O The purpose of this document is to provide a... management process for Information and Communications Technology. A...
advertisement

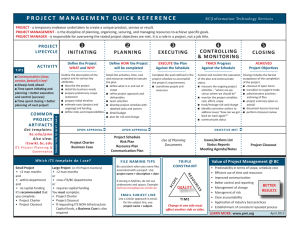
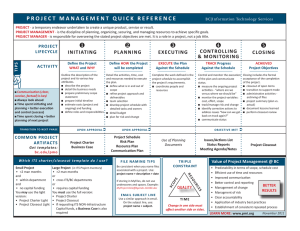
Project Management Process OVERVIEW Purpose The purpose of this document is to provide a high level overview of a standard project management process for Information and Communications Technology. A full project management process will be developed in the future as we implement our Project Portfolio Office. Project Life Cycle The following diagram highlights the five key stages of any project: initiation, planning, execution, closure, and asset maintenance. It shows the flow of events across these stages from the perspective of the project flow, the decision-making steering committee, and the appropriate control mechanisms. -- 1 -- Project Management Process Key project flow events Initiation phase: development of the project charter • • • • Project charter is required for new projects over 20 person days or $5,000 Purpose of project charter o Business case to justify the project o Document project parameters o Guide project development o Acquire formal authorization to proceed to the next step in the project o Authorize the use of resources to develop detailed project plan o Sufficient information to help the steering committee make their decision Standard template shown in subsequent section Generally brief: 5 pages maximum Planning phase: development of project plan • • • • • • • Project plan is required for any project over 40 person days It is a document used to used to: o Guide project execution and control o Document project planning assumptions o Facilitate communication amongst stakeholders o Define key management review activities o Provide a baseline for project measurement and control Standard template shown in subsequent section Second stage of approval process for steering committee Changes over time as project circumstances dictate Scalable Sufficient level of detail for: o Steering committee to commit resources o Project manager to run the project Execution phase: reporting and change requests • • • Project manager responsible for implementing project according to project plan Required to submit regular project status updates covering accomplishments for the current reporting period, plans for the next reporting period, and challenges that could prevent the project from meeting its objectives Change requests must be submitted for any material modification of the project plan -- 2 -- Project Management Process o o A material request means any change to the budget, scope, schedule, quality, risk, or resourcing of the project that could impact the project objectives A change request template is included in a subsequent section Closure phase • • • • • • A lessons-learned document is produced for every project Template shown in subsequent section Purpose is stop re-inventing the wheel every time for every project All projects are expected to document their lessons learned Must store those ideas in a re-useable form New projects are expected to review lessons learned from previous similar projects and apply appropriate knowledge to the current project -- 3 -- Project Charter April 6, 2015 PROJECT CHARTER TEMPLATE Template Purpose The following document outlines the content and format of project charters to be used for all projects. A project charter should be written for each project requiring authorization or funding. A charter could also be completed for smaller-scope projects if there is a departmental preference or obligation to mitigate risk. Any project requiring over 20 person days (one month) of effort or $20,000 of funding requires a project charter. All sections are mandatory. Please replace the existing text with your own. Each project charter is intended to clearly document the project parameters, guide project development, and acquire formal approval to proceed with the project. The charter will be reviewed by the ICT Leadership Team, and potentially brought to the appropriate stewardship committee for further approval. There must be sufficient information in this document for these groups to make a decision. The decision will be one of the following: i. Approval in principle • Approval in principle to proceed with the project subject to certain conditions. These conditions require follow-up with the steering committee before proceeding with project plan development or project execution. ii. Approval to plan • Approval to spend the resources necessary to develop a detailed project plan (large, complex projects) iii. Approval to execute • Approval to proceed with project execution (small, inexpensive, shorter projects) iv. On hold • Approval in principle with the project concept, but further work is put on hold until certain conditions are met. No work is to proceed on the project until the steering committee judges all of the criteria are met. v. Rejection • The project charter does not meet the project evaluation criteria and all work on the project will halt. Note: If you are seeking Approval to Plan, please ensure you clearly indicate so. Example: Indicate which costs are for developing the plan, versus which are necessary for executing the project. Project charters must be submitted to the ICT Project Portfolio Office. You must submit 1 week prior to the ICT Leadership meeting you would like