IMT and IMS Technologies In Developing Countries IMT2000 Systems and beyond
advertisement
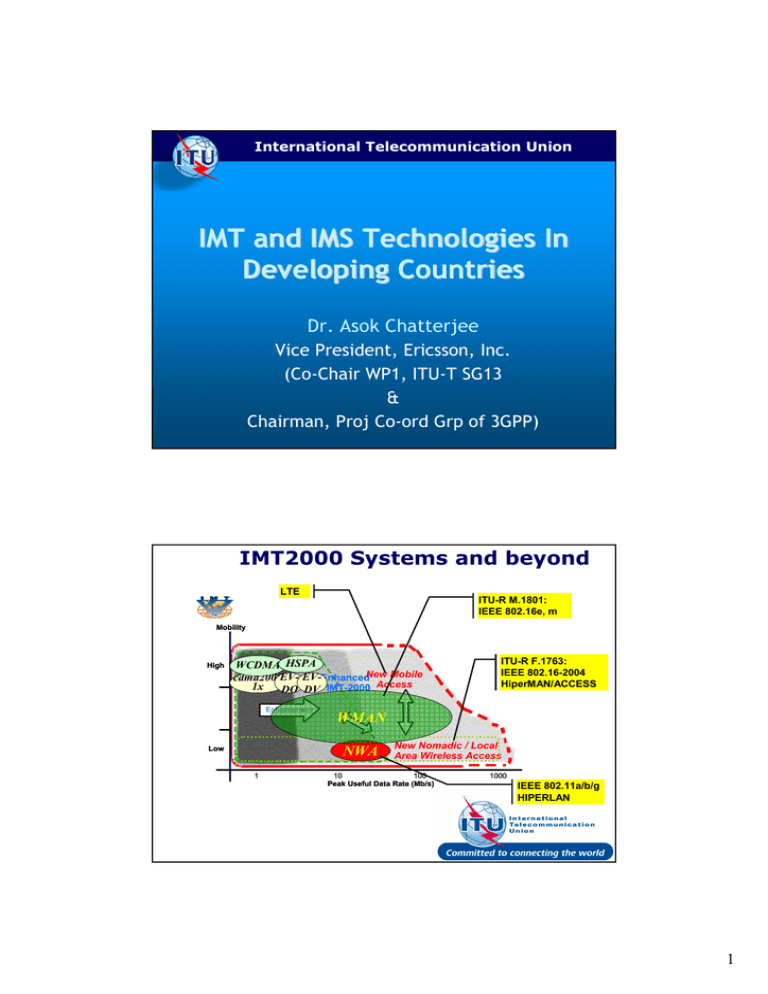
International Telecommunication Union IMT and IMS Technologies In Developing Countries Dr. Asok Chatterjee Vice President, Ericsson, Inc. (Co-Chair WP1, ITU-T SG13 & Chairman, Proj Co-ord Grp of 3GPP) IMT2000 Systems and beyond LTE ITU-R M.1801: IEEE 802.16e, m Mobility High WCDMA HSPA EV-EnhancedNew Mobile cdma2000EV-Enhanced IMT-2000 1x DO IMT-2000 DV IMT-2000 Access Enhancement t Enhancemen Low WMAN NWA 1 ITU-R F.1763: IEEE 802.16-2004 HiperMAN/ACCESS New Nomadic / Local Area Wireless Access 10 100 Peak Useful Data Rate (Mb/s) 1000 IEEE 802.11a/b/g HIPERLAN 2 1 IMT-2000 Standards: 3G Partnerships IMT-2000 GSM- based UMTS + IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS) ITU-T SG 13 ITU-R WP 5D ARIB /TTC ATIS TTA TIA IS-41 + CDMA2000 + Multimedia Domain (MMD) 3 3 3GPPs and ITU-R WP 5D Specifications TSG-C SDO standards Approved TSG-RAN Updated Transposed Submitted by SDOs to ITU-R etc Rec. M.1457.n (next version: n = 9) • High level description of air interfaces • References SDOs' standards (ETSI, ATIS, ARIB, TTA, CCSA, etc.) 4 4 2 ITU-T Gives Mobile Systems Prominence o WTSA-2000 created the Special Study Group (SSG) on “IMT-2000 and systems beyond” o Based on the accomplishments of the SSG and the continuing growth of mobile networks, WTSA-2004 upgraded SSG to a regular SG: SG 19 “Mobile telecommunication networks” o Considering the closed cooperation on mobile systems and mobility by co-located SG meetings of SG13 and SG19 for the whole study period 2005-2008 WTSA-2008 merged SG13 and SG19. 5 IMT-2000 in ITU-T o Users will only get “service” if there are both: • Radio access interfaces • A suitable core network infrastructure o Hence need for ITU-R and ITU-T to continue to work closely together to ensure a “complete package” • It’s not only about radio access, “wired” users expect broadband access, too! 6 3 IMT-2000: 3GPPs & ITU-T SG13 Specifications TSG-N/P TSG-CN SDO standards Approved Updated Transposed Submitted by SDOs to ITU-T etc. Rec Q.1741.n (next n=5), Q.1742.m (next, m=7) • 3G road map • Refers out to the SDOs' standards (ETSI, ATIS, TTA, TTC, CCSA, etc.) 7 Q.174x.y Series Recommendations o “IMT-2000 references to release to GSM evolved UMTS core network with UTRAN access network Release <#>” • • • • • • o Q.1741.1 Q.1741.2 Q.1741.3 Q.1741.4 Q.1741.5 Q.1741.6 Release Release Release Release Release Release 1999 4 5 6 7 8 (in preparation 10/09) “IMT-2000 references to ANSI-41 evolved core network with cdma2000 access network (as of <date>)” • • • • • • • Q.1742.1 Q.1742.2 Q.1742.3 Q.1742.4 Q.1742.5 Q.1742.6 Q.1742.7 as as as as as as as of of of of of of of 17 Jul 2001 11 Jul 2002 30 Jun 2003 30 Jun 2004 31 Dec 2005 31 Dec 2006 30 Jun 2008 8 8 4 Q.10/13 - Identification of evolving IMT-2000 systems and beyond o o Determination of architectures and detailed specifications produced by recognised SDOs which make up the evolving IMT systems and beyond Facilitating the recognition of those systems and their adoption by the broader ITU community 9 Mobile networks as