Unit 3 Test Review – Cells Name ____KEY_________ Hour _____
advertisement

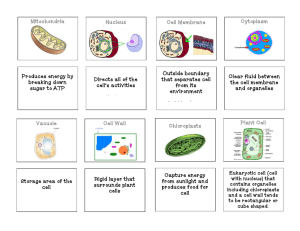
Unit 3 Test Review – Cells Name ____KEY_________ Hour _____ List the 4 scientists who worked with early cell discovery & explain what they viewed under the microscope. a. Anton Van Leeuwenhoek – he used a simple light microscope to view objects/had one lens. Observed pond life, blood, etc. he sketched what he saw. b. Robert Hooke – used compound light microscope to study cork (oak tree bark) and saw geometric shapes that he called “cells”. c. Matthias Schleiden (1830’s) – observed plants & concluded that all plants are made of cells. d. Theodore Schwann – observed animals and concluded they are made of cells. Use the diagram to the right to fill-in the spaces below with the correct cell structure or organelle. A. vacuole B. endoplasmic reticulum C. ribosomes D. cell/plasma membrane E. Golgi body/apparatus F. nucleus G. nucleolus H. mitochondria J. lysosome The cell theory is composed of three ideas. What are they? a. All organisms are composed of one or more cells. b. The cell is the basic unit of organization of organisms. c. All cells come from preexisting cells. List the features that are shared by all cells (both prokaryotic and eukaryotic). In other words what do they have in common? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Ribosomes – protein synthesis Plasma/cell membrane – selective barrier Cytoskeleton – cell structure and support Cytoplasm – gelatinous fluid that the organelles reside in DNA – code of life, man! Plant Cells vs. Animal Cells Fill in the following for Plant Cells Distinguishing Organelles Distinguishing Shapes/Features Organized, rectangular shape, bigger vacuole Cell Wall Chloroplast Plant Cell Organelles shared with Animals Prokaryotic or Eukaryotic? Cytoskeleton, ER, Lysosome, Mitochondria, Ribosome, vacuole, Golgi body, nucleus, cell membrane, nucleolus, cytoplasm Eukaryotic Distinguishing Organelles Distinguishing Shapes/Features Centrioles, cilia, flagella Circular in shape Animal Cell Organelles shared with Plants Cytoskeleton, ER, Lysosome, Mitochondria, Ribosome, vacuole, Golgi body, nucleus, cell membrane, nucleolus, cytoplasm Prokaryotic or Eukaryotic? Eukaryotic In what ways are eukaryotes different from prokaryotes? Prokaryotic-simple cells, appeared 3.5 billion years ago, smaller in size, always unicellular, always has a cell wall, do not have a nucleus or organelles, DNA is circular and free floating, example: Bacteria Eukaryotic-complex cells, appeared 2.5 million years ago, larger in size, can be unicellular or multicellular, cell wall found in all except animals, has a nucleus and organelles, DNA located in the nucleus, examples: plants and animals Fill in the chart below: Plant, Animal, Both Organelle Function Nucleus Control center of the cell, houses DNA BOTH Mitochondria Transforms energy BOTH Plasma/Cell Membrane Selectively allows materials in and out of the cell Cytoplasm Clear fluid, allows for transport and movement of organelles BOTH Site of where ribosomes assemble proteins, carries proteins from one part of the cell to another. Rough ER has lots of ribosomes on it, Smooth ER has no ribosomes on it BOTH Endoplasmic Reticulum Ribosome Site of protein synthesis, assembles proteins in the cell BOTH Vacuole Storage space BOTH Golgi Body/Apparatus Modifies proteins and sends them to proper location Cytoskeleton Part of the cytoplasm that keeps cell structure from collapsing BOTH Nucleolus Assembles ribosomes, located in the nucleus BOTH Cell wall Protects, supports and gives shape to a plant cell PLANT Lysosome Digests foods and recycles old parts of the cell using enzymes BOTH Chloroplasts Site where photosynthesis takes place PLANT Cilia Short, hair-like projections of the cell that help with movement ANIMAL Flagella Watch me whip! And move. ANIMAL BOTH BOTH As a scientist you are looking at two samples of cells. One specimen is from a plant and one from an animal. List at least 3 things you can look at to know which the plant is and which is the animal cell group: Two main structures that are found in a plant cells that would not be found in animal cells are the cell wall and chloroplasts. The cell wall would give the plant cell support, shape and structure. Chloroplasts capture sunlight and use it to make food in plant cells. In a plant cell, the vacuole would be much larger than it would be in an animal cell. The overall shape of the two cells is also different. Plant cells would be more square/rectangular while animal cells would be more round/spherical. The cell wall that is found in plant cells tends to make the cell more square for structure and support. In an animal cell, you might see cilia or flagella for