to present at. These meetings are usually held every two weeks. Remove this page from your project charter before submission. The total number of pages in the final document must not exceed 5 pages. Project Plan April 6, 2015 PROJECT CHARTER Meaningful, yet concise Automatically assigned by the ICT SharePoint Project Inventory: Project ID: https://itshares.usask.ca/projects/SitePages/Home.aspx Author(s) of Charter: Author(s) and contributors Project Name: Project Manager: Name Submission Date: Date submitted Summary Sponsor: Completion Date: Name Total Monetary Planned OneTime Costs: $ $ Planned Recurring Costs: $ $ Month, Day, Year Other projects with Linkages: dependencies Total Asset Consumption Planned Person Total Person Days Days: PURPOSE What are the reasons for undertaking the project? What is the purpose for doing it? Identify the key needs that the project is designed to meet. Include background material on reasons why these needs have arisen. On larger projects it is helpful to describe the overall mission of the project. This charter is a request to the ICT Leadership committee for permission to proceed with work. Choose one of the following options and state your request: 1. Approval in principle 2. Approval to plan 3. Approval to execute SPONSOR Define who wants the project to be implemented. These individuals are known as project sponsors or owners. Who will own and manage the project results once it is completed? These individuals provide key sources of funding for the project. CLIENT(S) & KEY STAKEHOLDERS What are the departments in the organization that will utilize the results of the project? Identify the key users of the system and where in the University they are located. What will the impact of this project be on administrators, educators, learners, researchers, and/or the community? BENEFITS & SUCCESS CRITERIA From the perspective of a return on investment, why should ICT undertake this project? Example benefits: • Lower the cost to operate the organization • Deliver products and services faster • Handle more work with same resources • Improve customer service and satisfaction Project Plan April 6, 2015 What exactly are the direct and indirect benefits to the University? How are the benefits to be achieved? When will we know if the overall project was a success? Benefit (What?) Strategy (How?) Success Criteria (When?) 1. IN SCOPE What features and functions will the project deliver? Identify all the major deliverables of the project. Describe the final product or process to be created by the project. This section forms the agreement between the project manager and the sponsor about the expected results of the project. OUT OF SCOPE Identify what is not part of the project. These are features that are not part of the project but may be mistaken to be part of the project. This section is included to help clarify the boundary between what is in the project and what is not. WORK BREAKDOWN STRUCTURE What are the key deliverables for the project? When are they expected and what should be delivered on these dates? Only the first or second level of the Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) needs to be documented at this point in the project (but milestones must be included in your WBS). Focus on what and when, not how; how is for your Project Plan (if applicable). If you are seeking Approval to Plan, you will include only the work required for the planning stage. WBS # 1.0 2.0* 3.0 4.0* 5.0* What Project Management 1.1* Project Charter 1.2* Project Plan 1.3 Monitoring 1.4* Close-Out Report Requirements Gathering 2.1 Use Case Documentation 2.2 Technical Specification Develop System System Test 4.1 Testing Report 4.2 User Acceptance Testing Move To Production 5.1 Production Checklist 5.2 System Deployment * = Milestones By When 2015-09-31 2015-08-01 2015-08-10 2015-09-31 2015-09-31 2015-08-02 2015-08-20 2015-09-05 2015-09-15 RESOURCES Based on the work breakdown structure, identify the resources required and document approximately how many person-days will be needed to complete the project. This list should include the project manager, functional analysts, and technical analysts who will contribute to the project throughout the life of the project. It also includes any subject matter experts to be included on a part-time basis as needed. This section is mandatory and must be supplied for all project charters. If reasonably accurate numbers cannot be determined, estimates must be supplied with a statement explaining the degree of confidence in the estimates. If you are seeking Approval to Plan, you will include only the work required for the planning stage. Project Plan WBS # 1.0 2.0 April 6, 2015 Resource Project Manager Systems Administrator Function Management of the project Acquisition/build of test server Name M. Jagger K. Richards Person Days: Effort Confidence 25 5 30 95% 75% COSTS Monetary costs represent cash expenses paid to do the work, upgrade infrastructure, purchase software, outsource, or hire external resources. One-time monetary costs are incurred during the life of the project and are paid for by the project budget. Postimplementation costs of maintaining the project results are also identified here as recurring monetary costs (always identified annually). For example: Monetary Costs: One-Time WBS # 3.1 4.1 Monetary Costs: Recurring WBS # 5.1 Description 3 IBM Server Contract programmer