Organic Chemistry Chapter 24
advertisement

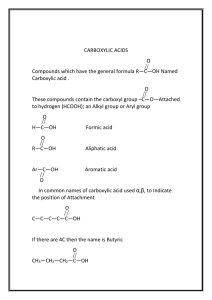
Organic Chemistry Chapter 24 Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Common Elements in Organic Compounds 24.1 Classification of Hydrocarbons 24.1 Alkanes Alkanes have the general formula CnH2n+2 where n = 1,2,3,… • only single covalent bonds • saturated hydrocarbons because they contain the maximum number of hydrogen atoms that can bond with the number of carbon atoms in the molecule CH4 C2H6 C3H8 methane ethane propane 24.2 Structural isomers are molecules that have the same molecular formula but different structures 24.2 How many structural isomers does pentane, C5H12, have? H H H H H H C C C C C H H H H H H H CH3 H C C H CH3 H n-pentane H H H CH3 H H C C C C H H H H 2-methylbutane H C H 2,2-dimethylpropane 24.2 Alkane Nomenclature 1. The parent name of the hydrocarbon is that given to the longest continuous chain of carbon atoms in the molecule. CH3 CH3 1 CH2 2 CH2 3 CH 4 CH2 5 2. An alkane less one hydrogen atom is an alkyl group. 24.2 CH4 methane CH3 methyl CH2 6 CH3 4-methylheptane 7 Alkane Nomenclature 24.2 Alkane Nomenclature 3. When one or more hydrogen atoms are replaced by other groups, the name of the compound must indicate the locations of carbon atoms where replacements are made. Number in the direction that gives the smaller numbers for the locations of the branches. CH3 CH3 1 CH 2 CH2 3 CH2 4 CH3 5 CH3 2-methylpentane CH3 1 CH2 2 CH2 3 CH 4 CH3 5 4-methylpentane 24.2 Alkane Nomenclature 4. Use prefixes di-, tri-, tetra-, when there is more than one alkyl branch of the same kind. CH3 1 CH3 CH3 CH CH 2 3 CH2 CH2 4 CH3 5 6 2,3-dimethylhexane CH3 CH3 1 CH 2 C 3 CH2 4 CH2 5 CH3 6 CH3 3,3-dimethylhexane 24.2 Alkane Nomenclature 5. Use previous rules for other types of substituents. CH3 1 Br NO2 CH CH 2 3 CH3 4 2-bromo-3-nitrobutane Br CH2 1 NO2 CH2 2 CH 3 CH3 4 1-bromo-3-nitrobutane 24.2 What is the IUPAC name of the following compound? CH3 CH3 1 CH C2H5 CH2 2 3 CH 4 CH2 5 CH2 6 CH2 7 CH3 8 2-methyl-4-ethyloctane What is the structure of 2-propyl-4-methylhexane? C2H5 CH3 1 CH 2 CH3 CH2 3 CH 4 CH2 5 CH3 6 24.2 Alkane Reactions Combustion CH4 (g) + 2O2 (g) CO2 (g) + 2H2O (l) DH0 = -890.4 kJ Halogenation light CH4 (g) + Cl2 (g) CH3Cl (g) + HCl (g) Cl2 + energy Cl• + Cl• H H Cl• + H C H H •C H H H C • + Cl H H + HCl H Cl H C H Cl + Cl• 24.2 achiral chiral 24.2 Cycloalkanes Alkanes whose carbon atoms are joined in rings are called cycloalkanes. They have the general formula CnH2n where n = 3,4,… 24.2 Cycloalkanes 24.2 Alkenes Alkenes have the general formula CnH2n where n = 2,3,… • contain at least one carbon-carbon double bond • also called olefins CH CH2 CH2 CH3 CH3 CH 1-butene Cl Cl C H Cl H C cis-dichloroethylene CH3 2-butene C H CH H C Cl trans-dichloroethylene 24.2 Cis-Trans Isomerization in the Vision Process 24.2 Alkene Reactions Cracking C2H6 (g) Pt catalyst CH2 CH2 (g) + H2 (g) Addition Reactions CH2 CH2 (g) + HBr (g) CH3 CH2 CH2 (g) + Br2 (g) CH2Br CH2Br (g) CH2Br (g) 24.2 Alkynes Alkynes have the general formula CnH2n-2 where n = 2,3,4,… • contain at least one carbon-carbon triple bond CH C CH2 1-butyne CH3 CH3 C C CH3 2-butyne Production of acetylene CaC2 (s) + 2H2O (l) C2H2 (g) + Ca(OH)2 (aq) 24.2 Alkyne Reactions Hydrogenation CH CH (g) + H2 (g) CH2 CH2 (g) Addition Reactions CH CH (g) + HBr (g) CH2 CH CH (g) + Br2 (g) CHBr CH CH (g) + 2Br2 (g) CHBr2 CHBr (g) CHBr (g) CHBr2 (g) 24.2 Chemistry In Action: Ice That Burns Aromatic Hydrocarbons H H H H C C C C C C H H H H H C C C C C C H H H 24.3 Aromatic Compound Nomenclature ethylbenzene CH2CH3 aminobenzene NH2 Cl chlorobenzene 6 2 5 3 4 nitrobenzene Br Br 1 NO2 Br Br 1,2-dibromobenzene 1,3-dibromobenzene 24.3 Aromatic Compound Reactions Substitution reaction H Br H H + Br2 H H H FeBr3 catalyst + HBr H H H H H H CH2CH3 H H + CH3CH2Cl H H H H H AlCl3 catalyst + HCl H H H 24.3 Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons 24.3 Functional Group Chemistry Alcohols contain the hydroxyl functional group and have the general formula R-OH. 24.4 Biological production of ethanol C6H12O6 (aq) enzyme 2CH3CH2OH (aq) + 2CO2 (g) Commercial production of ethanol CH2 CH2 (g) + H2O (g) H2SO4 CH3CH2OH (g) Metabolic oxidation of ethanol CH3CH2OH alcohol dehydrogenase CH3CHO + H2 24.4 Functional Group Chemistry Ethers have the general formula R-O-R’. Condensation Reaction CH3OH + HOCH3 H2SO4 catalyst CH3OCH3 + H2O 24.4 Functional Group Chemistry O Aldehydes and ketones contain the carbonyl ( C functional group. O ) • aldehydes have the general formula R C H O • ketones have the general formula R C R’ O O O H C H H C CH3 H3C C CH3 formaldehyde acetaldehyde acetone 24.4 Functional Group Chemistry Carboxylic acids contain the carboxyl ( -COOH ) functional group. 24.4 Functional Group Chemistry Esters have the general formula R’COOR, where R is a hydrocarbon group. O CH3COOH + HOCH2CH3 CH3 C O CH2CH3 + H2O ethyl acetate 24.4 Functional Group Chemistry Amines are organic bases with the general formula R3N. CH3NH2 + H2O CH3CH2NH2 + HCl RNH3+ + OH- CH3CH2NH3+Cl- 24.4 24.4 Chemistry In Action: The Petroleum Industry Crude Oil