Formulaes to Remember
advertisement

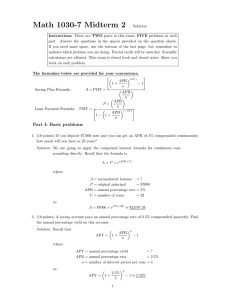
Formulaes to Remember This is not allowed to take to the final. 1. Use percentage as fraction A is p% of B. p% = A , B A = p% × B, B= A p% 2. Use percentage as changing Old value rise p% to new value. p% = (new value) − (old value) old value new value = (1 + p%) × (old value), old value = new value 1 + p% 3. Use percentage to compare Compared value is p% more than reference value. p% = (compared value) − (reference value) , reference value compared value = (1 + p%) × (reference value), reference value = compared value 1 + p% 4. Compound interest formula for interest paid ONCE a year A = P × (1 + APR)Y , APY = APR 5. Compound interest formula for interest paid more than once a year µ ¶nY APR A=P × 1+ , n µ APY = 1+ APR n ¶n −1 6. Compound interest formula for interest paid continuously A = P × e(APR×Y ) , APY = eAPR − 1 7. Rate of change rule rate of change = absolute change in dependent variable absolute change in independent variable 8. General formula for a linear model dependent variable = (initial value) + (rate of change) × (independent variable) Formulaes 9-12 are for a quantity growing exponentially at a rate of P % per time period. 9. Approximate doubling time formula (rule of 70) Tdouble ≈ 70 P WARNING: Be aware of the unit! 10. Exact doubling time formula Tdouble = log10 2 log10 (1 + P %) 11. General formula for an exponential growth with respect to doubling time new value = (initial value) × 2t/Tdouble 12. General formula for an exponential growth new value = (initial value) × (1 + P %)t Formulaes 13-16 are for a quantity decaying exponentially at a rate of P % per time period. 13. Approximate half-life formula Thalf ≈ 14. Exact half-life formula Thalf = − 70 P log10 2 log10 (1 − P %) 15. General formula for an exponential decay with respect to half-life new value = (initial value) × µ ¶t/Thalf 1 2 16. General formula for an exponential decay new value = (initial value) × (1 − P %)t 17. Perimeters and areas of two-dimensional objects see Examples on 11/29 for pictures Object Circle Square Rectangle Parallelogram Triangle Perimeter 2πr 4l 2l + 2w 2l + 2w a+b+c Area πr2 l2 lw lh 1 2 bh 18. Surface areas and volumes of three-dimensional objects see Examples on 12/1 for pictures Object Sphere Cube Box Cylinder Surface area 4πr2 6l2 2lw + 2wh + 2hl 2πr2 + 2πrh Volume 4 3 3 πr l3 lwh πr2 h