Recovery from? ICT capital ICT base budget Total One-Time: Description Vendor service agreement Recovery from? Total Cost $10,000 +/- 5% $50,000 +/- 10% $60,000 +/- 10% Total Cost ICT base budget Total Recurring: $250 / year $250 / year Asset consumption costs represent resources consumed that are not paid for by the project budget. One-time asset consumption costs are incurred during the life of the project. Recurring asset consumption costs are incurred after the project is complete. For example: Asset Consumption Costs: One-Time WBS # Description 5.0 5.0 Initial disk storage Initial tape backup Asset Consumption Costs: Recurring WBS # Description 4.1 5.0 IT application support Server hosting (x3) Units Consumed Total Cost 25GB 50GB Total One-Time: Units Consumed 20 person days / year $600 / server / year Total Recurring: $6,000 $2,000 $8,000 Total Cost $40,000 / year $1,800 / year $41,800 / year 2014/15 ASPA (Specialist/Professional/IT/Managerial) Full Position Costing Estimates (Target Salary/Per Year): $69,000 (Phase 1), $87,000 (Phase 2), $108,000 (Phase 3). ALTERNATIVES What other approaches have been considered? List the alternative project strategies available to develop the project such as outsourcing, purchasing off-the-shelf software, customized code development, etc. and why they were not selected. CONSTRAINTS What are the strategic directives that will guide decision-making throughout the life of the project (if any)? Document the overarching project themes. Typically, but not necessarily, these themes cover cost, timeliness, and quality. RISKS What are the risks that may impact successful completion of the project? For each risk, identify the probability of occurrence and expected impact of the risk if it occur. Use H/M/L for High/Medium/Low. For example: Project Plan April 6, 2015 Description Probability Impact M H Lack of available resources Furthermore, please document the risks to the institution if ICT does not deliver on this project, or if the project is unsuccessful. SUPPLEMENTAL PROJECT CONSIDERATIONS Metric Will this project be exposed to - or be expected to manage - sensitive personal or institutional information? For example, does the project have HIPA, PCI or PIPEDA implications? Does this project align with the principles of ICT’s enterprise architecture? Value (Yes, No, Unsure) If “yes” or “unsure”, please contact ICT Access & Compliance (Yes, No, Unsure) If “no” or “unsure”, please contact the ICT Enterprise Architect (Your completed project charter must not exceed 5 pages in length) Project Plan April 6, 2015 PROJECT PLAN TEMPLATE Template Purpose The following document outlines the content and format of project plans to be used for major projects. Any project requiring greater than 40 person days of effort requires a project plan. A project plan should be written for each project charter granted approval to plan by a stewardship committee. Completed project plans are submitted to the ICT Management Team and if approved will be escalated to the appropriate stewardship committee for formal approval. There must be sufficient information in this document for these groups to make a decision. The project plan is a formal, approved document used to manage project execution. The project plan is a document or collection of documents that should be expected to change over time as more information becomes available about the project. There are many ways to organize and present the project plan, but all of the sections identified in this document should be included. Each project plan is intended to clearly document how the project will be executed and will serve as guide during the execution phase of the project. There must be sufficient information in this document to help the steering committee make their decision to proceed with the project, as well as sufficient detail to enable the project manager to run the project. Project plans should be submitted to the ICT Project Portfolio Office. You must submit 2 weeks prior to the meeting you would like to present at. These meetings are usually held every two months. As the project progresses through the execution phase and project circumstances change, this document will be updated to reflect these changes. These changes must be submitted to the steering committee for approval. The document shell outlined below identifies the key sections needed for any project plan. Anything in red Italics is simply a description of the kind of information that should be entered. All text in red Italics in this document is instructional and should be removed from the final version of each project plan. Remove this page from your project charter before submission. The total number of pages in the final document is not restricted. Project Closeout April 6, 2015 PROJECT PLAN Project Name: Project Code: Meaningful, yet concise Assigned by ICT Author(s) of Charter: Author(s) and contributors Author(s) of Plan: Author(s) and contributors Project Manager: Name Submission Date: Date submitted Summary Sponsor: Completion Date: Name Month, dd, yyyy Other projects with Linkages: dependencies Total Monetary Total Asset Consumption Planned One-Time Costs: $ $ Planned Recurring Costs: $ $ Planned Person Days: Total Person Days Project Strategy ......................................................................................................................................................................................... 