Document 12456308
advertisement

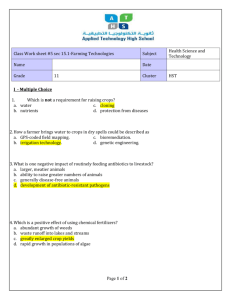
Lec.8 Dr. Saad Ali Ihsan Types of Natural Antibiotics using traditional herbs and plants as natural antibiotics is a practice now being supported by modern science. As pharmaceutical antibiotics cause an increasing number of side effects in people, such as digestive problems, allergies, decreased immune function and antibiotic-resistant microbes such as MRSA, doctors and patients are both looking for new alternatives in the fight against infections. Some plants have been supported by medical research to actively fight a range of bacteria and viruses, while stimulating our own immune defenses at the same time. 1. Garlic (allium sativum) o Considering that garlic can be cheaply purchased and consumed daily as a food, this makes it a truly effective and economical immune support. In addition to stimulating white blood cells, garlic is effective against a range of microbes, including candida albicans, e. coli, salmonella, influenza, the common cold virus and staphylococcus aureus. Researchers Vinay Kumar Sharma, Ph.D. and Amit Kumar, Ph.D. published findings in "The Journal of Nutritional Science and Vitaminology" in 1999 that showed garlic was also an effective antimicrobial agent against antiobiotic-resistant strains of bacteria such as MRSA. Note: Garlic may reduce blood pressure in some people, and should be avoided by people taking warfarin. 2. Echinacea root (echinacea spp.) The root of Echinacea is rich in plant chemicals that stimulate the production and synthesis of white blood cells within the body. Because of this, Echinacea is beneficial in supporting recovery from all infectious diseases, as it strengthens natural defenses against microbes. Researcher Sachin Shah and colleagues from the University of Connecticut published findings in the prestigious medical journal "The Lancet" in 2007 that showed purple Echinacea was effective in reducing both the incidence and duration of the common cold. 3. Goldenseal (Hydrastis canadensis) and Barberry (Berberis canadensis) c Barberry and goldenseal share a common chemical called berberine that fights infection. This chemical is antiviral, antibacterial, antiprotozoal and antifungal, supporting the use of these two plants in treating colds, flus and other infections. According to Hyeon-Hee Yu and colleagues who published their study in "The Journal of Medicinal Food" in 2005, berberine was used alongside antibiotics in treating MRSA (Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus ) .This combination was found to be more effective in treating MRSA than when using the antibiotics alone. Note: Goldenseal may increase blood pressure, and should be avoided in those taking blood pressure medications. 4. Tea tree oil (Melaleuca alternifolia) Tea tree oil is an essential oil made from the leaves of the Australian plant Melaleuca alternifolia. When diluted in a base of carrier oil, cream or ointment, tea tree oil can be used for its potent antibacterial, antifungal, antiviral, antiprotozoal and anti-inflammatory properties externally. Tea tree is effective against salmonella, e. coli, candida albicans, MRSA, tinea pedis, herpes simplex and trichomonas vaginalis. In a review of scientific research published in "Clinical Microbiology Reviews" in 2006, researcher C.F. Carson and colleagues from the University of Western Australia found that the majority of research supports the topical use of tea tree oil in fighting microbes. 5. Manuka Honey Manuka honey comes from a plant native to New Zealand and contains a chemical called "Unique Manuka Factor" which makes it effective as a tissue healer and antibacterial agent for treating wounds, ulcers and burns. According to Talal Alandejani, M.D. and colleagues who published research in the scientific journal "Otolaryngology" in 2008, manuka honey was more effective than antibiotics when treating a range of bacteria, including MRSA. 6- Propolis Propolis is a mixture of natural resins that bees collect from flower buds, plant sap and other plant sources. They use it not only to seal small gaps in the bee hive, but also to prevent decomposition within the hive. For example, if a small animal like a lizard enters the hive and dies there, the bees would seal it with propolis - making it like a mummy - and rendering it harmless and odorless. 7- Olive leaf extracts In recent years, olive leaf and olive leaf extracts (OLE) have become popular health supplements. They are said to be powerful antioxidants, with one 2005 study by Dr L Stevenson of Southern Cross University, Australia, reporting it to be twice as powerful an antioxidant as green tea and four times more powerful than Vitamin C. And yes, olive leaf extracts are also claimed to enhance immune function and act as natural antibiotics - and also as anti-virals and anti-parasites. 8- Colloidal silver Yet another product widely marketed (usually by multi-level marketing companies) as an alternative to antibiotics is Colloidal Silver. This is NOT something that I would recommend, but I feel it is useful to discuss it here because it is quite widely touted. 9- Hydrogen peroxide ( H2O2 ) If you don't mind something that is perhaps not totally natural - in the sense that it is not normally consumed as food – then hydrogen peroxide is a good option. It is effective, inexpensive and, if used properly, perfectly safe. Used properly means, for example, putting a drop or two of pharmaceutical grade 3 percent hydrogen peroxide inside the ear canal. Let it bubble for about two minutes, then tilt your head to drain it off. With its natural antibiotics and anti-viral properties, this can help prevent a flu from becoming fullblown if it is administered in the early stages. When you already have a flu, it helps to regularly sip highly diluted hydrogen peroxide - a few drops of already diluted 3 percent hydrogen peroxide, added to a big jug of water. Take one or two sips regularly throughout the day. Killing bacteria in the atmosphere Besides killing bacteria inside your body, there may be times when you want to destroy them in the air - for example, to disinfect your home when someone at home is ill with an