PRACTICE FINAL EXAMINATION ORGANIC CHEMISTRY 2210 1.
advertisement
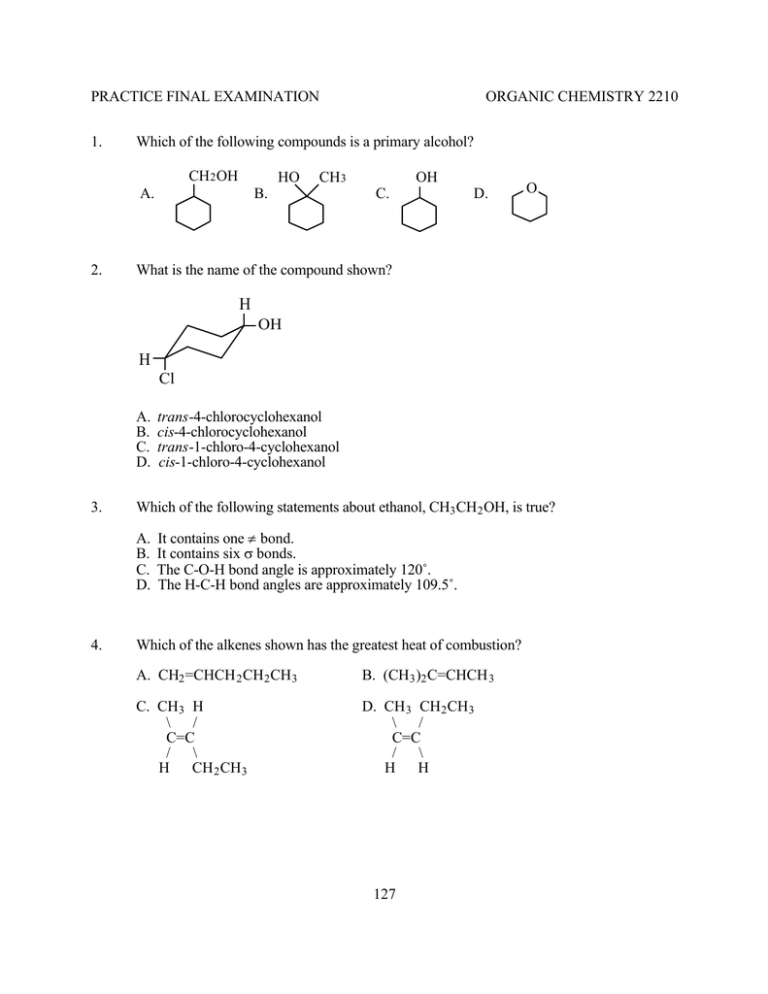
PRACTICE FINAL EXAMINATION 1. Which of the following compounds is a primary alcohol? CH2 OH HO A. 2. ORGANIC CHEMISTRY 2210 CH3 B. OH C. D. O What is the name of the compound shown? H OH H Cl A. B. C. D. 3. Which of the following statements about ethanol, CH3 CH2 OH, is true? A. B. C. D. 4. trans-4-chlorocyclohexanol cis-4-chlorocyclohexanol trans-1-chloro-4-cyclohexanol cis-1-chloro-4-cyclohexanol It contains one π bond. It contains six σ bonds. The C-O-H bond angle is approximately 120˚. The H-C-H bond angles are approximately 109.5˚. Which of the alkenes shown has the greatest heat of combustion? A. CH2 =CHCH 2 CH2 CH3 B. (CH3 )2 C=CHCH 3 C. CH3 H \ / C=C / \ H CH 2 CH3 D. CH 3 CH2 CH3 \ / C=C / \ H H 127 5. Which of the compounds shown is isobutyl chloride? A. B. C. D. 6. What is the name of the compound shown? A. B. C. D. 7. CH3 CH2 CH(CH 3 )2 \ / C=C / \ H CH 3 E Z cis trans What is the most important reason for the fact that cyclohexane is the most stable of the cycloalkanes of twelve carbons or less? A. B. C. D. 9. Bicyclo[4.1.0]heptane Bicyclo[3.1.1]heptane Bicyclo[3.2.0]heptane Bicyclo[5.4.0]heptane Which of the following designations describes the compound at right? A. B. C. D. 8. (CH3 )3 CCl CH3 CHClCH2 CH3 (CH3 )2 CHCH 2 Cl CH 3 CH2 CH2 CH2 Cl There is eclipsing along two of the carbon-carbon bonds in the boat conformation. There is eclipsing along four of the carbon-carbon bonds in the chair conformation. Both torsional and bond angle strain are minimized in the chair conformation. Both torsional and bond angle strain are minimized in the boat conformation. What is the relationship between the compounds shown? H H Cl Cl Cl Cl H H A. Same compound 10. B. Enantiomers C. Diastereomers Which of the following nucleophiles is the most reactive? A. CH3 COOH B. CH3 COO – C. CH3 OH 128 D. CH3 O– D. Structural isomers 11. Which of these is the best method for preparing 1-bromopropane, CH3 CH2 CH2 Br? CCl4 A. CH3 CH2 CH3 + Br2 -------> light B. CH3 CH2 CH3 + Br2 --------> peroxides C. CH3 CH=CH 2 + HBr --------------> no peroxides D. CH 3 CH=CH 2 + HBr ------------------> 12. What is the relationship between the compounds shown? CH3 CH2 CH3 CH2 Cl H C | CH3 A. Same compound 13. B. Enantiomers C. Diastereomers D. Structural isomers What is the name of the compound shown? H OH H H A. B. C. D. 14. CH3 Cl C | H CH2 CH3 CH(CH 3 )2 4-heptanol 2-methyl-3-hexanol 1-isopropyl-1-butanol 1-isopropyl-2-ethylethanol Two structures are both superimposable