2 Scope.......................................................................................................................................................................................................... 2 Scope Statement .................................................................................................................................................................................... 2 Scope Management Plan ....................................................................................................................................................................... 2 Schedule ..................................................................................................................................................................................................... 2 Schedule Baseline .................................................................................................................................................................................. 2 Schedule Management Plan .................................................................................................................................................................. 2 Budget ........................................................................................................................................................................................................ 3 Cost Baseline .......................................................................................................................................................................................... 3 Cost Management Plan .......................................................................................................................................................................... 3 Quality Management ................................................................................................................................................................................. 4 Quality Definition ................................................................................................................................................................................... 4 Quality Management Plan ..................................................................................................................................................................... 4 Resources ................................................................................................................................................................................................... 4 Staff Baseline ......................................................................................................................................................................................... 4 Staffing Management Plan..................................................................................................................................................................... 4 Asset Management Plan ........................................................................................................................................................................ 4 Communications ........................................................................................................................................................................................ 4 Communications Strategy ...................................................................................................................................................................... 4 Communications Management Plan ...................................................................................................................................................... 4 Risks ........................................................................................................................................................................................................... 5 Risk Management Plan .......................................................................................................................................................................... 5 Risk Response Plan ................................................................................................................................................................................. 5 Procurement Management Plan................................................................................................................................................................ 5 Stakeholder Management Plan……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………6 Supporting Detail ....................................................................................................................................................................................... 