movement. Looking at 2 plant cell samples from the same plant, you see a big difference in the number of chloroplasts in each sample. What conclusions can you draw about where on the plant the samples were taken? Chloroplasts are more numerous in parts of the cell that are photosynthesizing. Samples with high amounts of chloroplasts might be on the leaves, where smaller amounts of chloroplasts might be found on the lower parts of a stem or in the roots of that specific plant. The diagram below shows healthy red blood cells and the red blood cells created by a disease called Sicklecell anemia. How does the structure of red blood cells relate to their function? How does the sickle red blood cell’s structure create a problem? Red blood cells are rounded, flattened, and very small. This allows them to move about the blood vessels with ease. If they encounter a bump along the way, they bounce around them (kind of like bumper boats). They also lack a nucleus so they can have more room to carry oxygen. In sickle cell anemia patients, the red blood cells are misshaped and are not round but sickle shaped (hence the name) and they do not move around in blood vessels as well. When they encounter a barrier, they often collect and cause plugs to form in the blood vessels that can be very painful and life-threatening. How does the branching shape of a neuron help in its function in the body? The neuron has many long projections off of the cell’s body (look like tree branches) which allows them to have many connections to many other cells. This helps them accomplish their primary mission to transmit electrical (nerve) impulses back and forth very fast. This is how we are often able to react very fast to certain stimuli. How does the shape of a fat cell relate to its function in the body? Fat, lipid, or adipose cells are comprised mostly of a giant fat globule inside the cell’s cytoplasm. This fat globule helps cushion each cell and offers insulation. The fat globule is also where we store that long-term energy that is characteristic of lipids. When a whole bunch of lipids cells get together, they form tissues that protect organs and offer good insulation from temperature change. List the following words in order from LEAST to MOST complex. (tissue, organ, cell, organism, organ system). Least Complex – cell – tissue – organ – organ system – organism – Most Complex Label the parts of the microscope to the right. A. __Base_______ B. __Arm_________ C. __Nose Tube_______ D. __Light Source/Mirror______ E. __Ocular lens/Eyepiece_____ F. __Revolving Nose Piece____ G. __Objective lens_____ H. __Course Adjustment____ I. __DONT WORRY ABOUT THIS_ J. __Fine Adjustment______ K. __Stage______ M. __Diaphragm_________ If the ocular lens or eyepiece was 10X magnification and the total magnification was 300X, then what is the magnification of the objective lens? Show your math!!! 10 x objective lens = 300, so divide 300 by 10 to get 30X. The objective lens is 30X magnification What are some of the differences between compound light and electron microscopes? Compound microscopes are cheaper to purchase, can only view up to 1000x, and you can use these scopes to view living organisms. Electron microscopes are very expensive, can view up to 2,000,000x, cannot be used to view living things, and objects are magnified using a beam of electrons (hence the name electron microscope!) __D__ Some researchers now believe that Alzheimer's disease is caused by the release of destructive enzymes in the cytoplasm of nerve cells. The enzymes are thought to be released by organelles whose membranes ruptured while trying to digest harmful proteins. Which organelles might be responsible for the release of these destructive enzymes? A. Nuclei B. Rough ER C. Ribosomes D. Lysosomes __A__ Human muscle cells would contain a lot of which organelle and why? A. Mitochondria to convert food into energy. B. Mitochondria to convert light energy into sugar. C. Chloroplasts to convert sugar into energy. D. Chloroplasts to convert light energy into sugar. Match the following functions to the structure that is responsible. A. Vacuole B. Cell Wall E. Mitochondria F. Nucleus C. Cell/Plasma Membrane G. Golgi Apparatus/Body D. Endoplasmic Reticulum H. Ribosomes __F__ Houses the DNA of the cell __A__ Root cells in plants use these to store water __E__ Generates energy for the cell to carry out life processes __B__ This structure is not found in animal cells __C__ Helps the cell maintain homeostasis by controlling what enters and exits the cell __D__ Helps transport proteins inside the cell and where some reactions occur to build proteins __H__ The major players in protein synthesis __G__ Once a protein is made, it is processed – packaged and prepared for export by this organelle