A Robust SSD Position Fingerprint Approach for Wireless Networks
advertisement

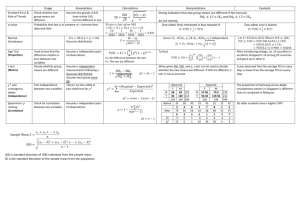
International Journal of Engineering Trends and Technology (IJETT) – Volume 8 Number 9- Feb 2014 A Robust SSD Position Fingerprint Approach for Wireless Networks P.V.Sindhu 1 , Ms.S.P.Godlin Jasil 2 1 P.V.Sindhu1 Student of post graduation, Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Sathyabama University, Chennai, India. 2 Ms. S.P.Godlin Jasil2 Faculty of Computer Science and Engineering, Sathyabama University, Chennai, India. Abstract-- Fingerprint-based method is widely adopted for indoor localization purpose. The analytically robust position fingerprint definition, the signal strength difference (SSD) is used for Localization purpose. Two well-known localization algorithms (K nearest Neighbour and Bayesian Inference) are used to demonstrate the robustness of SSD. The difference of the Signal Strengths between the user with the different access points, are analysed to identify a highest and nearest access point from the user’s point of position. While user requesting data from one access point and moving to the next access point, the Signal strength difference (SSD) will be calculated and then automatically the data will be delivered to the user from the highest and nearest access point, which has strongest signal. So that it can reduce the data loss problem in mobile computing environment. Keywords-- Position Fingerprint, Signal strength difference (SSD), Access point, Wi-Fi. I. INTRODUCTION Received Signal Strength (RSS) varies significantly across multiple different device hardware even it is used under the same wireless conditions. The analytical robust position fingerprint definition, SSD is used for overcoming few problems in mobile computing environment. The signal strength difference (SSD) is a robust position Fingerprinting technique. It is used for calculating the difference between signal strengths. Two well-known localization algorithms (K Nearest Neighbour and Bayesian Inference) are used when proposed fingerprint is applied. These two algorithms demonstrate the robustness and working of SSD. Calculation of Signal strengths is done when used an SSD Approach. User’s Signal Strength is calculated so that the difference of the Signal Strength between the user with the different access points, are analysed to identify a highest and nearest access point from the user. While requesting data from one access point and moving to the next access point, the Signal strength difference (SSD) will be calculated and then automatically ISSN: 2231-5381 the data will be delivered to the user from the highest and nearest access point, which has strongest signal. So that it can reduce the data loss & time consumption problem in mobile computing environment. II. RELATED ARTICLES This paper proposed the evaluation shows that the solutions can address the signal strength heterogeneity problem. According to them, heterogeneous wireless client’s measure signal strength differently. This is the basic elementary problem for indoor position fingerprinting, and it has a high impact on the position precision. So this presents an automatic mapping-based method that avoids calibration by learning from online measurements [1]. This paper gives a description of Ekahau Site Survey is a tool. It is used for Wi-Fi network planning, for Real-Time Position Systems. It runs on Microsoft Windows and supports 802.11 a/b/g/n/ac wireless networks. It provides a ground-level view of WLAN (Wireless Local Area Network) coverage and performance based on the data collected during passive and active surveys. It is optimized for only 802.11n family of WiFi. It is also capable of performing predictive surveys that facilitates WLAN planning at pre-deployment stage [2]. This paper focuses on Received signal strength, which is one of the most capable strategies in wireless communications. The stationary signal strength is the averaged using RSS value and the result is a stationary Gaussian process; which includes some experimental results [3]. This paper discusses about indoor localization techniques, which uses position fingerprints. Position Based Services (LBS) are the applications of mobile computing, where an LBS relies on a user’s position, which is used to deliver context aware applications. In this paper, they investigated many aspects of fingerprint-based position systems, in order http://www.ijettjournal.org Page 506 International Journal of Engineering Trends and Technology (IJETT) – Volume 8 Number 9- Feb 2014 to improve their accuracy. WLAN can be implemented