N u
advertisement

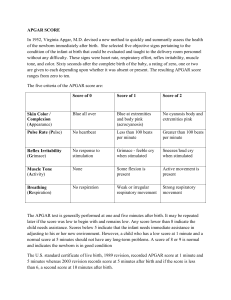
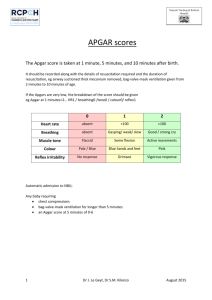
Nursing Care for the Newborn (( The Assessment )) الدكتور عبد المهدي عبد الرضا حسن جامعة بابل/ كلية التمريض Mental Health Nursing & PhD, pediatric APGAR scoring: The Initial Assessment •The most frequently used method to assess the newborn’s immediate adjustment to extrauterine life is the APGAR scoring system. •The score is based on observation to heart rate, respiratory effort, muscle tone, reflex irritability, and color, items measured 0,1,2 grades. •The APGAR scoring is taken 1 & 5 minutes after birth, and repeated after newborn’s condition stabilizes. •It assesses the physical & neurological status. APGAR SCORE APGAR Score Interpretation Example •A newborn assessed using APGAR scoring system, found with heart rate = 120 bpm, slow and weak cry, well flexed, the newborn found crying and sneezing as a response , and pale ….. how much in APGAR? And what will be your intervention ????. Answer Assessment for gestational age (Ballard scale) •Posture : With infant quite and in supine position, observe degree of flexion in arms and legs. Muscle tone and degree of flexion increase with maturity . Full flexion of the arms and legs = 4. •Square window: with thumb supporting back of the arm below wrist , apply gentle pressure with index and third fingers of dorsum of hand without rotating infant’s wrist. Measure angle between base of thumb and forearm=4 •Arm recoil: with infants supine, fully flex both forearms on upper arms, hold for 5 minutes; pull down on hands to fully extend and rapidly release arms. Observe rapidity and intensity to of recoil to a state of flexion. A brisk return to flexion = 4 •Popliteal angle: With infant supine and pelvis flat on a firm surface, flex lower leg on thigh and then flex thigh on abdomen. While holding knee with thumb and the index finger, extend lower leg with index finger of other hand . Measure degree of angle behind knee. An angle of less than 90 degrees = 5. •Scarf sign: With infant supine , support hand in midline with one hand; use other hand to pull infant’s arm across the shoulder so that infant’s hand touches shoulder. Determine location of elbow in relation to midline . Elbow doesn't reach midline = 4 •Heal to ear sign: With infant supine, and pelvis flat on a firm surface, pull foot as far as possible up toward ear on same side. Measure distance of foot from ear and degrees of knee flexion ( same popliteal angle). Knees flexed with a popliteal angle of less than 90 degree = 4 Weight related to gestational age •Appropriate for gestational age 10th-90th . •Small for gestational age < 10th . •Large for gestational age > 90th . •The normal birth weight is 2700- 4000g . Growth measures •Head circumference : 33- 35.5 cm •Chest circumference : 30.5- 33 cm, 2 cm less than head circumference. •Abdominal circumference. •Length: head (cephalic) to heal: 48- 53 cm •Body weight : 2700- 4000 g. ( loses 10% of weight in the first 3 to 4 days after birth). Vital signs •Axillary temperature: 36.5- 36.6 . Avoid rectal in the first day . •Pulse : 120- 140 bpm •Respiration : 30- 60 bpm •Blood pressure : 65/41 mmHg in the first 3 days. Compared with lower extremities. •Vital signs must be checked every hour for 2 hours, then once every 8 hours until discharge.