflow to the Matlab server under four
configuration models
• Visualise results
• enable to visualise the images generated by one of the workflow
components in Matlab
• Integration with DB
• enable to archive a workflow with metadata to the DB
• enable to retrieve a particular workflow from the DB via providing a
query string such as comment, file name etc.
© Geodise Project, University of Southampton, 2001-2004.
http://www.geodise.org/
Summary
• The GUI tool enables the user to construct a
workflow once and use it many times
• The users can be benefit from using the existing
components without any Matlab knowledge
• The users can also be benefit from sharing both
compute and software resources
© Geodise Project, University of Southampton, 2001-2004.
http://www.geodise.org/
Future Work
• Monitor and Steering a workflow
• runtime visual feedback
• runtime results monitor
• enable to get a decoupled steering information during runtime
• Integrate with knowledge support technology
• workflow components loaded from a trip instance store
© Geodise Project, University of Southampton, 2001-2004.
http://www.geodise.org/
Computational Aeroacoustics for
Aeroengine Inlets
Mike Giles, Mihai Duta
& Sergo Campobasso
Oxford University Computing Laboratory
giles@comlab.ox.ac.uk
© Geodise Project, University of Southampton, 2001-2004.
http://www.geodise.org/
Rolls-Royce Trent 700
© Geodise Project, University of Southampton, 2001-2004.
http://www.geodise.org/
New ARCADIA aeroacoustics code
• potential flow modelling for aeroengine inlets and
bypass ducts, giving reduced cost compared to
Euler/Navier-Stokes methods
• novel spectral decomposition for non-axisymmetric
inlets, again reducing the number of unknowns
• very effective preconditioning with axisymmetric
operator leads to rapid iterative solution
• novel asymptotic analysis gives good accuracy for farfield radiation integrals at even lower cost
– excellent for design optimisation
© Geodise Project, University of Southampton, 2001-2004.
http://www.geodise.org/
Axisymmetric Geometry
Engine bypass duct validation against ACTRAN code, without
and with acoustic liner
© Geodise Project, University of Southampton, 2001-2004.
http://www.geodise.org/
Non-axisymmetric Engine Nacelle
© Geodise Project, University of Southampton, 2001-2004.
http://www.geodise.org/
Radiated Noise Functional
Change in a downward-biased weighted integral of radiated
noise – relatively linear with scarf angle
© Geodise Project, University of Southampton, 2001-2004.
http://www.geodise.org/
Nacelle Optimisation
Wenbin Song
School of Engineering Sciences
University of Southampton, UK
w.song@soton.ac.uk
© Geodise Project, University of Southampton, 2001-2004.
http://www.geodise.org/
Optimisation Services
•
What are Optimisation Services
– State and search history for each service instance
Multiple service instances supported on the same server
– Basic interfaces to answer the following questions
Return the initial point (gradient-based methods) or first generation (GA)
Assign objective functions/constraints
Return the next point or next generation
– Possibly advanced features
Security
Accounting and charging
•
Conventional Optimisation packages use callbacks
– Restrictions on code choices for computing objective/constraints
– Firewall issue
•
Optimisation as Services
– Elimination of callbacks
– Use of SOAP over HTTP, no restrictions on user’s choice of code for computing
objective/constraints
– Firewall friendly
– Additional schedulers can be readily plugged in
– Client tools required
– Complicate the control flow
© Geodise Project, University of Southampton, 2001-2004.
http://www.geodise.org/
Comparison of Optimisation Workflows
© Geodise Project, University of Southampton, 2001-2004.
http://www.geodise.org/
Use of Geodise Toolkits
• Geodise Compute Toolkit
– Submit CAD jobs to ProEngineer server via Globus-Condor
(gd_condorsubmit)
– Submit analysis jobs to computing servers (Globus)
• Geodise Database Toolkit
– Archive Matlab vars/structs into Database
– Archive files with Metadata
– Grouping model data logically (CAD models, Gambit journal files, Fluent
journal files)
– Archive results file (STEP file, Gambit mesh file, Fluent case/data file)
using concept Project/Tasks/Runs/DesignPoints
• OptionsMatlab – Optimisation package within Matlab
© Geodise Project, University of Southampton, 2001-2004.
http://www.geodise.org/
A Hierarchy data structure – a logical view
• Project is the top-level concept, for example, a Nacelle study
• Each project contains a number of tasks, which is related to a
particular design (a ProEngineer CAD model)
• Each task contains a number of runs, for example, a DoE run on a
particular set of geometry parameters
• Each run represents a particular operation conditions, and it consists
of number of design points
• Each design point contains a geometry (STEP/IGES file), a mesh
file, and a number of Fluent solutions
© Geodise Project, University of Southampton, 2001-2004.
http://www.geodise.org/
Application Examples
Two dimensional Airfoil Design Two Parameter Nacelle Shape Design
© Geodise Project, University of Southampton, 2001-2004.
http://www.geodise.org/
Globus / Condor pool
ABAQUS - OPTIMIZATION
Ivan Voutchkov
CEDC, School of Engineering Sciences
Mechanical Engineering Department
University of Southampton
© Geodise Project, University of Southampton, 2001-2004.
http://www.geodise.org/
Structural optimization
Aim: Reduce structure’s
Weight (Volume)
Constraint: Maximum
stress and displacement
values should not exceed
specifications.
