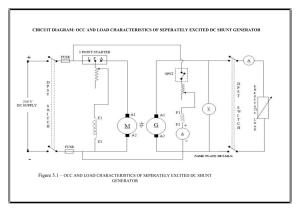
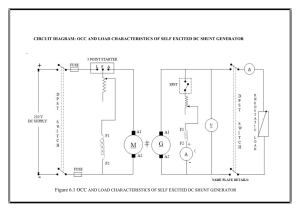
Lab Information -- Direct Current Machine Experiments
advertisement

Lab Information -- Direct Current Machine Experiments EXPERIMENT 4 LOAD CHARACTERISTICS OF A SELF-EXCITED SHUNT GENERATOR PURPOSE: To study the load characteristics of a self-excited shunt generator at rated speed and voltage and to determine the generator internal characteristics. APPARATUS: 1. Two DM-100/A DC Machine (one as generator, one as motor). 2. One SLA-100/D Tachometer 3. One 0 to 150 volt DC voltmeter 4. One 0 to 2.5 A DC ammeter 5. One 0 to .5 A DC ammeter 6. One resistance load RL-100/A 7. One 0 to 125 V/5A DC power supply PROCEDURE: 1. Couple the DC generator to the DC Motor and make the connection shown in Figure 4. Make sure power supply is in OFF position. 2. Adjust the generator's field rheostat knob to its max. resistance; (fully CW position). Adjust the motor's field rheostat to its minimum resistance, (fully CCW position). 3. Have the instructor check your connections and then start the motor. 4. Adjust the speed to 1800 rpm by slowly increasing the output of the 125V DC supply to 125 volts and then use the motor's rheostat knob to bring the motor up to speed. Adjust the generator's output to 130 volts by means of its rheostat. 5. Perform a load test on the generator from no-load to approximately 1.2 amperes load. This is done by decreasing the resistance load, first no load and then from 1000 ohm to approximately 83.33 ohm. It is necessary to adjust the 125V DC supply after each load step is applied to maintain 1800 RPM. Record the armature volts, load current, field current, and speed. 6. Measure the resistance of the armature circuit the same way it was done in exp. 1. REPORT: Using the data obtained, plot the armature terminal voltage as ordinate versus the load current as abscissa. Explain the shape of this curve. Calculate the voltage drop due to armature resistance (add two volts for brush drop). QUESTIONS: 1. How does each of the following cause voltage drop in a self-excited generator? A. Armature circuit resistance B. Armature reaction 1. Reduction of field current 2. Was there an additional cause of voltage drop in this experiment aside from the above three sources? 3. Calculate the percent voltage regulation? FIGURE 4