ALCOHOLS AND ETHERS ABLE TO: 1.
advertisement

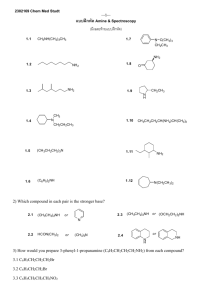
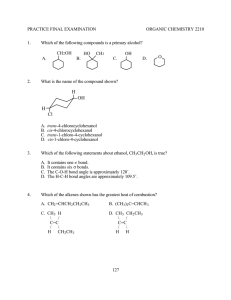
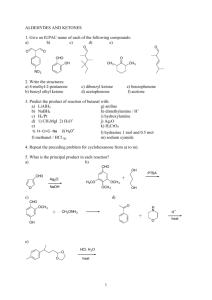
ALCOHOLS AND ETHERS A STUDENT WHO HAS MASTERED THE MATERIAL IN THIS SECTION SHOULD BE ABLE TO: 1. Give the IUPAC name when given the structure, and draw the structure given the name, of open-chain and monocyclic alcohols and ethers (alcohol nomenclature was first covered in Module 3; ethers are named as alkoxyalkanes). Also, draw the structure when given the common name, and name when given the structure: ethylene glycol, tetrahydrofuran, dioxane, and simple alcohols and ethers containing any of the alkyl groups listed in the objectives for Module 3. Also, draw examples of, and identify the functional groups in, thiols, thioethers, and disulfides. Note: thiols, RSH (alcohols, ROH) thioethers RSR (ethers ROR) disulfides RSSR (peroxides ROOR) 2. Predict relative physical properties, including boiling points and relative solubilities, of alcohols, ethers, sulfur-containing compounds, and other compounds. The principles involved were covered in previous modules. 3. Given the starting materials and reaction conditions, predict the products of the following reactions involving alcohols and ethers. Preparations of alcohols: Hydration of alkenes (see Module 8) Hydroboration-oxidation (hydroboration is a syn addition; replacement of the B by OH in the oxidation step occurs with retention, and the overall process is a net syn addition). Oxymercuration-Demercuration Reactions of alcohols: Acid-base reactions involving alcohols and their conjugate bases. The order of relative acidity is: mineral acids > carboxylic acids > water > alcohols > terminal alkynes > ammonia and amines > alkanes. Formation of carboxylate and tosylate esters Formation of alkyl halides from alcohols using hydrogen halides, PBr3 , and SOCl2 . Preparation of ethers: The Williamson synthesis of ethers (the SN2 reaction of an alkoxide with an alkyl halide). Note that methyl and 1˚ alkyl halides give the ether as the product; 2˚ and 3˚ halides give alkenes by an E2 reaction. 4. Using any of the above reactions, propose syntheses of compounds that can be made using alcohols as starting materials or intermediates. As always, synthesis problems may require any reaction that you have studied in the course so far. 5. Propose mechanisms, and predict and explain experimental results using your knowledge of mechanism. Important reactions include: Hydration and dehydration (covered in the previous two modules). Reaction of alcohols with hydrogen halides. 