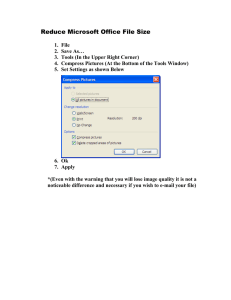
26 O
advertisement

26 education SUNDAY, DECEMBER 19, 2010 A comprehensive study of teachers’ absence The study of teachers’ absence aims to define the problems and find solutions. According to the study the absence of male average is higher than female teachers. At the same time the average absence of unmarried teachers is higher than married people. The study finds many reasons for this problem O ne of the most important tasks of educational systems worldwide is their effective investment of human resources in order to ensure quality education, enlightened by strategic plans which are aimed at raising the efficacy of performance. This can only be realised when these resources work efficiently to achieve expected targets, which causes a sense of anxiety for those in charge of such systems. Teachers’ absence negatively affects the educational process especially when it is related to job dissatisfaction and laws and regulations which govern the operation of educational institutions. Within this framework, Dr Saliha A Alissan, Associate Professor in the College of Education at SQU, in co-operation with researchers from the Ministry of Education, conducted a study entitled: ‘Reasons for Teachers’ Absence in the Light of some Demographic Variables’ to investigate this matter. Objectives The study conducted by Dr Alissan aims to execute an analytical study of the reasons for teachers absence in the Sultanate of Oman, an obstacle which impedes the process of learning and teaching in government schools. The study also aims to look for the most efficient solutions to raise the efficacy of school performance through the following: 1) To find the reasons for teachers absence in Oman and to discover the relationship between this absence and specific demographic variables. 2) To get acquainted with the previ- ous literature on this question to discover the most important factors and variables causing teachers absence and teachers’ attitudes towards the teaching profession. 3) To suggest mechanisms which aim to reduce this absence and lead to a better investment of human resources. The study investigated the reasons behind teachers absence in Oman in order to know the role such variables as gender, experience, social status and location of residence play in such absence. To achieve these goals a seventy-five item — questionnaire distributed into six themes has been developed and applied to a random sample of seven thousand teachers (male and female) chosen from five educational regions. The results indicated that among the most significant reasons for teachers absence are: 1) Job dissatisfaction 2) Teacher professional training programmes 3) School internal competence 4) Laws and regulations 5) Family and social status and 6) Finally teachers’ health condition. The demographic changes had a significant statistical influence, the gender variable had a higher percentage among the males while in the experience variable there where more reasons (for absence) given by those with less experience, while centage of absence among single teachers in the social condition variable the per- was higher among the married, and finally in the location of residence variable the percentage of absence among teachers working outside their resident locations were higher among those working within the same area of their residence. Job Satisfaction Teachers’ absence is caused by four major reasons: the wearisome school day with a mean of (4.23), the lack of definite criteria to assess good performance for promotion, and committed attendance with a mean of (4.12) followed by lack of correlation between incentives and salaries and the teaching load with a mean of (3.96) followed by the unavailability of chances for teacher professional development with a mean of (56). Means of minor reasons behind teachers absence varied (this highest 3.34) was in response to item teacher rarely have a chance to teach the subject he knows best in school, while the lowest 2.61 was in response to Early Warning Flood Detection System Based on Wireless Sensor D r Ayman El Najjar has conducted a research project on “The Design Of An Early Warning Flood Detection System Based On Wireless Sensor Networks.” The project was triggered by the advent of the adverse weather conditions that hit many parts of Oman in June 2007 and caused loss of life and damages to property worth hundreds of millions of Omani Rials. Yet the long-term effects of these floods are significantly worse and the recovery efforts are substantially more challenging due in part to the lack of early warning systems and infrastructure. Dr El Najjar believes that the early warning of authorities and communities against the incoming flood provides an effective solution because it gives them sufficient time to evacuate and protect their properties. It also allows authorities to take some actions like rerouting traffic away from wadis, automation of the road closure process in case of wadi crossings, and sending SMS warning messages through mobile phones to those who reside near the path of the wadi. Dr El Najjar’s research proposal aims to design and deploy an early warning system using wireless sensor networks to detect floods. Traditional flood warning systems, he argues, usually require complex centralised computing that can be difficult without adequate infrastructure. Dr El Najjar explains that we need to explore new techniques for distributing the computation of flood detection within a wireless sensor network, along with developing an automated warning system that could be linked, for example, to the ROP. This early warning system can first be tested by its deployment at Wadi Al Lawami in the Wilayat Al Seeb, because of its closeness to SQU. If the test is successful, it will be implemented in other Wadis. the item lack of trustworthy co-operation between the headmaster and the teachers in delivering