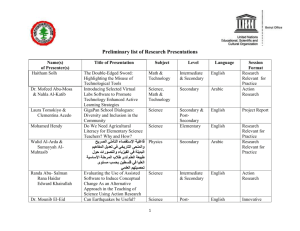
SSCs 2015‐2016 Arabic Syllabus C Prerequisite for entry
advertisement

UCL CENTRE FOR LANGUAGES & INTERNATIONAL EDUCATION SSCs 2015‐2016 Arabic Syllabus C Prerequisite for entry Successful completion of Arabic Syllabus B at the UCL CLIE or a similar course and have experience of dealing with relevant authentic material. Course duration Year 1 students: double‐block (16 x 3‐hour classes. Block 1: 8 x 3‐hour classes; Block 2: workshops and tutorials related to Project). Year 2 students: single block (8 x 3‐hour classes). Self‐Study 40 hours in total. Course codes LCAM6003. Aims and Objectives The main aim of the course is to enable students with a good basic knowledge of Arabic to develop the four skills further. Students should then be able to converse reasonably fluently with native speakers and discuss personal, social and current issues using appropriate structure. Cultural awareness will be further developed. Language learning skills, including autonomous learning and how to approach authentic materials will be enhanced. Some transferable skills will also be covered. Medical related issues/vocabulary will also be covered. Functions Relating past events; Hobbies, interests and daily life activities further description (giving reasons and comments); Next holiday or visit (opinions and expectations); Describing places and things: further details; Parties and occasions; Plans and ambitions; Stories and films (comments and basic criticism); Culture and society: Arabic and other cultures; Media and culture; Arabic Dialects (Introduction); Accidents & Emergency; Public Health. Course Content Main topics/themes to be covered Talking about something that happened in the past; Talking about hobbies interests or daily life activities; Talking about next holiday; A city or a place you would like to live in (reasons and opinions); Your future ambitions (to be a doctor); Story or film: opinion and comment; News items and some media articles; Prevention is better than cure; Common disease in the Middle East ( diabetes and blood pressure); Arabic civilisation and its role in medicine. Linguistic Structures Grammar Past & Present Tenses Forms (5‐10); Relative nouns; Broken plural: other forms; Imperative verb forms 1‐4; Verbal nouns; Active and passive: forms 1‐5; Nouns ending cases: nominative, accusative and genitive; Verb ending cases: nominative, accusative and jussive; Basic dialects grammar and pronunciation. Learning Resources There will be no specific textbook, however various materials from different books and sources will be distributed to all students. Additional Material Al‐Kitaab fi Ta'allum Al‐Arabiyyeh, M. Al‐Batal and others (Georgetown University Press) 1995 – ISBN: 9781589011045 Standard Arabic, An Elementary‐ intermediate course, Eckehard Schulz and others (Cambridge University Press) – ISBN: 9780521774659 Elementary Modern Standard Arabic: Peter F. Abboud, & Ernest N. McCarus (Cambridge University Press) 2004 – ISBN: 9780521272957 Arabic ‐ English / English – Arabic dictionary, M. Baalbaki, R. Baalbaki & R. Baalbaki (Dar El Ilm Limalayin) – ISBN: 9789953631097 HANS WEHR, A Dictionary of Modern Written Arabic, J. Milton Cowan (Spoken Language Service. Inc.) – ISBN: 9780879500030 www.BBC.co.uk/arabic www.aljazeera.net A selection of authentic material will also be used. In addition there is a wide range of language learning materials available for self‐study in the Self‐Access Centre.