with the least effort, but WLAN aims to provide local wireless access to fixed network architectures [4]. This paper discusses an effective technique in locating a source, which is based on intersections of hyperbolic curves defined by the time differences of arrival of a signal received at a number of sensors is proposed. This approach is non-iterative and also gives an explicit solution. Received signal strength (RSS) when referred to a signal propagation model, is used to find user position, where it is one of the most capable strategy in wireless connections. This paper develops simple methods which are based on relative signal-strength capacity that is, the difference in inactive signal strength measured at the user position from multiple base transceiver stations (BTSs) [5]. This paper is focused to discuss about the context-awareness. Current indoor localization systems need to be manually adapted to work optimally with specific hardware and software. Evaluating the efficiency is a difficult task. One type of context information is position information of wireless network clients. This paper focuses on Research in indoor localization of wireless network clients based on signal strength. Not much of this research is directed towards handling the issue of adapting signal strength based indoor localization system to the hardware and software of a specific wireless network user, it can be a tag or a PDA or a laptop. Therefore current indoor localization systems need to be manually adapted to work optimally with specific hardware and software [6]. This paper describes that, RSS based position estimation. This technique of position estimation has been proposed as a low-cost, low-complexity solution for many position-aware applications. This work studies radio propagation path loss model, which is assumed, known a priori in position aware applications. This paper presents a detailed study on the RSSbased joint estimation of unknown positions and coordinates the distance-power gradient which is a parameter of path loss model. A nonlinear least-square estimator improves the performance of the algorithm. From simulation results, which are based on CRB, shows that the proposed joint estimator is especially useful for estimation of position in unknown or changing environments [7]. This paper is focused to discuss the Wireless LAN. WLAN is efficiently used for effective indoor positioning system. It is sufficiently robust to enable for a variety of position aware applications without requiring special-purpose hardware or complicated training and calibration procedures. This paper demonstrates probabilistic techniques that allows for remarkably accurate localization. This system is sufficiently robust to enable a variety of position-aware applications without requiring special-purpose hardware or complicated training and calibration procedures [8]. III. EXISTING SYSTEM In the existing system, the popular position fingerprint, Received Signal Strength (RSS) varies significantly across multiple different device hardware even it is used under the same wireless network conditions. The system while using RSS was not that effective when compared to SSD. If the user in mobile computing environment requests for a data from internet, the server will send the data to the user from that particular tower region or an access point. Also if the gets the signal from the next tower, the data consumption from the new tower will be a very time consuming process. There is a chance for data loss and request time out. It is also a tough task to find the users movement using RSS mechanism. Disadvantages of existing system are, There is a chance for data loss & Request time out, while the getting the data from nearest tower. The data consumption from the new tower will be a very time consuming process. It is difficult to predict the user’s movement using RSS mechanism. IV. PROPOSED SYSTEM In the Proposed System, using an SSD Approach is to identify best matched tower from the user’s point of position. The user’s Signal Strength is calculated, so that the difference of the Signal Strength between the user with the different towers are analysed to identify a best matched or nearest Tower from the user point of view. The disadvantages of existing system can be improved in proposed system. Advantages of proposed system are, automatically data delivered to the user. There is a chance for reducing the time consumption and data loss problem in mobile computing environment. It can be easy to track the user movement using SSD Approach. V. IMPLEMENTATION This paper focuses on implementing two