Approach patient with asthma :---
advertisement

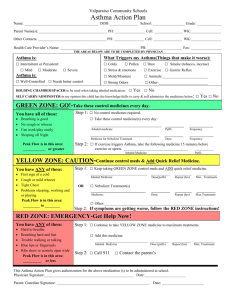
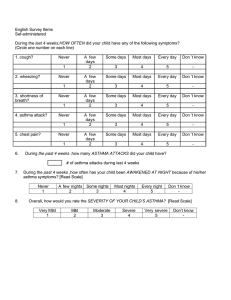
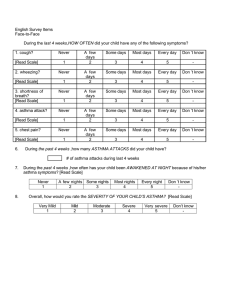
Approach patient with asthma :--to asses severity of asthma by :-- a- scoring of asthma b- classification of severity of asthma A- scoring of asthma :- depend on many factors including mental state , cyanosis , accessory muscle , air exchange , pulsus parodoxus , Pao2 , Paco2 Scoring :-- 1-0-4 no needs admission impending resp failure – 5-6—2 more than 7 – resp failure – needs -3 I.C.Uwith intubation -1 - :-Scoring of asthma zero mental state normal cynosis non accessory muscle none air entery good pulus paradoxus < 10 PaO2 70-100 PaCO2 <40% 1 2 agitated or depressed in room air moderate fair 10-40 < 70% in room air 40-65 coma- 1 in 40% o2-2 marked-3 poor-4 > 40- 5 < 70% in 40% o2-6 > 65-7 :-Scoring no immediate danger ---------- home discharge :- 0-4 -1 impending respiratory failure ------ hospital admission :- 5-6 -2 respiratory failure --------- intensive care unit :- 7- > 3 -2 - B-classification :- can asses severity of acute exacerbation in children : S&S Mild Moderate severe 1-altertness normal&may be agitated N or usual agitated usually agitated color normal pale cyanosis- 2 • resp rate normal to 30% 30-50%above normal 3-more than-3 • above normal 50% dyspnea mild dyspnea on walking moderate sever at rest-4 speak in normal speak in phrases in single word sentences or partial sentences partial phra accessory no to mild moderate retraction sever with-5 muscle retraction intercostal, sternal nazal flaring • used hyperinflation of chest auscultation expiratory expiratory + inspiratory silent chest-6 PEFR 70-90% above normal 40-70% less than 40%-7 Pco2 less than 42% less than 42% more than 42%-8 O2 saturation more than 95% 90-95% less than 90% -3 • • • • • • • • • -9 Aims of therapy :-1-to reverse asthmatic symptoms . 2-prevent or diminished the frequency of recurrence of symptoms 3-maintain normal or close to normal pulmon. Function test • .maintain normal activity level including exercise-4 :---Treatment of acute asthma • • )depend on severity & location ( home , emergency ward ,hospital :--Home management • • PEFR :- done every 2-3 times per day ( if PEFR is decreased -1 • needs medical intervention & if decreased between 50-80% • needs change in medical therapy & if below 50% needs acute • intervention • inhalation therapy by ventolin inhalor-2 • incomplete response needs short course of cortico steriod-3 • 1-2mglkg lday • medical attention for sever exacerbation & persistent resp- 4 • ---distress . --4 In emergency ward :-1-O2 therapy :-to improve oxygenation . 2-ventolin or albuterol nebulizer:-0.15mglkg every 20 minutes for one hour. Inhaled iprotropium bromide ( given every 6 hr in adose o.25 mg for 6 • may need systemic C.S either orally or I.V-3 ) years of age and o.5 mg for those 12 years of age • in sever case , used S.C adrenalin o,o1ml/kg given once or -4 • twice at interval 20 minutes to obtain optimum relief ( 0.5 ml • )is often effectively • :-after one hr ---re-asses • if sustained improvement of symptoms , normal physical finding -1 • O2 saturation of more than 92% , PEF of more than 70% for & • .hr ----home discharge 3 • if discharge , on 1-ventolin inhalor for above 5 years or oral butadine 2-.3-7 day course of C.S • if no response ( persistent symptoms ) ---asses & hospital -2 admission :---a- if moderate distress needs ward admission • b- if sever distress needs I.C.U • --5-- Indication