111 A STUDENT WHO HAS MASTERED THE OBJECTIVES ON THE PREVIOUS PAGE SHOULD BE ABLE TO SOLVE THE FOLLOWING PROBLEMS AND RELATED ONES: 1.1 1.2 2.1 Name each of the following compounds. a) HOCH 2 CH(CH 3 )2 b) CH3 CH2 O CH(CH 3 )2 | c) CH3 CH2 CH(CH 3 )C(OH)CH2 CH3 d) Draw each of the compounds named. a) 2-methoxy-5-methylheptane b) 3-tert-butyl-4-methylcyclohexanol c) tetrahydrofuran d) isopropoxycyclopentane B. CH3 (CH2 )2 CH(OH)CH2 CH3 D. (CH 3 )2 CHOCH(CH3 )2 Which of the following compounds is the least soluble in water? A. CH3 CH2 COOH 3.1 OH HO Which of the following compounds has the lowest boiling point? A. CH3 (CH2 )4 CH2 OH C. (CH3 CH2 CH2 )2 O 2.2 OH B. CH3 CH2 CH2 OH C. CH 3 CH2 COONa D. CH3 CH2 CH2 Cl Predict the products of the reactions given below (if any). a) (CH3 )3 C– + CH3 NH 2 -----> b) OH – + CH3 CH2 OH -----> c) (CH3 )3 C– + CH3 C≡CH -----> d) OH – + CH3 CH2 CH3 -----> e) CH3 NH – + CH3 CH2 OH -----> 3.2 Predict the organic product(s) of the reactions given below, including stereochemistry whenever appropriate. a) OH + PBr3 -----> 112 BH3 , THF H2 O2 , OH ---------------> -----------------> b) c) H3 PO 4 =CH 2 + H2 O ----------> COOH OH d) O || + CH3 CH2 C-Cl -----> e) (CH3 )2 CHO – + CH3 CH2 CH2 Br -----> CH3 f) CH3 O + -----> Br Hg(OAc)2 , H2 O NaBH 4 , OH ---------------------> -------------------> g) 4. Propose a synthesis of each of the compounds shown, from the given starting materials and any other needed reagents. O O || || a) CH3 CH2 CO from CH3 CH2 C-Cl b) c) from CH3 CH2 OH and O CH2 OH from =CH 2 CH3 d) from =CH 2 OH 113 OH 5. Propose a mechanism for each of the following reactions. H2 SO 4 , heat a) CH=CH 2 + H2 O ------------------> CH2 CH3 OH H2 SO 4 b) (CH3 )3 CCHOHCH3 ----------> H2 O + (CH3 )2 C=C(CH 3 )2 SOLUTIONS TO SAMPLE PROBLEMS: 1.1 1.2 Names of the compounds shown: a) isobutyl alcohol or 2-methyl-1-propanol c) 3-ethyl-2,4-dimethyl-3-hexanol Structures of the compounds named: a) 2-methoxy-5-methylheptane CH3 CHCH 2 CH2 CHCH 2 CH3 | | OCH 3 CH3 c) tetrahydrofuran b) cis-3-ethoxycyclohexanol d) ethylene glycol or 1,2-ethanediol b) 3-tert-butyl-4-methylcyclohexanol (CH3 )3 C H3 C OH d) isopropoxycyclopentane O-CH(CH3 )2 O 2.1 D 2.2 3.1 Predict the products D a) (CH3 )3 C– + CH3 NH 2 -----> (CH3 )3 CH + CH3 NH – b) OH – + CH3 CH2 OH -----> no reaction c) (CH3 )3 C– + CH3 C≡CH -----> (CH3 )3 CH + CH3 C≡C– d) OH – + CH3 CH2 CH3 -----> no reaction e) CH3 NH – + CH3 CH2 OH -----> CH3 NH 2 + CH3 CH2 O– 114 3.2 Predict the product(s) of the reactions given below, including stereochemistry whenever appropriate. a) OH + PBr3 -----> Br BH3 , THF H2 O2 , OH ---------------> -----------------> b) H OH c) =CH 2 OH H3 PO 4 + H2 O ----------> CH3 COOH OH d) O || + CH3 CH2 C-Cl -----> COOH O– CCH2 CH3 || + HCl O e) (CH3 )2 CHO – + CH3 CH2 CH2 Br -----> (CH3 )2 CHO-CH 2 CH2 CH3 + Br– CH3 f) CH3 O + CH3 + CH3 OH + Br -----> Br g) 4. Hg(OAc)2 , H2 O NaBH 4 , OH ---------------------> -------------------> Synthesis: O || a) CH3 CH2 C-Cl + HO O || -----> CH3 CH2 CO b) CH3 CH2 OH + HBr -----> CH3 CH2 Br + H2 O (CH3 )2 CHOH + Na -----> (CH3 )2 CHONa + 1/2 H2 CH3 CH2 Br + (CH3 )2 CHONa -----> CH3 