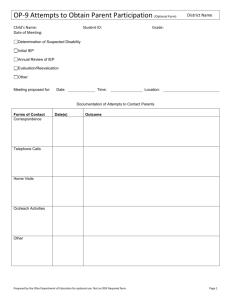
XXX Public Schools Assessment of Programming for
advertisement

SCHOOL NAME XXX Public Schools Assessment of Programming for Students with Moderate to Severe Disabilities Author: Christine Peterson, PhD This document is a companion tool for use with Program Development and assessment. For more information related to this Program Assessment tool, contact Christine Peterson, University of Wisconsin-Stout, 715-232-2182. sharing or selling this document without permission of author is prohibited. Directions for Use: This Assessment protocol is designed for use in tandem with its companion Program Development tool. As programs are in the process of development, this tool will be a useful guide for future planning. As well, this tool can be used to assess the status of a program across a variety of critical domains, for purposes of identifying strengths areas of focus, and to inform continuous improvement efforts. This tool is designed as a formative guide. It is does not include normative standards for interpretation of results. For this reason, no total scores are derived. Rather, evaluators are encouraged to review scores within each discrete domain, to analyze and discuss ratings and performance. Each item is rated along a 1 to 5 scale. Domains and individual items align directly with the Program Development tool, for easy referencing. Ratings should be considered with the following guidelines in mind: 1 = This item has not been addressed, is not in place, or is otherwise absent in the program. 2 = This item has very recently begun, and/or is minimally in place and requires a significant amount of further development to achieve the desired standard for the program 3 = This item is in place, but requires a moderate amount of further development to achieve the desired standard for the program 4 = This item is currently in place and requires only minimal further development to achieve the desired standard for the program. 5 = This item is in place, and is operating at a level that is consistent with the desired standard for the program. 2 Personnel: Staff play a critical role in the successful programming for students with intensive learning needs. Teachers, paraprofessionals, related services providers, school psychologists, and other staff contributing to the program should be appropriately trained and knowledgeable in best practices for educating students with moderate to severe disabilities. (New and/or untrained staff are prioritized for and receive appropriate training in a timely fashion). 1. Staff are trained and knowledgeable in the following domains related to students with moderate to severe disabilities: a) Characteristics and profiles of learners with moderate to severe disabilities (i.e., academic, social, communication, behavioral, adaptive) b) Appropriate assessment methods (i.e., state standards, alternative assessment, individual assessment measures) c) Development of IEP’s that reflect comprehensive and intensive learning needs d) Instructional methods, curriculum and environmental adaptation and accommodation needs of students with moderate to severe disabilities e) Use of assistive technology and augmentative/alternative communication mechanisms (i.e., dynavox devices, modified keyboards, etc.) f) Appropriate classroom and individual behavior support needs, and training for preventive and crisis intervention strategies (i.e., CPI, Mandt) Assessment: Comments: a) 1 2 3 4 5 b) 1 2 3 4 5 c) 1 2 3 4 5 d) 1 2 3 4 5 e) 1 2 3 4 5 f) 1 2 3 4 5 2. Staff participate in continuing professional development, designed to further knowledge and skills (i.e., workshops, conferences, consultation, professional reading and research). 1 2 3 4 5 3. Staff are available on a ratio that allows students to accomplish IEP goals, and adequately meet student’s daily care needs. 1 2 3 4 5 4. Teacher and related service providers have regular and frequent access to individual IEPs, for purposes of on-going instructional planning and progress monitoring. 1 2 3 4 5 5. Teacher and related service providers collect appropriate data to regularly monitor progress toward IEP goal achievement. 1 2 3 4 5 3 6. Teacher and teaching team have access to on-going support and technical assistance to meet the unique needs of the program and/or individual students (i.e., assist. tech consultation, behavior specialist). 1 2 3 4 5 Notes: 4 Program Characteristics: Students with moderate to severe disabilities present with unique and intensive learning needs. A program designed to meet the needs of this group of learners should include a defined and comprehensive curriculum across all learning domains (academic, social, behavioral, adaptive, communication), and emphasis placed on student engagement . Assessment: Comments: 1. The length of the school day and school year should be at least equal 1 2 3 4 5 to that established for students in general education. 