6 Page 1 of 6 Project Closeout April 6, 2015 PROJECT STRATEGY Describe the project management approach or strategy. Provide a summary of the relationship between the project and organization strategy and policy. SCOPE Scope Statement The objective of the scope statement is to refine the project boundaries originally outlined in the Project Charter. Develop the Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) to the level at which management control will be exercised and the WBS becomes the project’s baseline scope document. Include the project objectives and the prime project deliverables. Scope Management Plan Describes how project scope will be managed and how scope changes will be integrated into the project. Include an assessment of the expected stability of the project scope (i.e. likelihood, frequency, and quantity of changes). The Scope Management Plan should also include a clear description of how scope changes will be identified and classified. SCHEDULE Schedule Baseline The project schedule lists planned dates for performing activities and meeting milestones identified in the project plan. It includes the following: • Start and finish dates for each task in the Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) • All dependencies amongst tasks in the WBS • Resources assigned to each task in the WBS Schedule Management Plan Define how changes to the schedule will be managed. Note: You will likely find it easiest to use a tool such as Microsoft Project for your schedule. Page 2 of 6 Project Closeout April 6, 2015 BUDGET Cost Baseline Estimate the cost of each deliverable in the WBS. Present it as an easy-to-read table that includes separate columns for One-time Monetary, One-Time Resource Consumption, Recurring Monetary, and Recurring Resource Consumption. Cost Management Plan Define how cost variances will be managed (including the different responses to major versus minor problems) and how they will be reported. Determine how budget revisions or forecasts will be developed and how frequently they will be made. The Project Manager must: • Explain how this project will be funded and describe this information here; • Separate capital and operating costs; • Use estimate confidence numbers for uncertain estimates (e.g. +/-10%); • If applicable, specify the source for funding; and, • Include all applicable taxes. Example of monetary costs: Monetary Costs: One-Time WBS # Description 3.1 4.1 3 IBM Server Contract programmer Budget Code Computer hardware Temporary salary Recovery from? ICT capital ICT base budget Total One-Time: Monetary Costs: Recurring WBS # Description 5.1 Vendor service agreement Budget Code Hardware maintenance Recovery from? ICT base budget Total Recurring: Example of asset consumption costs: Asset Consumption Costs: One-Time WBS # Description 5.0 5.0 Initial disk storage Initial tape backup Asset Consumption Costs: Recurring WBS # Description 4.1 5.0 5.0 5.0 IT application support Storage growth Backup growth Server hosting Units Consumed Total Cost $10,000 +/- 5% $50,000 +/- 10% 0 +/- 10% Total Cost $250 / year $250 / year Total Cost 25GB 50GB Total One-Time: Units Consumed 20 person days / year 100GB / year 100GB / year $600 / server / year Total Recurring: $6,000 $2,000 $8,000 Total Cost $40,000 / year $300 / year $100 / year $1,800 / year $42,200 / year Page 3 of 6 Project Closeout April 6, 2015 QUALITY MANAGEMENT Quality Definition Describe how the project will implement its quality policy. Test matrices and plans are considered part of the quality management process. The project quality system includes the organizational structure, responsibilities, procedures, processes, and resources needed to implement quality management. Quality Management Plan The quality management plan must address quality control, quality assurance, and quality improvement for the project. Define what quality means to customers in the context of this project and specifically how it will be measured. This plan must address benefits realization. What are the metrics to measure how benefits will be realized? Define the process by which these benefits will be measured the person(s) responsible for turning promised customer benefits into reality. RESOURCES Staff Baseline Identify the key or required staff and their expected cost and/or effort. Document the organizational structure of project. Staffing Management Plan Define when and how human resources will be added to and removed from of the project team. Asset Management Plan Define facility, technical, and physical resources needed to support the project. COMMUNICATIONS Communications Strategy Define the key messages to be sent externally and internally and identify stakeholders to receive messaging. Communications Management Plan Page 4 of 6 Project Closeout April 6, 2015 The communications plan is a description of the information to be distributed, including format, content, level of detail, and conventions/definitions to be used. It includes production schedules showing when each type of communication will be produced and who will receive the information. A method for updating and refining the communications management plan as the project progresses and develops should also be included. RISKS Risk Management Plan Identify key risks including constraints and assumptions, and determine planned responses and contingencies for each risk. Risk Response Plan Risk response plans should: • Identify risks, their descriptions, the area(s) of the project affected, their causes, and how they may affect project objectives; • Assign risk owners and their responsibilities; • Document results from the qualitative and quantitative risk analysis processes; • Identify agreed upon or approved responses including avoidance, transference, mitigation, or acceptance for each risk in the risk response plan; • Identify the level of residual risk expected to remain after the strategy is implemented; and • Document specific