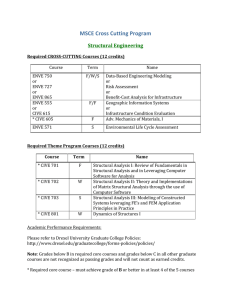
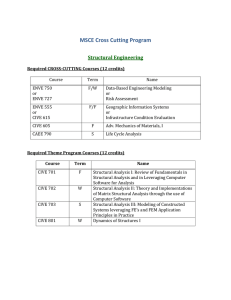
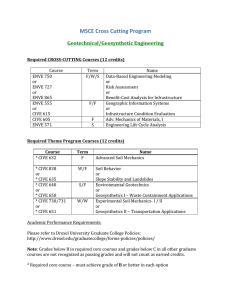
BSc (Hons) Town and Country Planning (P/T)-E415P
advertisement

BSc (Hons) Town and Country Planning (P/T)-E415P 1. OBJECTIVES The importance of the urban planner is increasing throughout the 21st century, as we begin to face issues of increased population growth, climate change and unsustainable development. An urban planner helps a community decide how to best use its land and resources with an eye toward future growth and revitalisation. Planning today retains its commitment to ideal urban environments, but has to work within challenging political contexts. The task of reconciling competing development and environmental goals in the interests of ‘sustainability’ usually falls to the planning function in government. Planners are an important part of a town's growth and development. A town planner's main responsibility is to ease or avoid social, economic and environmental problems within their town of employment. The planner is a professional who works in the field of urban planning/land use planning for the purpose of optimising the effectiveness of a community's land use and infrastructure. They formulate plans for the development and management of urban and suburban areas, typically analysing land use compatibility as well as economic, environmental and social trends. In developing their plan for a community (whether commercial, residential, agricultural, natural or recreational), urban planners must also consider a wide array of issues such as sustainability, air pollution, traffic congestion, crime, land values, legislation and zoning codes. The aims of this programme are: 2. to provide students with the theoretical and practical knowledge, understanding and skills required for sustainable land use planning: to provide a supporting environment in which students are able to fulfill their educational potential as well as enhance their employment prospects within and beyond the planning profession. GENERAL ENTRY REQUIREMENTS As per General Entry Requirements for Admission to the University for Undergraduate Degrees. 3. MINIMUM CREDIT REQUIREMENTS FOR DEGREE AWARD Law and Management 15 Humanities 6 Departmental (core) 79 TOTAL 100 (i) For award of the degree, all modules prescribed by the programmes structure must be completed. (ii) Minimum Credit Requirements for Diploma Award -60 credits 1 A student may opt for a Diploma in Town and Country Planning provided s/he satisfies the following minimum requirements. The request for exit at the Diploma level should be made in writing to the Dean of Faculty. A Diploma project is compulsory and would normally be of 12 weeks duration, commensurate with work input of at least 90 contact hours. 4. PROGRAMME DURATION - 4 years Minimum and 6 years Maximum 5. CREDITS PER SEMESTER - Minimum 3, Maximum 24 subject to Regulation 4. 6. ASSESSMENT Each module will be assessed over 100 marks (i.e. expressed as %) with details as follows (unless otherwise specified): Assessment will be based on written examination and continuous assessment. The written examination will be of 2-hour duration for semester modules. The continuous assessment will count for 20-30% of the overall percentage mark of the module(s). Continuous assessment may be based on field work and/or assignments and should include at least two class tests/assignments per module. An overall total of 40% for combined continuous assessment and written examination components would be required to pass the module, without minimum thresholds within the individual continuous assessment and written examination. Written examinations for the semester modules will be carried out at the end of the respective semester. 