on each other and the mirror images of one another. What is the relationship between them? A. B. C. D. Same compound Enantiomers Diastereomers Structural isomers 129 15. Which of the following reactions yields (CH3 )3 CCl? A. (CH3 )3 COH + HCl ---> CCl4 B. (CH3 )2 C=CH 2 + Cl 2 ------> C. (CH3 )2 CHCH 2 OH + SOCl2 ---> CCl4 D. (CH 3 )3 CH + Cl2 ------> 16. Which of the following acid-base reactions occurs as shown? A. B. C. D. 17. CH3 COONa + HC≡CH ---> CH3 COOH + HC≡CNa CH3 ONa + HC≡CH ---> CH3 OH + HC≡CNa NaOH + HC≡CH ---> H2 O + HC≡CNa CH 3 NHNa + HC≡CH ---> CH3 NH 2 + HC≡CNa What are the hybridizations of the carbon atoms numbered 1 and 2 in the structure shown? 1 2 A. sp2 , sp3 18. B. sp2 , sp2 C. sp, sp3 D. sp, sp2 Which of the following is NOT a meso compound? A. H H B. H HO H H C. H H OH OH OH OH 130 D. HO OH OH H 19. What are the major products of the reaction shown? CCl4 CH3 + Br2 -------> ? Br H3 C Br Br H H3 C H Br Br H CH3 Br Br CH3 IV H I II Br III A. I and III B. I and IV C. II and III D. II and IV 20. What is/are the major organic product(s) of the reaction shown? O 21. Na + CH3 CH2 CH2 Br ---> ? A. OH + CH2 =CHCH 3 B. + CH3 CH2 CH2 OH C. OCH 2 CH2 CH3 D. OCH(CH 3 )2 What is the configuration of the molecule shown? CH3 CH2 CH3 C—C H Br Br H A. 2S, 3S B. 2S, 3R C. 2R, 3S D. 2R, 3R 131 22. What is the major organic product of the reaction shown? BH3°THF H 2 O2 , OH– (CH3 )2 C=CHCH 3 -------------> ---------------> ? CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 | | | | A. CH2 CHCH 2 CH3 B. CH3 CCH2 CH3 C. CH3 CHCHCH 3 D. CH 3 CHCH 2 CH2 | | | | OH OH OH OH 23. What is the relationship between the compounds shown? CH3 CH2 CH3 H H CH3 OH H H CH3 A. Same compound 24. CH3 OH CH2 CH3 B. Enantiomers C. Diastereomers D. Structural isomers Which of the following solutions can be used in a test to distinguish between the compounds CH2 =CHCH 2 CH3 and CH2 =CHCH 2 CH2 Br? A. conc. H2 SO 4 B. Br2 /CCl4 C. AgNO3 /ethanol D. KMnO4 /H2 O 25. What is the best explanation for the relative stabilities of the gauche and anti forms of butane? The _____ form has more _____ strain. A. B. C. D. 26. gauche . . . torsional gauche . . . steric anti . . . torsional anti . . . steric What are the predicted shape and bond angle of formaldehyde, H2 C=O? A. B. C. D. Trigonal pyramid, 109.5˚ Trigonal planar, 109.5˚ Trigonal pyramid, 120˚ Trigonal planar, 120˚ 132 27. 