of hospital admission :-1-moderate to sever exacerbation that not improved within 1-2hr .from intensive therapy in emergency ward • has risk factors for morbidity & mortality ( risk factors for sever-2 • ) :---asthma • A- biological – 1-previous sever asthma exacerbation • sever air way obstruction-2 • rapid attack 4- sever air way hyper- -3 responsiveness • poor response to systemic C.S-5 • repeated visit to emergency ward in last 48 hrs-6 • .or more hospital admission of the past year 7-2 • :--B-economic & psycho-social • poverty 2- crowding 3-mother less than 20 -1 years • poor education 5-family dysfunction -4 • psychopath in parent & children -6 • C-environment :- 1- allergen exposure 2-smoking • air pollution 4-urban environment-3 • ---6--- Status asthmatics :-defined by increasing sever asthma that is not respond to treatment that are usually effective . :--- When diagnose , is made A-admission to I.C.U & doing chart for observation for PR,RR, BP send for CBP, S.electrolyte , cardiac monitor & blood gas , )analysis ( PO2, PCO2, PH :-B-start therapy O2 therapy 2- correction of dehydration- 1 bronch-dilator by a-continuous or frequent Nebulizer with O2- 3 b- aminophylin( 5mglkg ) or continuous in a dose 0.75-1.25 mglkg lhr c- anti muscurine like atropin sulfate ( o.o5- o.1mglkg atropin sulfate in adose of not > o.25mg ( S.E like mental confusion , )tachycardia iprotropium bromide has fewer S.E than atropin C.S ( methyl prednisolone in adose of 1-2 mg /kg /every 6 hr 5-- 4 mechanical ventilation for sever hypoxia o2 saturation of < 90% 6 .– sedation is Contra indication chest x-ray should be done in all patients & repeated as indicated -7 , to detect complication . 8-other therapy like Mg sulfate Chronic asthma :--classify into :-( mild , moderate , severe ) depend on history , physical .examination & pulmonary function test severity of asthma Day with symptom night sym FEV1 1-mild intermittent <2episode per wk <2 per month >80% • mild persistent 3-6 episode per wk 3-4 per moth >80%-2 moderate persistent daily symptoms >5night per month 60-80%-3 Sever persistent Continuous Sym. Frequent <60%-4 • • Prevention :-• • Mild intermittent :-- 1-no daily medication needed 2-used short acting inhaled B2 agonist ( salbutamol , albuterol ) as needed ( 1-3 puff every 4 hr ) • Mild persistent :- one daily medication like ( low dose inhaled • C.S 40micro-gram 1-4 puff per day ), intal ( cromolyn) ,nedocromil • & leukotrin antagonist like montolukast , zafirlukast • Lipo-oxygenase inhibition like zileuton which given above 12 years -8-- • • Moderate persistent:--either:-A-one daily medication by medium dose inhaled C.S ( 80micro-gram 2-4 puff / twice a day Or B-two daily medication like low to medium dose inhaled c.s + long )acting bronch-dilator especially for night time symptoms ( salmetrol • sustained released theophylin or long acting B2 agonist, :-Sever persistent :--3 daily medication • • +high dose inhaled c.s 80 micro gram puff l twice a day -1 • +long acting brncho-dilator( salmetrol )or B2 agonist-2 oral c.s in a dose 1 mg lkg l day of not exceed 60 mg l day then -3 gradually reduce dose to lowest dose which control symptoms • .correction comborbid condition & emotional disturbances -4 :--Exercise induced asthma :--prevented by • • inhalation adrenerhic drug immediately before exercise like -1 inhaled albuterol which give protection for 4 hr . OR inhaled .salmetrol given halve hr before exercise • inhaled cromolyn or nedocromil shortly before exercise -2 • ---thank you ---9 • • •