2 7. COURSE STRUCTURE Year 1 Semester 1 11 Credits Core Modules CIVE 1106(1) Semester 2 12 Credits Core Modules CIVE 1216(1) Technical Skills L+P 2+2 Credits 3 SOCI 1105(1) Introduction to Sociology 3+0 3 CIVE 1126(1) CIVE 1107(1) Planning Tools in Mauritius 3+0 3 CIVE 1127(1) CIVE 1118(1) Professional Communications 1+2 2 CIVE 1219(1) Organisation and Practice of Urban Planning in Mauritius Climate Change & the Physical Environment History & Philosophy of Urban Planning Introduction to Urban Design L+P 3+0 Credits 3 3+0 3 3+0 3 3+0 3 L+P 2+2 Credits 3 3+0 3 3+0 3 3+0 3 L+P 3+1 Credits 3.5 Year 2 Semester 1 12 Credits Core Modules MGT 1111(1) CIVE 1223(1) ECON 1215(1) CIVE 1222(1) Organisation and Management Principles of Geographical Information Systems Introduction to Economics Architecture in Relation to Urban Planning Semester 2 12 Credits Core Modules CIVE 3213(3) L+P DE Credits 3 2+2 3 CIVE 2229(3) 3+0 3 CIVE 3108(3) 3+0 3 LAWS 1128(1) GIS for planners Heritage and Conservation Statistical Analysis in Planning Urban Planning Law (PART I) Year3 Semester 1 12.5 Credits Core Modules 3117(5) MGT LAWS 2231(3) CIVE 2230(3) CIVE 2125(3) Leisure and Tourism Planning Urban Planning Law (PART II) Transport in Relation to Planning The Environmental Impact Assessment Process Semester 2 13 Credits Core Modules CIVE 4011(3) L+P 3+0 Credits 3 3+0 3 CIVE 3012(3) Civil Engineering in Relation to Planning 3+1 3.5 3+1 3.5 CIVE 3224(5) 3+0 3 3+0 3 CIVE 3013(3) Coastal Zone Management Research Methods 3+0 3 Site Planning and Analysis Year 4 Semester 1 9 Credits Core Modules CIVE 2208(5) CIVE 2217(5) CIVE 4009(5) CIVE 3000Y(5) Policy Making & Implementation Planning for Sustainable Development Liveable Neighbourhoods Semester 2 9.5 Credits+9 Core Modules CIVE 4007(5) L+P 3+0 Credits 3 3+0 3 CIVE 3+0 3 CIVE 4012(5) 3109(5) Degree Project Environmental Management Systems Development Process Waste Management L+P 3+0 Credits 3 3+0 3 3+1 3.5 9 Total number of credits – 100 3 8. LIST OF MODULES Code Module Name CIVE SOCI CIVE CIVE CIVE 1106(1) 1105(1) 1107(1) 1118(1) 1216(1) CIVE CIVE CIVE MGT CIVE ECON CIVE CIVE CIVE CIVE LAWS MGT LAWS CIVE CIVE CIVE CIVE CIVE CIVE CIVE CIVE CIVE CIVE CIVE CIVE CIVE CIVE 1126(1) 1127(1) 1219(1) 1111(1) 1223(1) 1215(1) 1222(1) 3213(3) 2229(3) 3108(3) 1128(1) 3117(5) 2231(3) 2230(3) 2125(3) 4011(3) 3012(3) 3224(5) 3013(3) 2208(5) 2217(5) 4009(5) 4007(5) 3109(5) 4012(5) 3000Y(5) 2010D(3) Technical Skills Introduction to Sociology Planning Tools in Mauritius Professional Communications Organisation & Practice of Urban Planning in Mauritius Climate Change & the Physical Environment History and Philosophy of Urban Planning Introduction to Urban Design Organisation & Management (DE) Principles of Geographical Information Systems Introduction to Economics Architecture in Relation to Urban Planning GIS for Planners Heritage & Conservation Statistical Analysis in Planning Urban Planning Law (PART I) Leisure and Tourism Planning Urban Planning Law (PART II) Transport in Relation to Planning The Environmental Impact Assessment Process Site Planning and Analysis Civil Engineering in Relation to Planning Coastal Zone Management Research Methods Policy Making &Implementation Planning for Sustainable Development Liveable Neighbourhoods Environmental Management Systems Development Process Waste Management Degree Project Diploma Project Hrs/week L+P 2+2 3+0 3+0 1+2 3+0 Credits 3+0 3+0 3+0 3+0 2+2 3+0 3+0 2+2 3+0 3+0 3+0 3+0 3+0 3+1 3+0 3+1 3+1 3+0 3+0 3+0 3+0 3+0 3+0 3+0 3+1 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3.5 3 3.5 3.5 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3.5 9 6 3 3 3 2 3 4 9. OUTLINE SYLLABUS CIVE 1106(1) - TECHNICAL SKILLS Types of structures and structural elements. Site preparation and layout. Computer aided drafting in Building and Civil engineering; Introduction to Autocad; Manipulating of CAD drawing; Basic drawing and editing command; Precision drawing and making changes in drawing Principles of Surveying. Control and Detailed Survey. Adjustments. Aerial Photography, levelling, contour mapping SOCI 1105(1) - INTRODUCTION TO SOCIOLOGY Understanding of patterns of human behavior and changes in our society. Forms of social structure - groups, organisations, communities, social categories (such as class, sex, age, or race), and various social institutions-such as kinship, economic, political, or religious- which affect human attitudes, actions, and opportunities; Culture, socialisation practices, social interaction, gender, family and marriage, population, Social Stratification and Schooling. CIVE 1107(1) - PLANNING TOOLS IN MAURITIUS An overview of the existing planning tools in Mauritius and their importance. The existing planning framework: including the different authorities, guidelines and legislation which govern the planning framework. The role of the national strategy plan – the National Development Strategy, the Outline Schemes and the Planning Policy Guidelines. The procedures for their implementation and enforcement. Critical assessment of the