CH2 OCH(CH 3 )2 + NaBr c) BH3 , THF H2 O2 , OH =CH 2 --------------> ----------------> 115 CH2 OH OH 4 Synthesis, concluded. H2 O, H2 SO 4 =CH 2 -----------------> d) CH3 OH 5. Mechanisms: a) CH=CH 2 H2 SO 4 , heat + H2 O ------------------> CH2 CH3 OH CH=CH 2 + H2 SO 4 -----> CHCH 3 -----> CHCH 3 + HSO 4 CH2 CH3 H CH2 CH3 + H 2 O ------> CH2 CH3 OH 2 CH2 CH3 + HSO 4 -----> OH 2 CH2 CH3 + H 2 SO 4 OH H2 SO 4 b) (CH3 )3 CCH2 OH ----------> H2 O + (CH3 )2 C=CHCH 3 (CH3 )3 CCHCH 3 + H2 SO 4 -----> HSO4 + (CH3 )3 CCHCH 3 | | HO OH 2 (CH3 )3 CCHCH 3 -----> H2 O + (CH3 )3 CCHCH 3 | OH 2 (CH3 )2 C—CHCH 3 -----> (CH3 )2 C—CHCH 3 | | CH3 CH3 (CH3 )2 C—CH(CH 3 )2 + HSO4 | H 116 -----> H2 SO 4 + (CH3 )2 C=C(CH 3 )2 Name ____________________________________________________ Ninth Drill Test (Sample) Organic Chemistry 2210 DR Answer All Questions 1) Draw cis-3-isopropylcyclopentanol 3) Which of the following compounds has the HIGHEST boiling point? CH2 OH CH3 OCH 3 4) 2) Name (CH3 )2 CHCH 2 CH2 CHOCH 2 CH3 | CH2 CH2 CH3 Cl Predict the product or products of each of the following reactions. a) OH + CH3 b) OH + -----> O || -----> Cl BH3•THF H 2 O2 , OH CH2 -------------> ------------------> O || d) (CH3 )2 CHCH 2 O + CH3 COH -----> c) 5) Propose a synthesis of each of the following compounds, beginning with the given starting material and using also any needed inorganic reagents or solvents. a) CH2 CHCH 3 | OH CH2 CH=CH 2 from b) (CH3 )2 CHCH 2 OCH 2 CH3 from 6) Propose a mechanism for the reaction shown: OH (CH3 )2 CHCH 2 OH + HCl -----> H 2 O + CH3 Cl CH3 117 Name ____________________________________________________ Ninth Drill Test (Sample) Organic Chemistry 2210 DR Answer All Questions 1. Give the IUPAC name of each of the following compounds. OH a) 2. b) OCH 3 B. CH3 CH2 CH2 OCH 2 CH2 CH3 D. CH 3 CH2 CH2 CH2 CHOHCH3 Predict the product of each of the following reactions. HBr OH ------> a) b) 4. c) Which of the following compounds has the LOWEST boiling point? A. (CH3 )2 CHOCH(CH3 )2 C. (CH3 )2 CHCHOHCH(CH3 )2 3. O PBr3 OH -------> Propose a synthesis of each of these compounds starting from 3,3-dimethyl-1-butene and any other needed reagents. a) 3,3-dimethyl-1-butanol b) 3,3-dimethyl-2-butanol 118 5. Complete the table of reactions by filling in the blanks with the letters corresponding to the appropriate compound or reagents. Not all answers will be used, and you may use an answer more than once. CH3 CH2 O Na CH3 CH=CH 2 CH3 CH2 OCH 3 H2 O, H3 PO 4 -----------------> BH3 •THF H 2 O2 , OH ---------------> ----------------> O CH3 CH2 C-Cl CH3 CH2 CH2 OH CH3 OH -----------> PBr3 -------> (CH3 )2 CHCH 2 Br CH3 Li A. -----------> B. CH3 CH2 CH2 OH C. CH3 CHOHCH3 D. CH 3 CH2 CH2 Br CH3 Br E. -----------> KMnO 4 , cold F. ------------------> H. CH 3 CH=CH 2 I. (CH3 )2 C=CH 2 O G. CH3 CH2 C-OH CH3 OH J. -----------> O K. CH3 CH2 C-OCH 3 119 L. (CH3 )2 CHCH 2 OH