algorithms; they are KNN Algorithm and Bayesian Algorithm. Two well-known localization algorithms are used, when our proposed fingerprint is used. They are K Nearest Neighbour and Bayesian Inference. KNN Algorithm is used to find the k closest training points (small || xi − x0 ||) according to some metric which is a distance calculation measure for ex. euclidean, manhattan, etc.). It uses predicted class with majority vote and predicted value with average weighted by inverse distance. It is a Memory-based model. In its basic form, it is one of the most simple machines learning Methods. Bayesian Algorithm gives the maximum likelihood estimation of the class and prior, posterior probabilities of the objects in a closet. The probabilities of the objects help in finding out the nearest object. ISSN: 2231-5381 http://www.ijettjournal.org Page 507 International Journal of Engineering Trends and Technology (IJETT) – Volume 8 Number 9- Feb 2014 While user is in mobile computing environment and requesting a data from the one access point and moving to the next access point, the Signal strength difference will be calculated and then automatically the data will be downloaded to the user from the next tower which is nearest & having strongest signal. So that it can reduce the time consumption &data loss problem in mobile computing environment. It will be easy to track the user movement using SSD. definition, the Signal Strength Difference (SSD) is used as Position Fingerprinting technique. SSD Approach includes the calculation of Signal Strength Differences. User’s point of position is the point from which access point user is getting signal for his internet data access. When the User is in mobile computing environment, the SSD approach helps in finding out the difference between Signal strengths of User’s point of position and to the next access point, which is nearer to the user and has highest signal strength. So it helps in reducing Data loss and Time consumption problem in mobile computing environment. ACKNOWLEDGMENT I would like to wish to the Head of the Department of Computer Science & Engineering, Ms. Bharati madam for the encouragement, which lead to enhancement of the paper work. To my guide, Ms. S.P.Godlin Jasil madam for the support and guidance in the improvement of the paper. REFERENCES [1] M.B. Kjærgaard, “Indoor Position Fingerprinting with Heterogeneous Clients,” Pervasive and Mobile Computing, vol. 7, no. 1, pp. 31-43, Feb. 2011. [2] Ekahau, “http://www.ekahau.com, 2012”. [3] J. Bardwell, “A Discussion Clarifying Often-Misused 802.11 WLAN Terminologies,” http://www.connect802.com/ download/techpubs/2004/you_believe_D100201.pdf, 2011. Figure 4.1: General block diagram of outdoor positioning. Wi-Fi in indoor & Above Figure gives general block diagram of Wi-Fi in indoor & outdoor positioning. In Indoor positioning, the radio frequency of signals will be permitted to 100 meters or within. They cannot be beyond that range. The Wi-Fi equipped devices can be connected to internet through fixed internet connection setup like LAN, BROADBAND or a DSL connection. In an Outdoor positioning, it provides the extension of connectivity. The radio frequency of signals will be up to 300 meters or beyond. Using an SSD Approach we can find out the nearest and highest frequency radio frequency signals. Here, we do not need any fixed connections. VI. CONCLUSION Fingerprint-based methods are most widely adopted for the purpose of indoor localization purpose because of their costeffectiveness. An analytically a robust position fingerprint ISSN: 2231-5381 [4] M. Hossain, H. Nguyen Van, Y. Jin, and W.-S. Soh, “Indoor Localization Using Multiple Wireless Technologies,” Proc. IEEE Int’l Conf. Mobile Adhoc and Sensor Systems (MASS),http://www.ece.nus.edu.sg/stfpage/elesohws/mass07. pdf, Oct. 2007. [5] B.-C. Liu, K.-H. Lin, and J.-C. Wu, “Analysis of Hyperbolic and Circular Positioning Algorithms Using Stationary Signal-Strength-Difference Measurements in Wireless Communication,” IEEE Trans. Vehicular Technology, vol. 55, no. 2, pp. 499-509, Mar. 2006. [6] M.B. Kjærgaard, “Automatic Mitigation of Sensor Variations for Signal Strength Based Position Systems,” Proc. Second Int’l Workshop Position and Context Awareness, 2006. [7] X. Li, “RSS-Based Position Estimation with Unknown Pathloss Model,” IEEE Trans. Wireless Comm., vol. 5, no. 12, pp. 3626-3633, 2006. [8] A. Haeberlen, E. Flannery, A.M. Ladd, A. Rudys, D.S. Wallach, and L.E. Kavraki, “Practical Robust Localization over Large-Scale 802.11 Wireless Networks,” Proc. ACM MobiCom, pp. 70-84, 2004. http://www.ijettjournal.org Page 508