actions required to implement the chosen response strategy, including budget and times for responses, and contingency plans and fall back plans. PROCUREMENT MANAGEMENT PLAN Describe how the procurement processes will be managed. Processes include: • Vendor solicitation • Source selection • Contract administration • Contract close-out Key questions to answer in the plan include: • What types of contracts will be used? • If independent estimates will be needed as evaluation criteria, who will prepare them and when? • How will the project management team work with the Purchasing department? • How will multiple providers be managed? • How will procurement be coordinated with other project aspects, such as scheduling and performance reporting? Page 5 of 6 Project Closeout April 6, 2015 STAKEHOLDER MANAGEMENT PLAN Identify the people, groups or organizations that could impact or be impacted by the project. Analyze those stakeholders’ expectations and their impact on the project, and to develop appropriate management strategies for effectively engaging stakeholders in project decisions and execution. Depending on the individual’s power and influence in relation to the project, decide on whether to monitor them, keep them informed, keep them satisfied or to closely manage them. SUPPORTING DETAIL Supporting details for the project plan include: • Outputs from other planning processes that are not included in the project plan. • Additional information or documentation generated during development of the project plan. • Technical documentation; such as requirements history, specifications, and conceptual designs. • Documentation of relevant standards. • Specifications from early project development planning. • Open issues and pending decisions. Page 6 of 6 Project Closeout April 6, 2015 PROJECT CLOSURE TEMPLATE Template Purpose The following document outlines the content and format of project closeout reports to be used for major projects. A closeout report should be written for all completed projects. Completed closeout reports will have been circulated for consultation and then submitted to the appropriate steering committee for review before sign-off and for archival by Project Portfolio Office. The project closeout report is a document used to formally complete project execution. Stakeholder sign-off is required in order to declare the project closed. The closeout report must include every section described in this document. Each closeout report is intended to clearly document how the project proceeded and will serve as a guide to improve performance on future projects. There must be sufficient information in this document to satisfy stakeholders that the project is complete and sufficient detail to enable improvement in future projects. The expected benefits section of the closeout report is very important for future benefits tracking. The document shell outlined below identifies the key sections needed for any project closeout report. Anything in red Italics is simply a description of the kind of information that should be entered. All text in red Italics in this document is instructional and should be removed from the final version of each project closeout report. Remove this page from your final closeout report. Always start by looking at existing Project Closeout Reports and always use the latest version of the template from the ICT Project Portfolio Office. Page 7 of 1 Project Closeout April 6, 2015 PROJECT CLOSEOUT REPORT Project Name: Project Code: Meaningful, yet concise Assigned by ICT Author(s) of Charter: Author(s) and contributors Author(s) of Plan: Author(s) and contributors Author(s) of Closeout: Author(s) and contributors Project Manager: Name Submission Date: Date submitted Summary Sponsor: Completion Date: Linkages: Name Month, dd, yyyy Other projects with dependencies Total Monetary Total Asset Consumption Actual One-Time Costs: $ $ Actual Recurring Costs: $ $ Actual Person Days: Total Person Days PROJECT SUMMARY Provide a brief summary of the project as completed. This is especially important if the project, as carried out, differs from what was presented in the project plan. DELIVERABLES Use the WBS from the final project plan to list the major deliverables achieved during the project; note that these may differ from the original planned deliverables. DOCUMENTATION List all documentation that was generated as a result of this project, including who wrote it, where it is stored, and how to access it. EXPECTED BENEFITS Now that the project is complete, what benefits were realized? What benefits can we still expect to realize? List the benefits included in your original Project Charter and indicate whether they were realized or will they be realized in the future. If any new benefits have emerged, list them here as well. Offer recommendations on how to perform benefits tracking; use the Success Criteria from the Project Charter for this purpose. Was the overall project a success? This will be presented to the steering committee. Page 1 of 3 Project Closeout April 6, 2015 LESSONS LEARNED Present a numbered list of lessons learned in the following format: 1 Challenge: Successes: Lessons: What was the problem encountered? How you were able to overcome or work around the problem and continue with the project? What you would do differently in future projects, or what you would pass on to future project managers? 