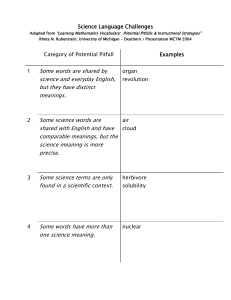
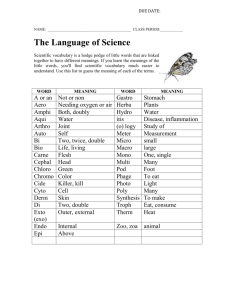
Chapter 4 Language 1
advertisement

Chapter 4 Language 1 Language: a collection of symbols governed by rules and used o convey messages between individuals. Language is Symbolic - Language is Body of Symbols Meanings are in people, NOT in words Language is Rule Governed 2 Meanings are in people, not words. Words have two levels of meaning: Denotation and Connotation Meaning varies depending on syntactic context Language will change over time Language of dominant group absorbs language from immigrants 3 Naming and Identity ◦ Influence on elections (Barrack who???) (G.W. Smith, 1998) ◦ Popular names (Steele and Smithwick, 1989) ◦ Names and ethnicity (California statistic) (Fryer and Levitt, 2004) ◦ Name and marriage (unity vs. independence) Credibility – Dr. Fox hypothesis Status Sexism and Racism 4 Equivocal language consists of statements that have more than one commonly accepted definition. (page 110) Family catches fire just in time Trees can break wind 5 Relative words gain their meaning by comparison good chance? unlikely? common? 6 Slang: language used by a group of people whose members belong to a similar coculture or other group. (groovy, tight…) Jargon: the specialized vocabulary that functions as a kind of shorthand for people with common backgrounds and experiences. (touchdown…) 7 As we move from abstract to specific, we also move from abstract to concrete. Gambling Games of Skill Card Games Poker Seven Card Stud Use Concrete, Precise, and Dated information! 8 Emotive language seems to describe something but actually announces the speaker’s attitude toward it. I’m not cheap, I am thrifty. 9 Euphemism – to use words of good omen ◦ She is “plump” or “thick” or “big-boned” ◦ She is NOT “fat” 10 Women (Feminine Styles of Language) Women Tend to Use More Intensifiers (He’s really cute.) and Hedges Women communicate to build relationships Women use words of empathy and support Discuss feelings, relationships, personal problems Women Ask Questions More Frequently ◦ To Gain More Information ◦ To Get Elaboration ◦ To Determine How Others Feel 11 Men (Masculine styles of Language) Use words of status and problem solving Emphasize making conversation fun Communicate to get the job done Offer advice Use statements to exert control, preserve their independence, enhance their status. Speech is judged more dynamic, aggressive, and strong. 12 Low-context Cultures: ◦ People say what they mean and get right to the point. ◦ Clear , eloquent speech is considered praiseworthy. ◦ Self expression valued 13 High-context Cultures: ◦ People present meanings indirectly, and expect others to use context cues to interpret meaning. ◦ Relational Harmony valued and maintained by indirect expression of opinions. ◦ Abstain from saying “no” directly ◦ Talk “around” the point by allowing others to fill in the missing pieces. 14

![Word Study [1 class hour]](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/007905774_2-53b71d303720cf6608aea934a43e9f05-300x300.png)