List as many questions as you Hinduism
advertisement

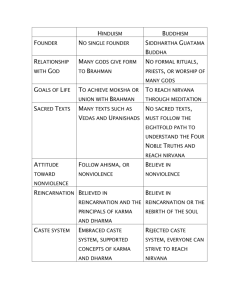
List as many questions as you can think of about the major world religions that we will study Hinduism Buddhism Judaism Islamic Christianity Bell Work: Finish up on “World Religions Research” from Friday. I will be checking this for a formative assessment grade Chart for completion – formative assessment grade World Religions Research: Any discoveries you would like to share? Any questions? Questions we will ask What are the characteristics of major religions? How are they similar and different? How have major religions affected culture? How have belief systems spread over large areas? Major Belief Systems Hinduism History Founded c. 3000 B.C. by Dravidians Aryans= nomadic invaders from Central Asia Bell Work: Take out your notebooks and write about yourself: 3 Truths 1 Lie Hinduism has no single founder, but originated from the mixing of Harappan and Aryan cultures in ancient India around 1500 BCE. Hindus believe in one unifying spirit, Brahman. Brahman can manifest in many, polytheistic, forms or in one, monotheistic. The caste system (outlawed since 1948) was an important part of Hinduism. Castes are social classes into which a person is born and lives their entire life. If a person has a good karma they may be reincarnated into a higher caste. This life Next life Good Karma Higher caste Born into A caste Bad Karma Lower caste The caste system separated Indian society into distinct social classes in which everyone knew their place and believed that if they followed the dharma of their caste, they would be reincarnated into a better caste. Brahmin Kshatriya Vaisya Sudra Untouchables Caste System Caste determines occupation and social status No marriage outside of caste No sharing of meals Outlawed since 1947, but still deeply ingrained in Indian society Hinduism is based on the concept of reincarnation (Spirits return to earth many times in different forms trying to become one with Brahman). The soul moves up or down a hierarchy depending on their behavior in life. A person moves closer to Brahman by obeying the law of karma. Karma is the sum of all your deeds, good and bad. Good deeds involve following your dharma, or duties dependent on your position, gender and occupation. Over the centuries Hindu beliefs were recorded into a number of sacred texts including the Vedas and the Upanishads. The Ramayana is a Hindu creation story. Beliefs • 3 main gods: Brahma – creator god • Shiva – the destroyer • Vishnu – the preserver • • Brahman – the “ultimate reality” • Hindus believe Brahman is the source of all things and is in all things. • All other gods are manifestations of Brahman. The Four Aims All Hindus live with 4 goals: Dharma – righteousness (right behavior) Artha – success/prosperity Kama – satisfaction of desires Moksha – release from “samsara,” the life cycle Atman= soul Every living thing has one The body is mortal, but the soul is immortal Reincarnation – soul is reborn in another form Dharma- your record Karma- law of consequences Samsara- transmigration & reincarnation Ultimate goal: moksha & nirvana Your atman blends with Brahman and becomes part of it. Hindu and the Caste System Very closely tied Karma determines reincarnation If your dharma is good, you will be reincarnated in a higher caste. If your dharma is bad….lower. You can even drop below castes into the world of beasts. What is sacred: The Vedas (sacred texts) The Cow http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=j31 veR74gSo&desktop_uri=%2Fwatch% 3Fv%3Dj31veR74gSo&nomobile=1 Questions: How many million Untouchables? What similarities can you see in our own American history? Exit Slip 1. Name one idea/fact that you remember most about Hinduism. 2. What question do you have about Hinduism? From your notes on Hinduism: Each person in your group: Create 3 truths 1 lie