Flooding and the environment – Learning Journey Flooding Introduction
advertisement

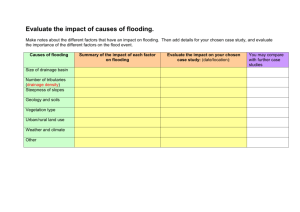
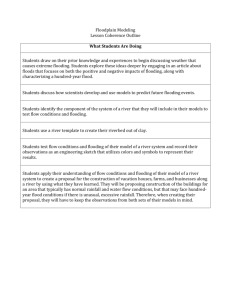
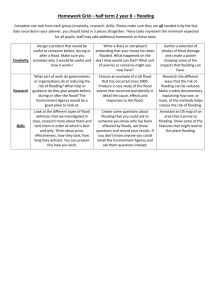
Flooding Introduction This learning journey is one of a series designed to support the learning and teaching of emergency and resilience education. In particular it focuses on flooding. Through studying the causes and impact of flooding learners will consider how to prevent and prepare for flood conditions. The learning journey includes opportunities for interdisciplinary planning and assessment. Helping learners understand flooding supports the delivery of key curriculum areas such as those which are the ‘responsibilities for all’ as well as those specific to subject areas. This learning journey covers the following learning experiences: Rivers and flooding Flooding and the water cycle. Flooding and the environment – Learning Journey Experiences and outcomes HWB I am learning to assess and manage risk, to protect myself and others, and to reduce the potential for harm when possible. HWB 0-16a – HWB 4-16a I know and can demonstrate how to keep myself and others safe and how to respond in a range of emergency situations. HWB 0-17a – HWB 4-17a Social Subjects I can describe the physical processes of a natural disaster and discuss its impact on people and the landscape. SOC 2-07b I can discuss the environmental impact of human activity and suggest ways in which we can live in a more environmentally-responsible way. SOC 2-08a (also SOC 3-08a) I can consider the advantages and disadvantages of a proposed land use development and discuss the impact this may have on the community. SOC 2-08b While learning outdoors in differing weathers, I have described and recorded the weather, its effects and how it makes me feel and can relate my recordings to the seasons. SOC 0-12a (also SOC 1-12a – SOC 3-12a) I can use a range of maps and geographical information systems to gather interpret and present conclusions and can locate a range of features within Scotland, UK, Europe and the wider world. SOC 3-14a (also SOC 4-14a) Prior knowledge Some of the activities in these learning journeys are progressive and build on earlier experiences and outcomes. However, no prior knowledge of flooding or resilience education is required before undertaking this learning journey. The learning experiences touch on aspects of weather and climate providing the opportunity to reinforce any knowledge learners already have of these areas. Technology I can use ICT effectively in different learning contexts across the curriculum to access, select and present relevant information in a range of tasks. TCH 4-03b 3-11a They have been designed to be modular so practitioners can pick and choose the activities more appropriate to their needs. http://www.educationscotland.gov.uk/readyforemergencies 1 Flooding and the environment – Learning Journey Flooding Learning experience: Possible tasks Rivers and flooding Practitioners may use the rivers fact sheet in the ‘Citizen Science Toolkit’ (see ‘Useful resources’) as a starting point to create their own tasks to support this learning experience. Learners visit a local river guided by a local official from the ranger service, SEPA or the council. Learners discuss the risk of flooding from the river, who is at risk, what land would be affected and what, if any, prevention strategies are in place. Learners use the information in the Citizen Science Toolkit and hand-out focusing on the White Cart Water Flood Prevention Scheme (see ‘Useful resources’) to develop their understanding of flood prevention strategies, and use this as a basis to write a report on the scheme. Introduction Learners consider the local processes which affect the flow of rivers and the engineering solutions we use to control flood events. Stimulus Some resources to support this learning experience are detailed in the ‘Useful resources’ section. A visit to a local river accompanied by an expert such as a representative from the ranger service, Scottish Environmental Protection Agency (SEPA) or the local council could provide additional support for this learning experience. Learning intention To identify the part that rivers may play in flooding events and look at ways to control their flow. Learners watch the flood simulation video (see ‘Useful resources’) and discuss what happens when the river rises, the impact on the surrounding area and what would happen in an urban area. Success criteria Learners can: identify how rivers can cause or contribute to flooding events identify methods of controlling the flow of a river to reduce risk. Possible evidence Learners can: discuss ways in which a local river might contribute to a flooding emergency discuss the flood prevention methods being used in the White Cart Water Flood Prevention Scheme draw a map showing areas most at risk of flood. Reflecting on learning Useful resources Download the ‘Citizen Science Toolkit’ and ‘White Cart Water Flood Prevention Scheme’ hand-out from the Ready for Emergencies website. What issues do planners and engineers have to consider when developing areas along the course of a river? Can you think of other ways in which we could help prevent flooding? Watch the ‘River Flooding Simulation’ on the Ready for Emergencies website. White Cart Water Flood Prevention Scheme – http://www.whitecartwaterproject.org/ SEPA: River and coastal flood map – http://www.sepa.org.uk/flooding/flood_extent_maps.aspx Taking it further This learning experience offers scope for further partnership working with environmental experts, the local council or engineers working on flood prevention schemes in order to develop an understanding of flood prevention strategy. http://www.educationscotland.gov.uk/readyforemergencies 2 Flooding and the environment – Learning Journey Flooding Learning experience: Possible tasks Learners create their own depiction of the water cycle, identifying areas which may contribute to a flooding event. Learners create and monitor their own rain gauges and use their results as a starting point to discuss how an increase in precipitation might contribute to a flooding event. Learners consider the impact different parts of the water cycle (specifically precipitation, surface run off and infiltration) can have on flooding. Learners use Google Maps as a starting point for creating their own map of an area of Scotland, marking areas which might be affected by increased precipitation or melting snow. Stimulus Some resources to support this learning experience are detailed in the ‘Useful resources’ section. Learners discuss the different types of surface in their local community, what happens to rain when it falls on each type of surface and the effect this might have on flooding. Learners complete the biodiversity or soil survey (see ‘Useful resources’) to gain an understanding of the importance of soil quality and how drainage affects flooding events. Flooding and the water cycle Introduction Learning intention To identify ways in which different sections of the water cycle impact on flooding. Useful resources Opal: Soil survey http://www.opalexplorenature.org/soilsurvey Opal: Biodiversity survey http://www.opalexplorenature.org/BiodiversitySurvey Links to soil and earthworm survey videos: http://www.environment.scotland.gov.uk/get-learning/land/thirdand-fourth-level/#tabResources Success criteria Learners can: identify different sections of the water cycle accurately describe the impact each section of the water cycle has on flooding. Possible evidence Learners can: create their own depiction of the water cycle explain how different parts of the water cycle can affect flooding. Reflecting on learning Why might an area where the soil contains a lot of clay flood more readily than an area with sandy soil? What could we do in our own communities to reduce the risk of flooding based on the lessons learnt? Taking it further Learners could investigate the geology of their local area and how this could impact on soil drainage / a flood event. Learners could work with the local council to investigate how the water in our drains is removed, treated and returned to the water cycle. Google Maps http://maps.google.co.uk Weather and climate change: The water cycle http:// www.educationscotland.gov.uk/ weatherandclimatechange/weather/thewatercycle.asp http://www.educationscotland.gov.uk/readyforemergencies 3