Method: Find appropriate
thickness and geometry
for the inner, outer rings
and the supporting spokes.
© Geodise Project, University of Southampton, 2001-2004.
http://www.geodise.org/
Twelve variables
OUTRING
SPOKES1
SPOKES2
SPOKES0
SPOKES3
INRRING
INRSMALL
SPOKES4
INRSUP
SPOKES5
SPOKES6
© Geodise Project, University of Southampton, 2001-2004.
http://www.geodise.org/
Initialization
Sets optimization variables
objectives and constraints
Options
Matlab
Performs optimization in
MATLAB environment.
Objective function is an
ABAQUS FE model
Archive
results
Finalizing and saving
results
© Geodise Project, University of Southampton, 2001-2004.
http://www.geodise.org/
Preparing
next run
Evaluate
Objective function
Options
Matlab
Archive and finish
YES
Optimum reached?
© Geodise Project, University of Southampton, 2001-2004.
http://www.geodise.org/
NO
>> prepare_condor_job
% --------------------- Submitting job to the local condor pool
classAD_Solaris.requirements = ‘(Arch == "SUN4u") && (Memory > 800) && (HasAbaqus)';
classAD_Solaris.executable = 'abaqus_executable';
classAD_Solaris.output = 'aba.output';
classAD_Solaris.error = 'aba.error';
classAD_Solaris.log = 'aba.log';
classAD_Solaris.arguments = ‘myabaqusjob.inp’;
classAD_Solaris.universe = 'VANILLA';
rsl.executable= '/usr/local/condor/bin/condor_submit';
rsl.arguments = 'abam.sub';
rsl.directory = rdirectory;
rsl.stdout = 'abam.stdout';
rsl.stderr = 'abam.stderr';
Evaluate
Objective function
hostname = ‘utp-51.mech.soton.ac.uk’
% Local machine is utp-10.mech.soton.ac.uk’
% utp-51 is a GLOBUS server AND a dedicated node in a CONDOR POOL
>> handle_Solaris = gd_condorsubmit(classAD_Solaris, rsl, hostname, 'NFS')
handle_Solaris =
https://utp-51.mech.soton.ac.uk:40001/27687/1080038291/
© Geodise Project, University of Southampton, 2001-2004.
http://www.geodise.org/
Evaluate
Objective function
>> !condor_q
-- Submitter: utp-10.mech.soton.ac.uk : <192.168.96.33:33752> : utp-10.mech.soton.ac.uk
ID
OWNER
SUBMITTED
RUN_TIME ST PRI SIZE CMD
273.0
iiv
3/23 10:52
0+00:00:00 I 0
0.0 abaqus_exe myabaq
>> !condor_status
vm1@utp-66.me
vm2@utp-66.me
vm1@paris2.me
vm2@paris2.me
vm1@paris3.me
vm2@paris3.me
vm2@UTP-03
LINUX
LINUX
SOLARIS28
SOLARIS28
SOLARIS29
SOLARIS29
WINNT52
INTEL
INTEL
SUN4u
SUN4u
SUN4u
SUN4u
INTEL
Unclaimed
Unclaimed
Unclaimed
Unclaimed
Unclaimed
Unclaimed
Unclaimed
Idle
Idle
Idle
Idle
Idle
Idle
Idle
0.000
1.000
0.540
0.000
6.980
1.000
0.002
1007
1007
512
512
3072
3072
1023
0+03:34:22
0+03:34:32
0+00:47:23
0+00:47:08
0+00:17:10
0+02:18:53
0+02:50:57
Job is executed by vm1@paris3
>> % Check if job is finished ?
>> ls -l myabaqusjob.odb
ans =
-rw-r--r-- 1 iiv
ses
13107732 Mar 23 13:02 myabaqusjob.odb
>> % Database file exists and is completed, i.e. Job is finished
>> % Read results, delete temporary files and return to optimization cycle
© Geodise Project, University of Southampton, 2001-2004.
http://www.geodise.org/
Options
Matlab
Preparing
next run
Evaluate
Objective function
Archive and finish
YES
Optimum reached?
