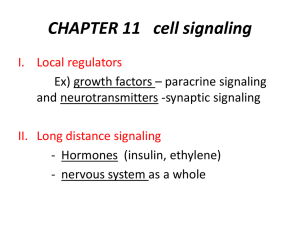
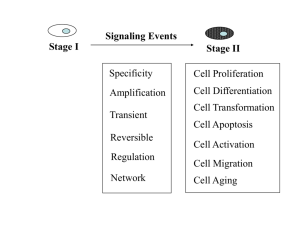
+ -
advertisement

Antigen recognition out + in Lipid bilayer of plasma membrane Signal transduction (contains one or more ITAMs) Src-family tyrosine kinase reversibly associated with receptor Consensus ITAM (amino acid) ….---.asp.---.---.tyr.---.---.leu.---.---.---.---.---.---.---.tyr.---.---.leu.---…. glu ile ile The one letter code is usually used: xx(D/E)xxYxx(L/I)xxxxxxxYxx(L/I) These tyrosines are phosphorylated by various src family kinases upon recognition receptor ligation Src-family tyrosine kinases Myristylation/palmitylation sites present in many family members, promotes association with membranes and membrane “rafts”. (e.g. CH3(CH)12CONH-Glycine..) Unique region reversibly associates with certain membrane receptors. Differs among family members. SH3 motif involved in binding to many proteins that carry a proline rich motif (e.g. P-X-X-P). SH2 motif involved in binding to phospho-tyrosines in certain sequence contexts, including phosphorylated ITAMs. Kinase domain motif catalyzes tyrosine phosphorylation. CD45 (plasma membrane tyrosine phosphatase) csk (cytoplasmic tyrosine kinase) Adapted from Molecular Cell Biology 3rd Ed., p894 Table 1. Expression of Src family kinases Src Fyn Yes Lyn Hck Fgr Blk Lck Ubiquitous; two neuron-specific isoforms Ubiquitous; T cell-specific isoform (Fyn T) Ubiquitous Brain, B-cells, myeloid cells; two alternatively spliced forms Myeloid cells (two different translational starts) Myeloid cells, B-cells B-cells T-cells, NK cells, brain Frk subfamily Primarily epithelial cells T Cell Receptor a b CD3 Antigen d e ge recognition out -+ +in CD3 z Signal transduction (with ITAMs) - CD3 functions both as signal transducers and in transport of antigen receptors to the plasma membrane B Cell Receptor Ig a b Antigen recognition out + in + Signal transduction (with ITAMs) - - + + - - syk Lyn Blk Hck Fyn Lck ACTIVATION! Antigen receptor signaling may be similar to that of other surface receptors such as receptor tyrosine kinases like epidermal growth factor in which receptor crosslinking leads to initial trans-phosphorylation. T Cell Receptor And coreceptor a b CD4 CD3 d e ge Cholesterol and sphingolipid rich microdomain out - -+ +- in Signal transduction (with ITAMs) Fyn Lck CD3 z T Cell Receptor a b CD4 CD3 d e ge - -+ +ZAP70 ACTIVATION! CD3 z Lck TABLE 2. Protein with Src homology-2 domains that may be associated with T cell-activation (partial list) Protein tyrosine kinases Fyn Lck Syk ZAP-70 Csk ltk Protein tyrosine phosphatases SHP-1 SHP-2 Proteins with enzymatic functions Phospholipase C g1 (PLC g1) Phosphatidylinositol 3”-kinase (P1 3-kinase), p85 subunit Adaptors and Regulators GTPase acttivating protein (GAP) SOS Vav Slp-76 Shc Nck Grb2 Crk From Fundamental Immunology 4th Ed, Paul WE Ed., pp 425 TABLE 3. Some of the proteins that are tyrosine phosphorylated following TCR stimulation. TCR subunits CD3 d, e, g , z Protein tyrosine kinases ltk Lyn Lck MAPKs Pyk2 Syk ZAP-70 Proteins with enzymatic function Phospholipase C g1 (PLC g1) Others Cbl CD5 CD6 Ezrin LAT Shc Slap-130 Slp-76 Shc a Tubulin Valosin containing protein Vav From Fundamental Immunology 4th Ed, Paul WE Ed., pp 427 T Cell Receptor activation (cont) a b CD4 CD3 ge d e Ca++ LAT CRAC - -+ +- DAG RasGRP RAS PIP2 ZAP70 Plcg PKC GTP Lck Ca++ Ca Ca++ Ca++ Ca++ ++ CD3 z GDP IP3 ACTIVATION! Raf-1 [Ca++]i calcineurin IP3 receptor Ca++ NFAT NFAT MEK Endoplasmic reticulum PO4 nucleus NFAT Fos/Jun IL-2 gene MAPK Immediate early genes Jun/Fos From Fundamental Immunology 4th Ed, Paul WE Ed., pp 428 T Cell Receptor activation (cont) a b CD4 CD3 ge d e LAT - -+ +- Grb2 ZAP70 sos Lck CD3 z ACTIVATION! GAPs Gads Slp-76 SLAP 130 vav Nck rho/rac Pak WASP Adhesion migration nucleus Ras GTP Ras GDP Ras effectors Actin/cytoskeletal reorganization Antigen presenting cell B7.1 or B7.2 T Cell Receptor activation (cont) a b CD4 CD3 ge d e “Costimulatory” B7 molecules on antigen presenting cells CD28 LAT - -+ +- PI3K Itk PKB Lck ACTIVATION! CD3 z ACTIVATION! nucleus p85 ? PIP2 PIP3 PI3K PI3K Removed by SHIP--1 P Where does cell type specificity come from? • Preexisting substrate differences. •Specificity of src and ZAP70/syk kinases •PKC isoform expression •PLCg isoform expression •NFAT isoform expression •Transcription factor isoform expression •Inhibitory receptor expression •etc…. Activating Receptors (on Monocytes, Macrophages, Neutrophils, Mast cells, and NK cells) 2-4 Ig-like extracellular domains “Antigen” recognition 1,2 Ig-like extracellular domains FcgRI FcgRIIa* FcgRIII FcaRI ILT1 ILT7 ILT8 LIR6a NKp46 NKp30 FcRIII 1,2-? Ig-like extracellular domains FcgRIII FceRI 1-3 Ig-like extracellular domains NK activatory receptors FcaRI Type 2 membrane protein NKp80 out +- +in Signal transduction (with ITAMs) Fc common g chain CD3 z DAP12 b Fc g chain Activating ligand Inhibitory ligand Activating receptor Motif: I/VxYxxL/V out + in ITAMs SHIP lipid phosphatase Src-family tyrosine Tyrosine kinase reversibly kinase associated with e.g., ZAP-70, receptor syk ITIMs Tyrosine phosphatase e.g., SHP-1 Normal cell Defective cell MHC class I “Missing self” “Natural killer” cell recognition + - + Weak signal no response Initiation of killing program nucleus nucleus APC APC Late in the response... B7 MHC/peptide CD28 TCR + + B7 CD28 + Ag signal + costimulation CTLA4 sequestered T cell downregulation late in response T cell activation nucleus - CTLA4 on surface CTLA4 signaling turns response off nucleus Inhibitory Receptors (on Monocytes, Macrophages, Neutrophils, Mast cells, and NK cells) 1-6 Ig-like extracellular domains ILT5 LIR8 ILT4 Siglec 6 “Antigen” CD33 recognition CD22 FcgRIIb PIRB SIRPs LAIR1 ILT3 LIR5 PD-1 out KIR2DL KIR3DL CTLA4 in Signal transduction (with ITIMs) Type 2 membrane proteins Ly49 CD94/ NKG2A CD72 Immunoprecipitation Detergent Anti-Y-PO4 precipitate antibodies with S. aureus protein A-coupled resin, wash, elute sample control markers Mobility inversely proportional to the Log of molecular weight + Fractionate by electrophoresis on denaturing polyacrilamide gel Generation of gene knockouts in mice: an important technique in establishing the role of signaling molecules in normal cells. Adapted from Molecular Cell Biology 3rd Ed., p294-5 Adapted from Molecular Cell Biology 3rd Ed., p296 Yeast two hybrid assay is one way that protein: protein interactions can be measure and is an important way that new molecules are discovered. Adapted from Molecular Cell Biology 3rd Ed., p896