28. Which of the following sequences can be used to make A. H2 SO 4 CH2 I2 OH ----------> -----------> heat Zn(Cu) B. KOH CH2 I2 OH ---------> -----------> heat Zn(Cu) C. H2 SO 4 CHCl3 Br ----------> ----------------> heat KOC(CH3 )3 D. KOH CHCl 3 Br ---------> ----------------> heat KOC(CH3 )3 ? An unknown alkene was subjected to ozonolysis, and the product of the reaction was the compound shown. What is the structure of the unknown? O CH 3 O || | || CH3 CCH2 CHCH 2 CCH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 B. A. CH3 C. CH3 D. CH3 CH3 CH3 29. Which of the arrows gives the direction of the dipole moment of the molecule shown? Br Br C H A. H B. C. D. 133 30. Which of the following sequences gives cyclohexane from cyclohexanol? A. B. C. D. 31. KOH, alcohol, heat; then Zn, HCl Zn, HCl; then H2 , Pd H2 , Ni; then H2 SO 4 , heat H 2 SO 4 , heat; then H2 , Pt Which of the following compounds is the least soluble in water? A. 32. OH B. OH Cl D. Cl What are the bases in the reaction shown? OH + NH2 I O- + NH3 II A. I and III 33. C. III B. I and IV IV C. II and III D. II and IV What is the value of ∆H in kJ mol-1 for the reaction below? Bond energies in kJ mol-1 are: CH3 CH2 -OH, 383; CH3 CH2 O-H, 431; HO-H, 498; CH3 CH2 -OCH 2 CH3 , 335. 2 CH3 CH2 OH ---> H2 O + CH3 CH2 OCH 2 CH3 A. +29 34. C. -67 D. -96 Which of the SN2 reactions below is the FASTEST? A. B. C. D. 35. B. -19 CH3 Br + HC≡C– ---> CH3 C≡CH + Br– CH3 Br + HC≡CH ---> CH3 C≡CH + HBr CH3 CH2 Br + HC≡C– ---> CH3 CH2 C≡CH + Br– CH 3 CH2 Br + HC≡CH ---> CH3 CH2 C≡CH + HBr One of the two carbon-carbon bonding orbitals in ethylene, H2 C=CH 2 , is formed from the overlap of ____ orbitals on the carbons, and the other is formed from the overlap of _____ orbitals. A. sp, p B. sp2 , p C. sp2 , sp D. p, p 134 36. Rate data for the reaction shown is given in the table at right. What is the mechanism of this reaction? Run no. [CH3 CH2 I] [CH3 O– ] Rel. Rate 1 2 3 0.01 0.02 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.02 1 2 2 CH3 CH2 I + CH3 O– ---> CH3 CH2 OCH 3 + I– A. SN1 B. SN2 C. E1 D. E2 37. Which of the carbocations shown do NOT rearrange? + + + + I. CH3 CH2 CH2 CH2 II. CH3 CHCH 2 CH3 III. (CH3 )2 CHCH 2 IV. (CH3 )3 C A. I and III B. I and IV C. II and III D. II and IV 38. Which of the following compounds has the highest boiling point? A. CH3 CH2 ONa B. CH 3 CH2 OCH 3 C. CH3 CH2 CH2 CH3 D. CH 3 CH2 CH2 OH 39. Which of the following is the best synthesis of cyclohexene from cyclohexane? A. B. C. D. 40. KOH, alcohol H2 SO 4 , heat Br2 , light; then KOH, alcohol Br2 , CCl4 ; then H2 SO 4 , heat Which of the following is a sigma (σ) bonding orbital? Nuclei are indicated by solid dots, and the signs of the wave functions are shown. + A. - + B. + D. C. - - 135 + +