© Geodise Project, University of Southampton, 2001-2004.
http://www.geodise.org/
NO
Initialization
Sets optimization variables
objectives and constraints
Options
Matlab
Performs optimization in
MATLAB environment.
Objective function is an
ABAQUS FE model
Archive
results
Finalizing and saving
results
© Geodise Project, University of Southampton, 2001-2004.
http://www.geodise.org/
Results
Optimized structure is
46% lighter.
© Geodise Project, University of Southampton, 2001-2004.
http://www.geodise.org/
Summary and Future Work
• More test problems for ABAQUS
• Running ProEngineer, SC03 and other
commercial packages using the Geodise
toolbox.
• Continue testing the toolbox and all its
components and suggesting improvements.
© Geodise Project, University of Southampton, 2001-2004.
http://www.geodise.org/
Exploiting Semantics in Geodise
Liming Chen, Feng Tao,
Colin Puleston, Carole Goble
& Nigel Shadbolt
Manchester & Southampton Universities
{lc, ft} @ecs.soton.ac.uk,
{colin.puleston, carole} @ cs.man.ac.uk,
nrs@ecs.soton.ac.uk
© Geodise Project, University of Southampton, 2001-2004.
http://www.geodise.org/
Knowledge and Application
Integration Architecture
Workflow Construction Environment
Semantic driven
Workflow Advisor
Workflow Wizard
Decision-Tree
Function/Workflow Manager
Archive Manager
Database
Archiving
Semantic
Archiving
Function
Archive
Semantic
Annotation
WorkflowTemplate
Archive
Semantic
Queries
Ontology
Manager
Workflow
Archive
Geodise Ontologies
© Geodise Project, University of Southampton, 2001-2004.
http://www.geodise.org/
Semantics-based Resource
Management Life Cycle
Generation of semantic
enriched content
Function Annotator
(FIW)
Function Ontology
Semantic Applications
(Workflow
advisor integrated with Text
mode and GUI mode workflow composer)
Query interface
Advisor APIs
Function/workflow
Semantic Repository
Function semantic annotations
© Geodise Project, University of Southampton, 2001-2004.
http://www.geodise.org/
Archive workflows
via GD APIs
Geodise Functions
Load functions
and workflows
via GD APIs
Consumption/Reuse
Function Characterisation and Ontology
Function Characterisation:
Knowledge acquisition
Function classification and
categorisation
Interface analysis and
abstraction
Terminology development
Function Ontology:
Ontological conceptualisation
Concept hierarchy construction
Relation definition
Domain experts evaluation and
validation
© Geodise Project, University of Southampton, 2001-2004.
http://www.geodise.org/
Function Annotation
Add metadata and semantics to functions
Use OWL as representation formalisms
Adopt instance store technology
Support DL-based complex reasoning
Function
Ontologies
Geodise
Functions
Function Annotator
Instance Store
Ontology-driven forms
generation
Ontology-assisted concept
selection and definition
Automatic information
extraction
Multi-level descriptions
© Geodise Project, University of Southampton, 2001-2004.
http://www.geodise.org/
Reusing Semantic Annotations in
Knowledge Advising
Purpose
Advise on workflow assembly (Vertical Advice) and component
configuration (Horizontal Advice)
Mechanism
Semantic matching for contextual advice (workflow assembly, VA)
Decomposing semantic annotations (component configuration, HA)
Granularity on component configuration
Low level at semantic level
What need to be filled out ( for a valid configuration)
High level at knowledge level
Filled out with what? Value suggestion (for a better configuration)
Integration
GUI mode Workflow Composer Environment (WCE)
Text mode workflow editor (Domain Script Editor)
© Geodise Project, University of Southampton, 2001-2004.
http://www.geodise.org/
Consuming Semantic MetaData
(knowledge advisor integrated with the WCE)
Context sensitive
advice
Advice on
workflow assembly
via advisor
Service matching
for contextual
components and
comments
© Geodise Project, University of Southampton, 2001-2004.
http://www.geodise.org/
Consuming Semantic MetaData
(knowledge advisor integrated with the domain script editor)
Horizontal advice on component configuration
Current deployed
component
Vertical advice on
what can be done
before and next
© Geodise
Auto-completion from instances
Project, University of Southampton, 2001-2004.
http://www.geodise.org/
Ontological type
Ontology-Driven Query
Consist of a set
expressions…
.. each specifying the
required value for a
particular field
Fields may be…
single-valued
multi-valued
Values may be…
ontological concepts
simple data-values
© Geodise Project, University of Southampton, 2001-2004.
http://www.geodise.org/