2. Based on individual need and evidence of regression in the absence of services, extended year programming is evaluated and considered for all students. 1 2 3 4 5 3. Staff are available on a ratio that allows students to accomplish IEP goals, and adequately meet student’s daily care needs. 1 2 3 4 5 4. Classroom placement prioritizes accessibility needs for students (i.e., considerations for bathroom accessibility; ability to install assistive equipment (swings, etc.) 1 2 3 4 5 1 2 3 4 5 6. Program planning for generalization is evident. Community based instruction occurs where appropriate, and students have opportunities for inclusive learning and activities. 1 2 3 4 5 7. There is an identifiable and consistent daily structure and routine, designed to promote understanding and enhance student learning. 1 2 3 4 5 8. The program includes a systematic plan for evaluating student outcomes and data-based decision making, both at the individual and program level. 1 2 3 4 5 5. A defined curriculum is identified and used to guide learning goals for students; systematically planned, developmentally appropriate and individualized educational activities are implemented toward the achievement of IEP goals. 5 District Resources: Successful development and maintenance of programming for students with moderate and severe disabilities requires intensive services and supports. The district commits to providing the appropriate resources to ensure the integrity and efficacy of the program. Assessment: Comments: 1. Staff are available on a ratio that allows students to accomplish IEP 1 2 3 4 5 goals, and adequately meet student’s daily care needs. 2. Teaching staff and related service providers receive professional development and training essential to successful implementation of programming for students with moderate and severe disabilities, as appropriate, given existing staff experience and expertise. 3. Staff coverage is available in the form of staff release time and/or substitute coverage, as appropriate to allow for professional development and training opportunities. 4. Individualized services and supports, as determined by the IEP team, are provided (i.e., assistive technology for communication needs, extended year programming; skilled nursing services) to ensure adequate progress toward IEP goals and objectives. 5. Teacher and teaching team have access to on-going support and technical assistance to meet the unique needs of the program and/or individual students (i.e., assistive technology consultation, behavior support specialist). 1 2 3 4 5 1 2 3 4 5 1 2 3 4 5 1 2 3 4 5 Notes: 6 Curriculum: The program uses a defined curriculum that addresses the comprehensive learning needs of students with moderate to severe disabilities, and is adaptable to meet the individual learning needs of each student. Assessment: 1. The curriculum addresses the comprehensive learning needs of all students: a) 1 2 a) Pre-academic and/or academic skills Comments: 3 4 5 b) Adaptive, daily life-skill development and self-management b) 1 2 3 4 5 c) Social relationships (including classroom and non-disabled peers) c) 1 2 3 4 5 d) Communication and language e) Play and leisure activities d) 1 2 3 4 5 f) Strategies for teaching adaptive skills to replace maladaptive e) 1 2 3 4 5 behaviors f) 1 2 3 4 5 g) Pre-vocational skills g) 1 2 3 4 5 h) Student engagement h) 1 2 3 4 5 2. Curriculum is individualized and adapted to the needs of each student. 1 2 3 4 5 3. Through the curriculum (and appropriate adaptations), students are exposed to organized learning themes, throughout the course of the school year. Individual instruction and goals are implemented via the curriculum. 1 2 3 4 5 Notes: 7 Instructional Methods: Instructional methods reflect evidence-based, developmentally appropriate practices that are designed to meet the individual and unique needs of learners. 1. Instructional methods are empirically validated and evidence-based, or convey solid evidence of efficacy over time. Assessment: 2. Instructional methods are focused on the functional application of skills Comments: 1 2 3 4 5 1 2 3 4 5 3. Instructional methods: a) Reflect high expectations for learners a) 1 2 3 4 5 b) Promote student engagement b) 1 2 3 4 5 c) 1 2 3 4 5 d) 1 2 3 4 5 e) 1 2 3 4 5 1 2 3 4 5 c) Promote high levels of successful responding (i.e., task analysis) d) Emphasize positive reinforcement strategies for learning e) Incorporate programming for generalization of skills across settings 4. Instructional methods are designed to develop student abilities to learn in a group setting, increasing peer and environmental tolerances. Notes: 8 Individual Instruction and Assessment: The program employs a variety of instructional activities, designed to engage learners and enhance functional application of skills. Assessment practices are designed from a strength-based perspective to develop a comprehensive learning profile, and results are linked directly to development of IEP goals and objectives. Assessment: Comments: 1. Instructional activities are differentiated to meet individual student needs (i.e., ages, abilities, and learning styles). 