Laboratory Fume Hoods California State University Fresno CSU Fresno, Environmental Health & Safety
advertisement

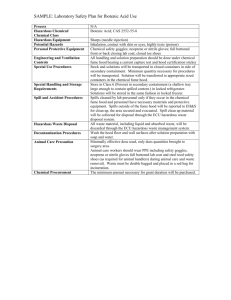
Laboratory Fume Hoods California State University Fresno In accordance with Title 8 CCR Section 5154.1, Ventilation Requirements for Laboratory-Type Hood Operations. CSU Fresno, Environmental Health & Safety (559) 278 - 7422 Introduction Purpose of a Laboratory Fume Hood Laboratory Fume Hoods help prevent exposure to fumes, vapors and particulate matter from hazardous substances. Introduction Functions of a Laboratory Fume Hood Fume hoods draw airflow inward, away from the worker. Operator Qualifications Training Requirements To operate a fume hood, one must be trained to: Use the hood properly and safely. Determine last performance test, and if requirements are met. Understand the general hood purpose, airflow characteristics, and potential for turbulent airflow and escape of hazardous substances from the hood. Know where the quantitative airflow monitor or alarm system is located on the hood and how it is used to indicate an inward airflow during hood operation 8 CCR 5154.1(f)(3) Pre-Use Inspection Overview Check for last inspection date by EHS. Postings or signs should be present when a fume hood is out of order and EHS is aware. If you suspect your hood is not working contact EHS immediately at 278-7422. Check quantitative airflow monitoring device to ensure hood is working properly. Use qualitative methods to ensure air is flowing in the proper direction. Pre-Use Inspection Determining last inspection Each fume hood must have inspection record indicating: Last date of inspection. Initials of the last inspector of the device. Whether the device passed or failed inspection. This data sheet is normally attached to the fume hood. Units that fail an inspection are tagged with a “Do Not Use” sign with a date the unit was taken out of service. Units must be re-inspected: Annually. After any repair. Following any addition of large equipment to the unit. Pre-Use Inspection Quantitative Monitoring Devices A hood user must quantitatively identify whether their fume hood is working properly. The method must measure an exact or approximate rate of inward airflow. Acceptable devices to determine quantitative airflow include: Inclined Manometers Diaphragm Pressure Gauges Vane Gauges An Airflow Alarm System is also acceptable, granted that the “system provides an audible or visual alarm when the airflow decreases to less than 80% of the airflow required by subsection” 8 CCR 5154.1(e)(3)(A) All values indicated on the device should be no less then those indicated on the certified “safe level” indicated by the label on the fume hood. Pre-Use Inspection Examples of Quantitative Monitoring Devices Inclined Manometer This device is very common on campus. Vaneometer Rare on campus, but acceptable. Diaphragm Pressure Gauge Rare on campus, but acceptable. Pre-Use Inspection Examples of Quantitative Monitoring Devices Fume Hood Alarm Device Alerts the user if there is inadequate inward airflow Visually Audibly These units should have a visual aid of some sort indicating that the unit is functioning and is safe to use. Pre-Use Inspection Examples of Quantitative Monitoring Devices If you do not have a working qualitative method to assess if the fume hood is functioning properly, contact EHS at 278-7422. Pre-Use Inspection Qualitative Inspection Methods Examples of Qualitative Devices include: Kimwipes / Delicate Wipes Tape Mylar Strips The device used must demonstrate airflow is flowing inward. Pre-Use Inspection Qualitative Inspection Methods The material used (kimwipe, mylar or tape) should be pulled in by the fume hood to indicate there is inward airflow. The material must be tested in multiple areas where the hood is open. If you are having trouble or do not note the inward movement of air, make sure you have remembered to turn the unit on. Using the Fume Hood Work Practices The sash of the fume hood may be raised completely during usage, unless marked otherwise. If marked the hood shall be opened no further then the safe operating level, indicated by the arrows, when in use. Using the Fume Hood Work Practices Store non-essential chemicals and other equipment outside of the fume hood. Keep the hood free from obstruction of large equipment whenever possible. Storage of hazardous waste containers not related to the wastes being generated within the hood is not advised. Incompatible wastes are required to be separated and closed during storage, except when it is necessary to add waste Do not put your face inside the fume hood when hazardous substances are present. Always keep your face and body outside the unit when in use. Have Concerns? When should you contact EHS with any concerns? Annual Inspection If you note that an inspection was not completed within one year. Maintenance Repairs Addition of Large Equipment Newly Installed Hoods You suspect your fume hood is not protecting you adequately for any reason. Training Completion Acknowledgement form Please either print out a copy of this slide or request a hard copy from your Department Safety Coordinator or Supervisor. Please sign/date in the spaces provided, and then forward it to your Department Safety Coordinator or Supervisor. I have read the slides presented in the Laboratory Fume Hoods Power Point presentation and have reviewed the associated department-specific plans. Name (Print)_________________________________________________ Signature ___________________________________________________ Department _________________________________________________ Date _____________________________ Contacting Campus Environmental Health and Safety For questions and concerns, please call California State University Fresno Environmental Health and Safety Department at: (559) 278 - 7422




![Safety%20Step%20by%20Step[1]. - thsicp-23](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/009097871_1-7065ff837c3ce091dcdb4239bcbcbee5-300x300.png)