2 Challenge: Successes: Lessons: What was the problem encountered? How you were able to overcome or work around the problem and continue with the project? What you would do differently in future projects, or what you would pass on to future project managers? CHANGE SUMMARY Use your list of change request forms to present a table of changes that were approved during the course of the project. Change # 0000 Description Short description of the change Impact Effect of the change on the project Date Date approved VARIANCES Scope How is your project scope different from the original plan? Cost Present baseline/actual cost differences here; justifications are not necessary. Schedule Present baseline/actual schedule differences here; justifications are not necessary. TRANSITION TO OPERATIONS If the project has created a new service, record how this product or service is to be operationally managed now that the project is over. Indicate if any Service Level Agreements (SLAs) or Operational Level Agreements (OLAs) have been created. Note what steps have been taken to transition to operations, as well as any recommendations for the future. It is highly recommended that you include a Responsibility Assignment Matrix using the RACI (Responsible, Accountable, Consulted, Informed) model. Responsibility Matrix Operational Activity Operational Activity Operational Activity Operational Activity Functional Area R A C C Functional Area A A I Functional Area A Functional Area C I I I Page 2 of 3 Project Closeout April 6, 2015 NEXT STEP OPPORTUNITIES Describe any future opportunities created by this project; include any information, which may be relevant in terms of initiating new future projects. Do you feel that this project is newsworthy? Yes No Completed projects that are considered to be “noteworthy” will be forwarded on to Marketing and Communications for advertising; they will determine where it should be published. SIGN OFF List the stakeholders signing off on the project and have them sign and date this report. A signed paper copy should be presented to the Project Portfolio Office for storage in the project repository. Sponsor Name Type the name here before printing this document out for signature. Signature Date Comments Any comments on the project, project team, this report, etc. Project Manager Name Type the name here before printing this document out for signature. Signature Date Comments Any comments on the project, project team, this report, etc. Stakeholder(s) Name Type the name here before printing this document out for signature. Signature Date Comments Any comments on the project, project team, this report, etc. Page 3 of 3 ICT Project Management Process April 6, 2015 PROJECT CHANGE REQUEST TEMPLATE Template Purpose The following document outlines the content and format to be used for change requests for chartered projects that are in the monitoring phase. All sections are mandatory. Prior to submission to the steering committee, the Change Request must be approved by the sponsor and stakeholders listed in the Client Approvals section. The request should be submitted to ICT Management and it can be submitted at any time during the execution of a project. This document shell identifies the key sections needed for any Project Change Request. Anything in red italics is simply a description of the kind of information that should be entered and should be removed from the final version. Remove this page from your project charter before submission. The total number of pages in the final document must not exceed 5 pages. ICT Project Management Process April 6, 2015 PROJECT CHANGE REQUEST Project Name: Project Code: Author(s) of Charter: Meaningful, yet concise Assigned by ICT Author(s) and contributors Project Manager: Name Submission Date: Date submitted Summary Sponsor: Completion Date: Linkages: Name Month, dd, yyyy Other projects with dependencies Total Monetary Total Asset Consumption Planned One-Time Costs: $ $ Planned Recurring Costs: $ $ Planned Person Days: Total Person Days PROPOSED CHANGE Description of change: Explain the details of the proposed change. Benefit of making the change: Define the reasons for making the proposed change. Consequence of not making the change: What are the consequences to the project and the sponsor if the change is not implemented? CHANGE IMPACTS Answer each of the following questions that apply to the change request. 1. What are the fiscal or base budget funding changes required as a result of this change? 2. What is the effect of this change on the project schedule, sequence of tasks, and key milestones? 3. How will this change affect project resources? 4. How will the change affect the outcome of any project deliverables? Page 1 of 2 ICT Project Management Process April 6, 2015 5. What is the impact of this change on project quality? 6. How does the request affect any of the risks identified in the project plan? 7. Will this change impact the technical, procedural, or physical security posture? 8. Will this change have an impact on any production functions or services provided? 9. Will there be a Change Advisory Board (CAB) request associated with this change? CLIENT APPROVALS Seek approval for your change request from the sponsor and affected stakeholders. Sponsor/stakeholder Name of Individual Name of Individual Name of Individual Approved Yes/no Yes/no Yes/no Date Current date Current date Current date Page 2 of 2