1 2 3 4 5 2. Students are engaged in a variety of instructional formats a) One-to-one instruction a) 1 2 3 4 5 b) Small and/or whole group instruction b) 1 2 3 4 5 c) Peer-mediated instruction c) 1 2 3 4 5 3.Instructional activities promote the development and use of communication skills (via language to augmentative/alternative communication mechanisms) 1 2 3 4 5 4.Instructional activities are designed to: a) Enhance student engagement a) 1 2 3 4 5 b) Emphasize a high rate of successful responding to promote skill mastery b) 1 2 3 4 5 c) Build in complexity, from basic to more advanced skill development c) 1 2 3 4 5 d) Individualized to achieve IEP goals d) 1 2 3 4 5 e) Promote the functional application of skills e) 1 2 3 4 5 a) 1 2 3 4 5 5.Student assessment practices emphasize multi-method, multi-modal approaches, designed to achieve a comprehensive and accurate profile of learners. Assessment protocols may include: a) Review of school and medical records 9 b) Teacher/parent interviews b) 1 2 3 4 5 c) Student observations c) 1 2 3 4 5 d) Informal, activity-based assessment of basic skills d) 1 2 3 4 5 e) Formal norm- and criterion- referenced assessments e) 1 2 3 4 5 f) Family input f) 1 2 3 4 5 1 2 3 4 5 6.Assessment practices are designed to measure comprehensive domains of learning (academic, social, adaptive, communication, etc.) 7.Assessment of communication skills occurs for both verbal and nonverbal students, with a focus on: a) 1 2 3 4 5 b) Receptive language b) 1 2 3 4 5 c) Expressive language c) 1 2 3 4 5 d) 1 2 3 4 5 8.Assessment are framed from a strength-based perspective, and outcomes highlight both areas of strength as well as need. 1 2 3 4 5 9.Assessment outcomes are clearly linked to instructional practices and interventions. Assessment outcomes are reported in written form, with an emphasis on recommendations to guide the IEP. 1 2 3 4 5 a) Communicative intent d) Augmentative/alternative communication technology needs Notes: 10 Development of Individual Education Program and Progress Monitoring: The IEP represents the blueprint for instructional programming for each child. The IEP should be comprehensive, and target goals should be observable and measurable. Goals should be written that can be accomplished in one year, and reviewed on a regular basis. The program employs an on-going systematic, data-based process for assessing student progress. Assessment: Comments: 1.Target objectives should be comprehensive, and should include consideration for the following (as appropriate per individual): a) Functional communication a) 1 2 3 4 5 b) Replacement of non-functional behaviors with functional b) 1 2 3 4 5 c) 1 2 3 4 5 d) 1 2 3 4 5 e) Play and leisure skills e) 1 2 3 4 5 f) f) 1 2 3 4 5 g) 1 2 3 4 5 1 2 behaviors c) Engagement d) Social skill development Functional life skills and adaptive behaviors g) Self-advocacy skills 2.Systematic assessment and review of IEP goals occurs on a frequent basis 3 4 5 3.Students individual instructional programming is altered when: a) Adequate progress is not observed for target objectives a) 1 2 3 4 5 b) target objectives have been met b) 1 2 3 4 5 c) changes occur in the student’s life (home, school, community) c) 1 2 3 4 5 11 4. Instructional Programming change options include (but are not limited to): a) Presentation of material a) 1 2 3 4 5 b) Schedule of prompting b) 1 2 3 4 5 c) Schedule of reinforcement c) 1 2 3 4 5 d) Modifications to curriculum material d) 1 2 3 4 5 e) Modifications to target objectives e) 1 2 3 4 5 f) Increase/decrease in student:teacher ratio f) 1 2 3 4 5 g) 1 2 3 4 5 5.Student progress is reported quarterly via IEP progress monitoring, and shared with caregivers. 1 2 3 4 6.Annual IEP review includes student summary and review by the collaborative educational team, including caregivers 1 2 3 4 5 g) Increase/decrease in 1:1 instructional time 5 Notes: 12 Challenging Behaviors: Students with disabilities may engage in challenging behaviors, influenced by a variety of factors. When challenging behaviors occur, systematic evaluation occurs and evidence-based interventions are employed, with a particular emphasis on teaching functional and adaptive alternative skills. 