Solid State Lighting Overview
advertisement
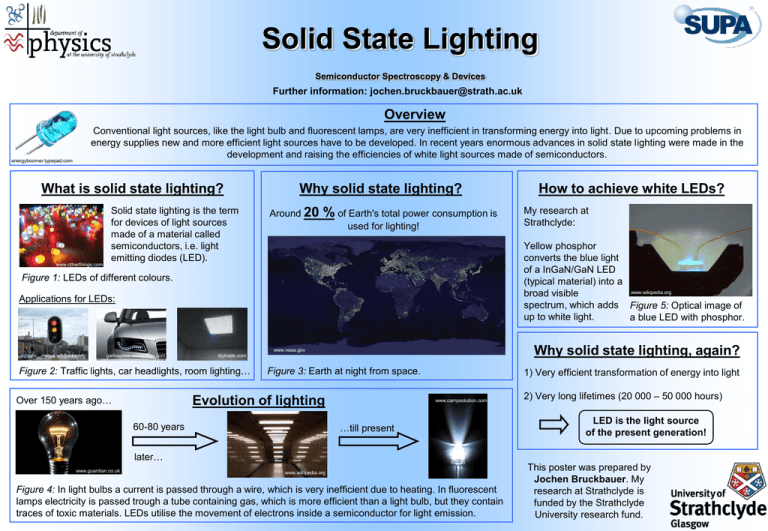
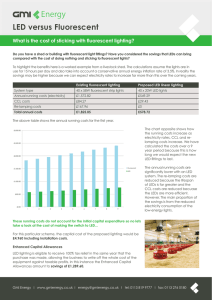
Solid State Lighting Semiconductor Spectroscopy & Devices Further information: jochen.bruckbauer@strath.ac.uk Overview Conventional light sources, like the light bulb and fluorescent lamps, are very inefficient in transforming energy into light. Due to upcoming problems in energy supplies new and more efficient light sources have to be developed. In recent years enormous advances in solid state lighting were made in the development and raising the efficiencies of white light sources made of semiconductors. energyboomer.typepad.com What is solid state lighting? www.otherthings.com Solid state lighting is the term for devices of light sources made of a material called semiconductors, i.e. light emitting diodes (LED). Why solid state lighting? Around 20 % of Earth's total power consumption is used for lighting! Applications for LEDs: Why solid state lighting, again? www.nasa.gov garbagebin.wordpress.com diytrade.com Figure 2: Traffic lights, car headlights, room lighting… Over 150 years ago… My research at Strathclyde: Yellow phosphor converts the blue light of a InGaN/GaN LED (typical material) into a www.wikipedia.org broad visible spectrum, which adds Figure 5: Optical image of up to white light. a blue LED with phosphor. Figure 1: LEDs of different colours. www.wikipedia.org How to achieve white LEDs? Figure 3: Earth at night from space. Evolution of lighting 1) Very efficient transformation of energy into light www.campsolution.com …till present 60-80 years 2) Very long lifetimes (20 000 – 50 000 hours) LED is the light source of the present generation! later… www.guardian.co.uk www.wikipedia.org Figure 4: In light bulbs a current is passed through a wire, which is very inefficient due to heating. In fluorescent lamps electricity is passed trough a tube containing gas, which is more efficient than a light bulb, but they contain traces of toxic materials. LEDs utilise the movement of electrons inside a semiconductor for light emission. This poster was prepared by Jochen Bruckbauer. My research at Strathclyde is funded by the Strathclyde University research fund.