Collisions
advertisement
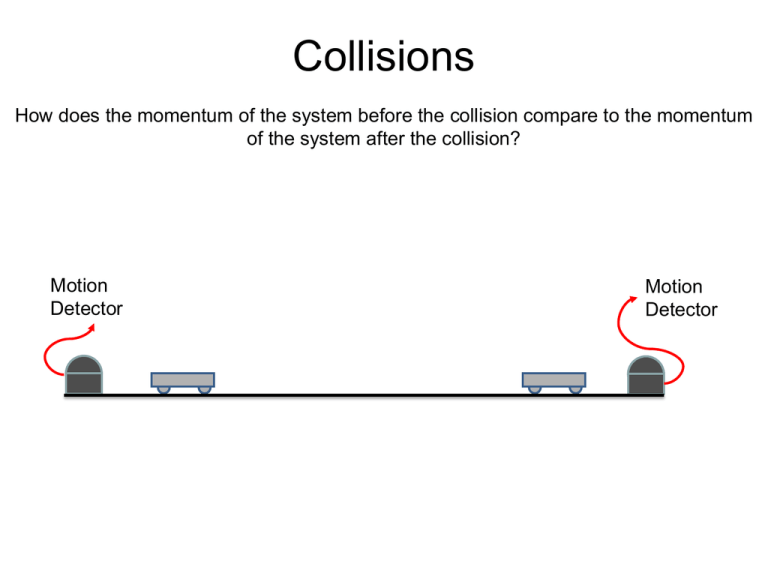
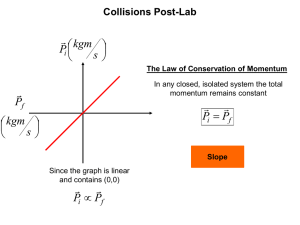
Collisions How does the momentum of the system before the collision compare to the momentum of the system after the collision? Motion Detector Motion Detector Collisions Elastic Collision – a collision during which kinetic energy is conserved. In other words, no energy is dissipated during the collision. Using the magnet ends… Motion Detector Motion Detector Collisions Inelastic Collision – a collision during which kinetic energy is not conserved. Some of the energy is dissipated and is usually stored as thermal energy or sound. Using the Velcro ends… Motion Detector Motion Detector Collisions Post-Lab kgm Pi s The Law of Conservation of Momentum In any closed, isolated system the total momentum remains constant Pf Pi P1fPf kgm s Since the graph is linear and contains (0,0) Pi Pf Proof 2 methods Method 1 FBR FRB Method 2 Newton’s Third Law! t BR t RB RB FBR t FRB t J BR J RB p1 p2 PTotal 0 dp F dt Newton’s Second Law The system is isolated and by Newton’s Third Law, any force between colliding objects would always have an equal and opposite pair and would therefore sum to 0! dp 0 dt p constant