1.A proactive system of reinforcement is in place, providing a Assessment: Comments: foundation for effectively managing through challenging student 1 2 3 4 5 behaviors. 2.A Functional Behavior Assessment process is employed to evaluate and intervention plan for challenging behaviors that: a) Employs multiple methods, such as direct observation, rating a) 1 2 3 4 5 scales, interviews b) Evaluative focus of the FBA is on identification of the function of behaviors, from an Antecedent-Behavior-Consequence perspective (attention, avoidance, tangible, sensory, etc.) b) 1 2 3 4 5 c) The team considers additional influences on behavior such as medical factors, curriculur factors, circumstances outside of school (lack of sleep, eating, changes at home, etc), current reinforcement/punishment practices, staffing (ratios, training, etc.) 3. Interventions are developed that: a) Are directly based on assessed functions (i.e., “function-based interventions”) c) 1 2 3 4 5 a) 1 2 3 4 5 b) Emphasis is placed on direct instruction of functional skills and alternative behaviors b) 1 2 3 4 5 c) 1 2 3 4 5 4.Intervention is monitored for effect and modified appropriately. 1 2 3 4 5 5.The team includes and/or has access to a professional with expertise in assessment and intervention planning for challenging behaviors and students with significant developmental disabilities. 1 2 3 4 5 c) Plans for reduction of dangerous behaviors (aggression, selfinjury) are carefully developed and very closely monitored 13 Program Evaluation: Systematic examination of program implementation and impact is evaluated, with an emphasis on individual student outcomes and family satisfaction. Parents/care-taker participation is encouraged and facilitated. 1.The program employs methods that assess program-wide effectiveness in the areas of: Assessment: Comments: a) Individual student progress on annual IEP goals and objectives a) 1 2 3 4 5 b) Student generalization of skills b) 1 2 3 4 5 c) Performance on state-wide and alternative assessments c) 1 2 3 4 5 d) Student progress toward long-term goals d) 1 2 3 4 5 2.The program evaluates short-term (i.e., weekly) intermediate (i.e., quarterly), and long-term (i.e., annual) student progress. 1 2 3 4 5 3.The program monitors program changes, ensuring active programming for all students. 1 2 3 4 5 4.Information obtained from individual and/or program evaluation is used directly to inform program improvement. 1 2 3 4 5 5.Parent/care-giver participation is facilitated, and parents/care-givers receive regular feedback and communication regarding their child’s progress. 1 2 3 4 5 6.Program evaluation includes a measure of consumer (family) satisfaction. 1 2 3 4 5 14 Summary and Analysis Directions: Once the tool is completed, the team is encouraged to identify strengths and weakness across each domain. Programs still in development may not wish to utilize this option, but established programs wishing to assign a “grade” for each domain and/or for the entire program, can do so, to inform the continuous improvement process. The following guideline is offered: Ratings are predominately 4s and 5s = This domain is fully implemented Ratings are predominately 4s, with 3s and 5s included = This domain is fully implement with small advances in process Ratings are predominately 3s, with 2s and 4s included = This domain is implement and advancement is in process Ratings are predominately 2s, with other scores included = This domain is in limited implementation, with significant advancement needed Ratings are predominately 1s and 2s, with minimal other scores included = This domain is not implemented, or is in beginning stages of implementation. Significant advancement is needed Domain Summaries Personnel: Grade(optional) = Strengths: 15 Areas of Need: Next Steps/Action Items: Program Characteristics: Grade(optional) = Strengths: Areas of Need: Next Steps/Action Items: District Resources: Grade(optional) = Strengths: Areas of Need: 16 Next Steps/Action Items: Curriculum: Grade(optional) = Strengths: Areas of Need: Next Steps/Action Items: Instructional Methods: Grade(optional) = Strengths: 17 Areas of Need: Next Steps/Action Items: Individual Instruction and Assessment: Grade(optional) = Strengths: Areas of Need: Next Steps/Action Items: Development of IEP and Progress Monitoring: Grade(optional) = Strengths: 18 Areas of Need: Next Steps/Action Items: Challenging Behaviors: Grade(optional) = Strengths: Areas of Need: Next Steps/Action Items: Program Evaluation: Grade(optional) = Strengths: 19 Areas of Need: Next Steps/Action Items: Overall Program Grade (optional)= Summary of Next Steps and Action Items Next Step/Action Item Who’s Responsible Action Timeline 20 21