existing framework with case studies. CIVE 1118(1) - PROFESSIONAL COMMUNICATIONS Perception and listening skills. The writing process - letters and memorandums, résumés (critical thinking & synthesis of technical articles), technical & laboratory Reports, presentation of tables, charts, histograms in reports. Oral Presentations, modes of speech delivery, presentation aids, speeches, non-verbal communication. Referencing, plagiarism & ethics in written and oral communication. Use of IT - Introduction to Computer hardware, Microsoft Office packages (Word, Excel and PowerPoint). Data manipulation in a spreadsheet. Introduction to networking and data communication - file sharing, internet. Use of computers for data acquisition and control CIVE 1216(1) - ORGANISATION AND PRACTICE OF URBAN PLANNING IN MAURITIUS The main actors, responsibilities and roles at the different levels, strategic planning at national level, national policies. Strategic planning; local planning – the land use and planning department and its organization, functions, Building and land use permits, enforcement CIVE 1126(1) - CLIMATE CHANGE AND THE PHYSICAL ENVIRONMENT Physical features in Mauritius – climate zones; microclimates: hydrological cycle; geology; topography and landforms; hydrology; water resources, waste water, urban water drainage systems; ecosystems; weathering, erosion. Climate change and its effects on land use planning; Global warming – causes and effects; different methods to reduce global warming CIVE 1127(1) - HISTORY AND PHILOSOPHY OF URBAN PLANNING Review of historical planning concepts, models, and reasons for urban settlements and their subsequent growth. Identification of historical core elements in modern planning and the philosophy linked, Concepts in modern town planning from 19th & 20th centuries. The students are expected to understand the history and the philosophy of the process of planning and managing urban and rural areas and to comprehend the contested nature of planning and management interventions in the built and natural environment 5 CIVE 1219(1) - INTRODUCTION TO URBAN DESIGN Theory, techniques and appreciation of design within the context of town planning, urban design and landscape design. The development of technical and communication skills, aesthetic appreciation of design and an understanding of design process. Analysis of land use planning and design ideas. Current urban design and theory. MGT 1111(1) - ORGANISATION AND MANAGEMENT (DE) Management Concepts and Functions. Development of Management Theories. The Internal and External Environments of the Organisation. Social Responsibility and Ethics in Management. Managerial Decision Making. The planning process. The nature of Organisation Structure. Organisational Control. Contemporary issues in Management. Management in Future CIVE 1223(1) - PRINCIPLES OF GEOGRAPHICAL INFORMATION SYSTEMS Definition & Components of a GIS; Spatial & Non-Spatial information: Vector & Raster formats: Creation of attribute tables; Joining attribute tables: Creation of thematic maps; Point, line & Polygon formats: Creation of Geodatabase: Simple spatial analysis- Overlay techniques; Buffers; Clip; Mosaic; Geostatistics; Preparation of maps for Reports: GIS Reporting. ECON 1215(1) - INTRODUCTION TO ECONOMICS Price Mechanism. Revenue and Elasticity. Consumer Choice. Theory of Production. Analysis of Costs. Market Structures. Factor Market Analysis. Market Failures and Externalities. National Income Determination. Consumption, Savings and Investment. Monetary Policy and Theories of Inflation. Unemployment. Fiscal Policy. IS-LM Model. International Trade, Balance of Payments and Exchange Rate Regimes CIVE 1222(1) - ARCHITECTURE IN RELATION TO URBAN PLANNING Principles and theories of architecture, and the influences of the history of ideas on both present and past environments and societies, at the scale of the landscape and settlement, the city and its urban design, and the individual building and its composition, making and materiality. Introduction to the consideration of issues of sustainability, human well-being, participatory design and vernacular architectures. CIVE 3213(3) – GIS FOR PLANNERS The use of GIS to analyse spatial data in order to improve land use planning and the management of resources and services. Spatial analysis and urban modelling techniques. The concept of an advanced and integrated GIS that acts