their professional duties. Professional training programmes A major reason for teachers absence is due to the lack of teacher education programmes which foster a sense of belonging to the teaching profession with a mean of (3.68) and because such programmes are not prepared by experts in teachers administrative role in school, the minor reasons ten in number had a mean higher than average in response to item number three (lack of concentration in teacher education programmes in creating the teachers professional culture with a mean of 3.50 while the lowest mean for minor reasons in response to the item (lack of classroom management skills in teaching education programmes had a mean of (2.87). School Internal Efficiency There are five reasons behind teachers absence which depend on school internal efficiency (means varied between 3.84 in answer to the item) on filling make-up classes causes teachers absence, and the mean of 3.52 response to item (numerous hours of duty within the school day). The minor reasons which cause teachers absence in this aspect are eight and their means varied: the highest 3.41 was in answer to item (breaks between classes were not enough) and the lowest 2.51 in answer to item (physical classroom environment is unhealthy), the remaining thirty reasons had no influence on the teachers absence. Laws and Regulations Most reasons for teacher absence related to laws and regulations are secondary and their means varied between the highest of 3.30) in answer to item (laws for checking teachers absence are not compatible with developments in the educational systems) while the lowest mean was in answer to item (2.61) (lack of data and laws concerning teacher absence). The conclusions of this theme included only two items which did not have any effect or influence on teachers absence like (justifications for teachers absence 0.47 and (loss of continuous follow-up of teachers absence 2.32. Social and Family Conditions There is one major reason behind teacher absence with a mean of 3.99 in answer to item (my absence depends on the sudden sickness of a family member). The means of the other four minor reasons varied; the highest (3.20) was in answer to item (due to my many family responsibilities) and the lowest 2.73 in answer to item (to take care of elderly family members). The five remaining reasons included in this team did not have any significant influence on teachers absence and their means varied between 1.91 to 2.48. Health Condition There are four minor reasons behind teacher absence in this variable, and their means varied between the highest 3.41 in answer to item (school teaching requires my standing for long hours) and the lowest in answer to 2.65 (accompany a family member due to his or her health condition). The rest of the ten items included in the sixth theme did not have any significant influence on teachers absence and their means varied between 1.59 to 0.35. Oil bioremediation by cyanobacterial consortia under extreme environmental conditions D r Raeid Abed, of the Department of Biology, College of Science, is currently conducting a research project entitled: “Oil Bioremediation By Cyanobacterial Consortia Under Extreme Environmental Conditions”. Dr Abed believes that oil pollution of the marine environment poses serious threats for the economy and tourism in Oman. The project aims at designing a new bioremediation approach based on the use of indigenous cyanobacterial consortia which dominate oil-polluted coastal microbial mats. It is hypothesised that the presence of cyanobacteria in these consortia will facilitate degradation processes and circumvent the expensive use of fertilisers by fueling the oildegrading bacteria with the necessary oxygen, nitrogen and organics via their nitrogen fixation, photosynthesis and fermentation processes. On the other hand, the microbial mats of Oman (Wadi Al Milh-Qurayat and oil-wells in Dakhilyah) are expected to be rich in novel halophilic and thermophilic oil-degrading bacteria, which will efficiently degrade oil components under the harsh local environmental conditions. Dr Abed explains that the proposed study will identify and characterise cyanobacteria and their associated oil-degrading aerobic chemotrophs from different polluted microbial mats using state-of-the-art molecular techniques such as denaturing. Dr Abed believes that oil pollution of the marine environment poses serious threats for the economy and tourism in Oman. The project aims at designing a new bioremediation approach based on the use of indigenous cyanobacterial consortia which dominate oil-polluted coastal microbial mats A Database on Arabian Sea Ecosystem I n his study entitled “A Database On The Arabian Sea Ecosystem”, Dr S Piontkovski from the College of Agricultural Engineering and Marine Sciences has observed that the Arabian Sea possesses one of the thickest oxygen-depleted layer known anywhere in the World Ocean, winds and currents occasionally push this layer up into the surface which indirectly leads to unpredictable mass killing of fish along the Omani coast. The physical-biological mechanism, linking water dynamics with these fish killing is still unknown. Dr Piontkovsk proposes to establish a basis for the analysis of this mechanism through the compilation of an oceanographical database, and the analysis of the physical-biological interactions between oceanic and coastal waters. A multilateral data from 10 international expeditions to the Arabian Sea, the SQU coastal surveys, and data from the MODIS satellite will be used. The proposal, Dr Piontkovski believes, will facilitate the ongoing coastal sampling and the taxonomical sample processing. The expected results will be presented in the form of the CD-mounted database (disseminated among the SQU faculty, post-graduate students, Omani Ministry of Fisheries), series of scientific papers, and included in appropriate SQU course materials.