Course Units 2015‐2016 Arabic Syllabus B Prerequisite for entry
advertisement

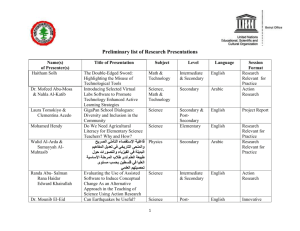
UCL CENTRE FOR LANGUAGES & INTERNATIONAL EDUCATION Course Units 2015‐2016 Arabic Syllabus B Prerequisite for entry Successful completion of Arabic Syllabus A at the UCL CLIE or a similar course and have limited experience of dealing with authentic material Course duration 20 x 2‐hour classes. Self‐Study 80 hours in total. Course codes LCAR6002, LCARG002, LCARM002, LCAR6012, LCARM012 (together with Arabic syllabus A), LCAR6023, LCARG023, LCARM023 (together with Arabic syllabus C). Aims and Objectives The main aim of the course is to give students an opportunity to revise their survival skills and acquire more sophisticated ways of dealing with practical matters. This includes revision and consolidation of vocabulary, grammar, morphology, syntax and phonetics. Students should be able to communicate in and understand Arabic on practical every day matters related to aspects of Arabic culture. Cultural awareness will be developed. Language learning skills, including autonomous learning and how to approach authentic materials will be enhanced. Some transferable skills will also be covered. Functions Talking about daily life routine in further details (using new verbs); Things you like or prefer and you do not like; Giving basic reasons and making some comments; Describing and comparing (people, places and other things); Travelling and tourism: booking and reserving flights and rooms at hotels; Talking about future plan (studying, jobs and holidays); Expressing opinions regarding people, things and places; Writing a CV; Months of the year (Arabic and non‐Arabic ones). Course Content Main topics/themes to be covered Hobbies, interests and daily activities; Shopping and bargaining at shopping centres; At a restaurant: reserving making orders and comments; A visit to a doctor; body parts and some feelings, expressions and phrases; Applying for a job and an interviews; A plan for future (studying, working, living or travelling); Comparison between two people, places or things. Linguistic Structures Grammar Sentence Structure; Future tense; further details and more verbs; Verbal Nouns; Verb Tenses: forms and patterns (1‐4); Broken plural : forms 1‐5; Comparison and superlative forms; Numbers: 11‐1000 (General introduction). Learning Resources There will be no specific textbook, however various materials from different books and sources will be distributed to all students. Additional Material Mastering Arabic (Part: 1‐2), Jane Wighwick and Mahmood Jaafar (Macmillan), New Edition ‐ ISBN: 9780230013100 Al‐Kitaab fi Ta'llum Al‐Arabiyya, M. Al‐Batal and others (Georgetown University Press) 1995 ‐ ISBN: 9781589011045 Standard Arabic, An Elementary‐ intermediate course, Eckehard Schulz and others (Cambridge University Press) 2004 – ISBN: 9780521774659 Ahlan wa Sahlan Functional Modern Standard Arabic for Beginners, Second Edition, Mahdi Alosh; Revised with Allen Clark – ISBN: 9780300122725 Arabic ‐ English / English – Arabic dictionary, M. Baalbaki, R. Baalbaki & R. Baalbaki (Dar El Ilm Limalayin) – ISBN: 9789953631097 www.BBC.co.uk/arabic www.aljazeera.net A selection of authentic material will also be used. In addition there is a wide range of language learning materials available for self‐study in the Self‐Access Centre.