as a decision support tool for land use planning. Decision making using GIS database – geostatistical analysis and mathematical modelling; spatial analysis and urban modelling techniques; application of GIS complex analysis in planning; multicriteria analysis and decision support CIVE 2229(3) - HERITAGE AND CONSERVATION Knowledge and critical understanding of the principles related to heritage sites conservation and management. Basic concepts and approaches to conservation, and built heritage in larger contexts. Particular attention given to historic urban landscapes, their socio-cultural characteristics and dynamic development. CIVE 3108(3) - STATISTICAL ANALYSIS IN PLANNING Statistics for planning: role of statistics in planning, data sources, the population and sampling, the need for samples; questionnaires, variables, summary statistical measures; frequency distributions, probability and sampling, binomial distribution, normal distribution, tests of significance, basic concepts of hypothesis testing. To analyse data and to present the material effectively in graphic form 6 LAWS 1128(1) - URBAN PLANNING LAW PART I Land law: Propriété, Possession, servitude. General principles of administrative law. Grounds of judicial review: illegality, irrationality and procedural impropriety. law related to land use planning: Town and Country Planning Act, Business Facilitation Act; Compulsory Acquisition, Compensation and Determination of claims, Penalty for contravention. MGT 3117(5) - LEISURE AND TOURISM PLANNING Analysis & application of national & regional planning policy to destination areas. Planning concepts, planning process: policies, objectives, goals, budgets, implementation. Principles of planning leisure & tourism programmes & the factors affecting their implementation & their functioning. Destination Management LAWS 2231(3) - URBAN PLANNING LAW PART II International laws and regulations in relation to urban planning, grounds and procedures for appeal in urban planning, The role of the Appeal Tribunal in the planning framework. Case studies from different countries-British Town and Country Planning Act, the evolution of the legislation during the past decades CIVE 2230(3) - TRANSPORT IN RELATION TO PLANNING The theoretical aspects of transport planning; contemporary transport policy; Transportation systems; the impacts of transport systems on the environment; Environmental dimensions of transport planning and management transport modeling; planning for walking, cycling and public transport, and transport and land use integration. Sustainable transport planning. Design of transport infrastructure. Traffic management and control. CIVE 2125(3) - THE ENVIRONMENTAL IMPACT ASSESSMENT PROCESS Environmental legislation, History and Background of the EIA process, The EIA process in Mauritius, the procedures leading to the obtention of the licence, enforcement and monitoring. The Environmental Problems in Mauritius, Air Pollution Control, Solid Waste Management, Noise Pollution Control, Global Environment Concern CIVE 4011(3) - SITE PLANNING AND ANALYSIS Investigation of the major components of physical planning and site design as they relate to achieving planning objectives. Review of regional landscape analysis, physical and man-made factor analysis, and watershed and program analysis. Special focus given to analyzing site suitability and sensitivity for development, site selection and feasibility studies and conceptual design that responds to site conditions. CIVE 3012(3) - CIVIL ENGINEERING IN RELATION TO PLANNING Overview of engineering, civil engineering, development and Infrastructure as they relate to the activities of planners. Relationship between infrastructure provision and country income level and investment. Description and application of civil engineering infrastructure (e.g. water resources, water quality and supply, transportation and land use, soils/geotechnical aspects of development and stormwater management) to planning. CIVE 3224(5) - COASTAL ZONE MANAGEMENT Definition of coastal zone, Integrated approach to coastal zone management, coastal processes and impacts, management of coastal resources, impacts of development on coastal zones, development control in coastal areas, strategies for sustainable management of coastal areas. Information collection, decision making, management and monitoring of implementation of these strategies 7 CIVE 