infectious disease. This is where essential oils come in handy as very powerful natural antibiotics. While bacteria and viruses have evolved into "superbugs" that are resistant to powerful drugs, none are known to have become resistant to essential oils. That's how potent and useful essential oils are. Essential oils usually refer to pure, aromatic oils extracted from herbs and spices. But they also include the oils of other plant products, such as lemon oil, or tea tree oil - which is one of the most powerful known disinfectants. Helpful essential oils for destroying bacteria and viruses include the oils of lemon, oregano, thyme, pine, cinnamon, cloves, peppermint, lavender, rosemary and tea tree. Most essential oils are too potent for direct human consumption. It is okay - and beneficial - to eat the herbs and spices from which these oils are extracted, but not ok to consume the oils directly. So one way to use these essential oils as natural antibiotics is to spray into the atmosphere. This, alone, is often good enough to destroy the bacteria and viruses present within one or two minutes. Another way is to add a few drops into a dehumidifier, atomiser or aromatherapy burner, and let it run for a few hours. And if you are wearing a flu mask, it would also be helpful to add a few drops of essential oils to your mask, so that you breathe in clean, disinfected air. Alternatively, add a few drops to your hankerchief and breathe through it every now and then. As you can see, there are lots of natural antibiotics to choose from. And many of these are actually more effective than the synthetic, unnatural and harmful antibiotics being peddled by the pharmaceutical industries. Biosynthesis of Penicillin’s : The amino acids ( Cysteine & Valine ) are incorporated into the ( 6 – aminopencillanic acid ) portion of pencillin molecules, and the acyl group of pencillin G ( Benzylpencillin ) is derived from phenylacetic acid. As in Fig. ( 11 – 8 ) the tripeptide, is the precursor of isopencillin N, Epimerization of the side chain yields pencillin N. In pencillin producting pathways, the side chain is subsequently cleaved at the amide bond and replaced with phenylacetic acid to yield pencillin G. In cephalosporin biosynthesis pathways, enzyme called an (Desacetoxycepnaiosporin C. synthase ) ( DOAC synthase or expandase ) acts upon pencillin N to generate the six – membered ring characteristic of cephalosporins. Further modification of the methyl group on this ring eventually yields Cephalosporins. The antibiotics which containing the B-lactam nucleus were solely the domain of fungi ( Pencillium & Cephalosporium ), we now know that many types of B-lactam metabolites are found also in several species of streptomycetes and some non-actinomycetes prokaryotes as well . Biosynthesis of Tetracycline’s : Studies confirmed that tetracycline antibiotics originated through acetatemalonate metabolism. These pathways involve head-to-tail condensation of two carbon units to form intermediates termed “Polyketides.” Their formation deviates from the fatty acid pathway by a disruption or lack of a normal reduction-dehydration-reduction sequence as the chain elongates. Subsequent metabolic steps yield the characteristics constituents. Mutant strains of tetracycline producing have been selected for genetic blocks in the biosynthetic pathway and have been used to clarify a number of the sequential steps. Its believed that a malonamyl-CoA residue serves as a primer and that eight malonate units undergo stepwise condensations with the addition of C-2 units and decarboxylation to yield a liner C-19 polyketide ( Fig. 11 – 13 ) P.256 . Carbonylmethylene condensations yield the tetracyclic pretetramide nucleus. Methylation of the C-6 position of the pretetramide is an early step in the biosynthesis of most tetracyclines, but this step is omitted in the formation of the naturally occurring demethyltetracyclines. Hydroxylation of the C-4 position and dearomatization to yield a 4-keto intermediate appears to precede 7-chlorination. Halogenation must precede introduction of the 4-amino group, which is methylated stepwise. Terminal reactions in the biosynthetic sequence are hydroxylation at C-6 and reduction of a double bond in ring B; it is interesting to note that the presence of a 7-halogen substituent apparently inhibits 5-hydroxlation. ( Fig. 11 – 13 ) show that : Polyketide ______________ 6 – methylpretetramide ___________ ( Compound ) _____________ ( Compound ) ____________ (Compound) ___________ Chlortetracycline. Isolation & Purification of Antibiotics : Liquid – liquid extraction using some water – immiscible organic solvent is the approach utilized for most antibiotics. Highly polar antibiotics such as neomycin and other aminoglycoside antibiotics, are usually recovered from the culture broth by adsorption on some suitable adsorbents . Many adsorbents remove antibiotics of this type from culture broths with varying degrees of selectivity. Use of charcoal of controlled activity grades and elution of the antibiotic with dilute acid is a typical example of this isolation approach. Once the crude antibiotics has been recovered from the nutrient broth, it is subjected to chromatography, recrystallization, or other standard manipulations to effect an appropriate degree of purification. It should be noted that attainment of chemical purity is usually considered impractical and unnecessary for therapeutic purposes. Separation of closely related antibiotics molecules is often unfeasible. The presence of up to 6% chlortetracycline in commercial tetracycline represents a practical application of such purification considerations. Accepted standards of purity for antibiotics and antibiotic preparations are controlled by the United States Pharmacopoeia. Qualitative and quantitative evaluations of antibiotic preparations for adherence to established standards utilize both biologically and chemically based tests. Calorimetric and spectrophotometric approaches and definitive measurements have largely replaced microbiologic assay and arbitrary units for quantitative purposes. ****************************************************************************