integral part of NGN access Yesterday Single service networks Today and Tomorrow Multiservice networks/client server NGN => Key issue mobility 10 5 IP Multimedia Subsystems (IMS) o The world of telecommunications is increasingly going packet-based digital, based on Internet Protocol (IP) o IMS is an architectural framework for delivering IP-based multimedia services o IMS does not standardize applications, but uses IETF protocols (e.g. SIP) to aid access of services from wireless and wireline terminals (separates applications from modes of access) o It can be viewed as a tool to get to FMC 11 Development of IMS o IMS was originally designed by 3GPP for mobile networks o It is now enjoying support from various sectors of telecommunications industry o Some core aspects of IMS are now being developed in close cooperation between 3GPP, 3GPP2, wireline, and cable industries 12 6 Resolution 44 - Bridging the standardization gap between developing and developed countries Motivation o Many mobile subscribers are in developing countries o Mobile networks are much more than radio access, and require sound network infrastructure to connect to o Mobility has become such an important issue that it needs to be studied carefully o Issues around IMT and IMS need to be well understood, especially in developing countries, for the desired level of success in deployment and implementation o There is a need for developing countries to have a greater say in the ongoing evolution of NGN networks Hence Question 15/13 (Applying IMS and IMT in developing country mobile telecom networks ) was adopted to address the above issues. 13 Q15/13 Expected outcomes o Document summarizing the findings of a gap analysis on the current status and trends of IMS and IMT in customer user needs, technology, market, and standardization requirements, if any, from the view-point of telecom networks in developing countries o Collection of scenarios in terms of services and deployments for applying IMS and IMT in the mobile telecom networks in developing counties o Requirements in terms of services and deployments for applying IMS and IMT in the mobile telecom networks in developing countries 14 7 Collaboration with External Industry Organizations o The real world experiences are available only from the organizations that represent the industry o Contacts established with GSM Association (GSMA), CDMA Development Group (CDG), WiMAX Forum o Issues being discussed • • • • • User requirements Technical requirements Roadmap/Migration Interoperability scenarios Operations/Product support 15 Collaboration with ITU-D o ITU-D has always been in the forefront of supporting developing countries for their future telecommunications needs o Both ITU-R and ITU-T coordinate with ITUD regarding deployment of IMT and IMS systems in developing countries o Between the three sectors of ITU, full support is available to the global community. 16 8 To learn more… For more information please visit the web site http://www.itu.int and SG13 web page in particular http://www.itu.int/ITUT/studygroups/com13/index.asp or contact asok.chatterjee@ericsson.com 17 Thank you for your attention! 18 9