3013(3) - RESEARCH METHODS Introduction to Research, Perspectives and Varieties of Social Research, Defining the Research Problem, The Research Design and Process, The Literature Review, Sampling Techniques, Preparation of a questionnaire, Surveys, Pilot studies, Data Collection, Processing and Analysis of Data, Analysis and Interpretation, quantitative Analysis, Report Writing CIVE 2208(5) - POLICY MAKING AND IMPLEMENTATION Analysis of the theories, practices and techniques applicable in the preparation of development; plans and policies; the main issues involved in preparation of such plans; the implementation of these plans and policies; decisionmaking process; concepts of development management, practice of regulation and enforcement; Monitoring, evaluation and assessment to ensure compliance to existing plans. CIVE 2217(5) - PLANNING FOR SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT Concepts of sustainable development; Sustainable planning with respect to economic development; integrated approach to planning taking into consideration physical features, neighborhoods, transportation, energy, infrastructure and services; Concept of mixed use development to achieve sustainable development. Comparison between short term social and economic benefits and longer social and environmental needs. CIVE 4009(5) - LIVEABLE NEIGHBOURHOODS Different ways to achieve Liveable Neighbourhood which is concerned with structure planning and subdivision for greenfield sites and for the redevelopment of large brownfield and urban infill sites, as per UN Habitat definitions. Impacts that directly affect people in a community, such as economic development, affordability, public health, social equity and pollution exposure. CIVE 4007(5) - ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT SYSTEMS Understand EMS concepts, components and applications. . The different ISO standards ISO 14000, Costs and benefits of EMS, Environmental compliance and monitoring, Risk assessment. The value of developing an EMS for various types of organizations, environmental review CIVE 3109(5) - DEVELOPMENT PROCESS Overview of the Property Development process and the role of planning. Sequence of operations and actions required to bring out the potential of land, from identification of client need to end-user occupation. Property development process; strategies and the role of land use planning; sequence of operations and actions required to increase the potential of land; forming the development concept; feasibility study; deal making – planning and financing; Project construction; operation or sale after completion of project. CIVE 4012(5) - WASTE MANAGEMENT Integrated Solid Waste Management, Solid Waste Management Planning, Why Local Authorities Need a Solid Waste Management Plan, How to Develop a Solid Waste Management Plan Hazardous Wastes Management, Recycling, Composting, Incineration, Landfilling. Waste water management, wastewater reuse and recycling. CIVE 3000Y(5) - DEGREE PROJECT This is a 9 credit module that is designed to allow a student to learn and apply the independent research skills that are expected from an honours degree graduate when investigating a relevant issue of their own choice. The student will be required to undertake a piece of critical and reflective academic research that will result in the production of a dissertation in Town and Country Planning and other related areas of about 8,000 to 12,000 words. Supporting guidance and personal support will be provided by the module project supervisor. Assessment will be through the finished written dissertation. 8 Students will be expected to conduct either field study or survey type questionnaire based research involving data collection analysis and interpretation. CIVE 2010D(3) - DIPLOMA PROJECT This is a 6 credit module that is designed to allow a student to learn and apply the independent research skills that are expected from a Diploma holder when investigating an issue, related to Town and Country Planning. The student will be required to undertake a study of a topic that will result in a dissertation. Supporting guidance and personal support will be provided by the module project supervisor. Assessment will be through the finished written dissertation. Students will be expected to conduct either field study or survey type questionnaire based research involving data collection analysis and interpretation. 9